Open banking technology is revolutionizing the financial landscape, and at pioneer-technology.com, we’re here to unpack it for you. Open banking uses APIs to allow third-party developers to access financial data securely, fostering innovation and competition in financial services. Want to dive deeper into the future of finance? Then explore pioneer-technology.com today to discover cutting-edge financial technologies, innovative banking solutions, and secure data sharing practices.
Table of Contents
- What Is Open Banking?
- How Does Open Banking Work?
- Examples of Open Banking Services
- Who Uses Open Banking?
- Benefits of Open Banking
- Challenges of Open Banking
- FAQ
1. What Is Open Banking?
Open banking is a financial services model that grants third-party developers access to financial data held within traditional banking systems through application programming interfaces (APIs). This innovative approach fundamentally reshapes how financial data is exchanged and utilized, driving advancements in financial services.
Essentially, open banking empowers consumers with greater control over their financial data while also enabling the creation of novel services and applications. For businesses outside the financial sector, this paradigm shift unlocks opportunities to offer customized financial services to their clientele, make more data-driven decisions, and drive innovation in payment processing and account management. Furthermore, with enhanced access to financial data, businesses can streamline payment workflows and unlock fresh revenue streams. According to a 2023 report by Juniper Research, the value of open banking payment transactions is projected to exceed $330 billion globally by 2027.
2. How Does Open Banking Work?
Open banking operates by enabling interoperable financial services through the use of APIs. These APIs facilitate the secure exchange of financial data between banks and authorized third-party providers, creating a more decentralized financial ecosystem.
Unlike traditional banking services, which often operate within a closed environment, open banking promotes a more interconnected and collaborative approach. In traditional banking, data often resides within individual institutions in proprietary formats, making it challenging for external applications to interact directly with financial accounts. Open banking overcomes this hurdle by mandating standardized data formats and secure communication protocols. This creates a level playing field where third-party services can interact with multiple banks under uniform rules, regulations, and technical standards.
The APIs used in open banking typically fall into three main categories:
- Data APIs: These provide read-only access to account information, balances, and transaction history.
- Transaction APIs: These APIs enable the transfer of funds, the establishment of direct debits, and the initiation of payments.
- Product APIs: These allow third parties to aggregate financial products, interest rates, and terms and conditions, often used for comparison websites or marketplaces.
By breaking down data silos and enabling interoperability between platforms, open banking has the potential to accelerate innovation in the financial services industry, providing businesses with more detailed data insights and an expanded range of financial service options.
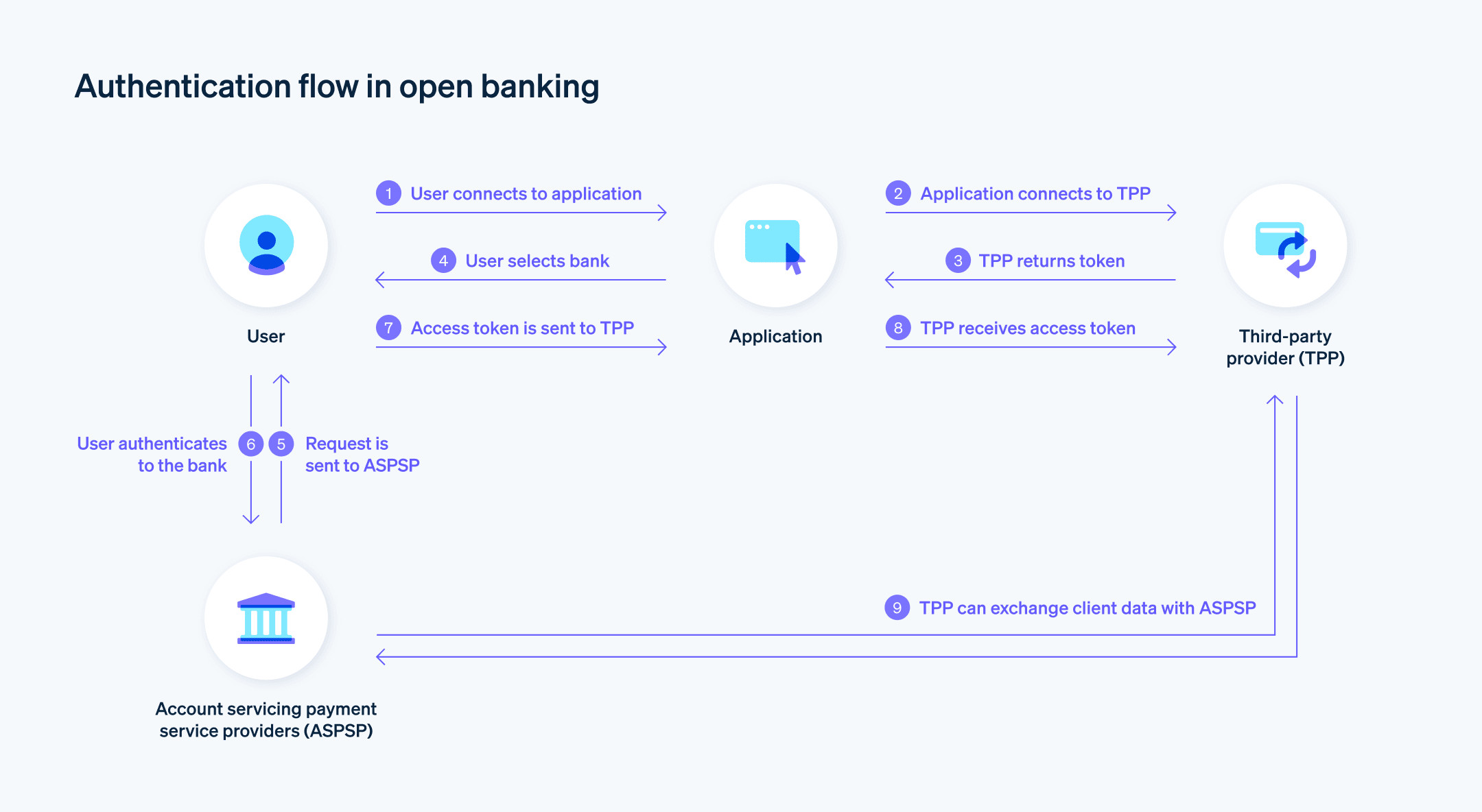 Authentication flow in open banking – Example of authentication flow in open banking
Authentication flow in open banking – Example of authentication flow in open banking
3. Examples of Open Banking Services
Open banking isn’t just a single product or service; it’s a framework that enables a wide array of financial services. As this field continues to evolve, the range of financial services that come to market will likely continue to expand. Here are a few examples of how open banking is currently being used:
- Payment Initiation Services: Retailers can initiate payments directly from a customer’s bank account without needing a traditional payment gateway. This method enables faster settlements and lower transaction fees.
- Account Aggregation: Financial advisors and wealth managers can pull data from multiple accounts, providing a more comprehensive view of a client’s financial status. This enables more accurate and tailored advice.
- Automated Budgeting: Businesses can provide their employees with an intelligent expense management system that automatically categorizes and monitors expenses from multiple bank accounts, simplifying financial reporting and control.
- Instant Loans and Credit Scoring: Financial institutions can access real-time data to assess creditworthiness more accurately, accelerating lending processes.
- Automated Invoice Reconciliation: Companies can use open banking APIs to automate the process of matching invoices with transactions, reducing administrative overhead and improving accuracy.
- Multi-Banking Platforms: A company operating in multiple markets can aggregate its accounts from different banks into a single dashboard, making it easier to monitor global activities.
- Personalized Marketing: Retailers can analyze transaction data to offer targeted promotions or loyalty rewards that are directly aligned with an individual’s purchasing habits.
- Real-Time Fraud Detection: By analyzing transaction data instantly, businesses can detect unusual activity more quickly than before, reducing the risk of financial losses.
These examples offer a glimpse into how open banking can transform the financial services industry. At pioneer-technology.com, we delve into these applications and more, providing you with the latest insights on leveraging open banking for your business.
4. Who Uses Open Banking?
Open banking is reshaping how businesses and consumers interact with financial data. Within the open banking framework, new financial services are emerging that cater to nearly every customer and B2B segment. Here are some of the groups that have been most impacted by open banking so far:
- Individuals: These customers are using open banking to access a wide range of financial services through third-party applications. They can review their spending habits, receive highly personalized financial advice, or automate transactions like bill payments.
- Financial Institutions: Traditional banks, credit unions, and other financial service providers are using open banking to modernize their offerings and improve customer experience. They can also partner with smaller technology companies to bring innovative services to market.
- FinTech Companies: Newer, technology-oriented companies are leveraging the secure data-sharing capabilities of open banking to develop specialized services. These range from budgeting apps to sophisticated financial management solutions for businesses.
- Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs): These businesses are using open banking to automate various tasks, such as reconciling invoices with bank transactions, and to gain a better understanding of their financial status.
- Regulatory Authorities: Organizations that set and enforce financial regulations find open banking useful for creating a standardized environment. This helps protect customers and ensure secure data-handling practices within the financial services industry.
- E-Commerce Businesses: Companies selling products or services online can process transactions more directly, often bypassing traditional payment systems and reducing costs.
- Accounting Platforms: Financial software can access real-time transaction data, which simplifies account management and reduces the need for manual data entry.
- Software Developers: With open banking APIs, software developers can create a range of useful services and tools for individual customers as well as businesses, opening up new avenues for innovation.
- Credit and Lending Institutions: These institutions can make faster and more accurate decisions because they can quickly access financial data, optimizing lending and credit-scoring processes.
Open banking touches numerous sectors, and pioneer-technology.com is your go-to source for understanding how it’s transforming each one. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a financial professional, or a business owner, our comprehensive coverage keeps you informed.
5. Benefits of Open Banking
Open banking offers businesses a multitude of opportunities to improve their operations, more easily comply with regulations, and offer value-added services that position them effectively for the future. Here’s how businesses can benefit from open banking:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: With open banking, businesses gain access to detailed financial data that can inform strategic decisions, from risk assessment to investment planning. The depth of information surpasses that of traditional financial statements.
- Operational Flexibility: Open banking provides a swift flow of data, speeding up transactions and enabling faster reconciliation. This speed translates into greater adaptability under fast-moving market conditions.
- Collaborative Interoperability: Open banking creates an environment where financial institutions and technology-oriented companies can innovate together. This results in a more extensive and sophisticated range of services for business clients.
- Streamlined Payment Processes: Open banking APIs enable more direct payment methods, often bypassing traditional gateways and leading to lower transaction costs.
- Regulatory Alignment: Open banking often incorporates standardized protocols and stringent data protection measures, making it easier for businesses to meet regulatory requirements.
- Customer Customization: Businesses can offer personalized financial services to their clientele, from specialized credit solutions to treasury services, all enabled by the extensive data accessible through open banking.
- Resource Allocation: Streamlined financial operations mean that employees can focus on other areas of the business. Whether it’s automating reconciliation or simplifying billing processes, open banking APIs lead to a more effective use of personnel.
- Market Penetration: Open banking can help businesses tap into new markets. Partnerships with local FinTech companies and easier access to customer data for localized customization streamline the process.
- Innovation Catalyst: For companies in the technology and finance sectors, open banking provides a dynamic means to offer new services that can be monetized, increasing revenue streams and customer loyalty.
With open banking, the possibilities are vast. At pioneer-technology.com, we highlight these advantages, providing insights and strategies for businesses looking to harness the power of open banking.
6. Challenges of Open Banking
While open banking offers many benefits and opportunities for innovation, it also poses challenges that businesses and financial institutions need to be aware of. From integration issues to security vulnerabilities, here are some of the potential downsides of open banking:
- Inconsistent Quality: While some third-party services are excellent, others might not meet the most stringent standards. Inconsistent quality can lead to service disruptions or unreliable data, causing operational difficulties and requiring costly adjustments.
- Integration Problems: Combining multiple services and APIs from third-party providers can lead to unforeseen technical challenges. These complications often require specialized expertise and additional hours for troubleshooting, impacting uptime and increasing costs.
- Limited Standardization: The absence of universal standards complicates communication between different services. This lack of consistency may require manual intervention to ensure systems are compatible and functional.
- Regulatory Hurdles: As open banking evolves, so do the regulations associated with it. Staying up-to-date with these changes can be a resource-intensive task, requiring a dedicated internal team or external experts. Failure to align can lead to penalties or legal issues.
- Accountability Gaps: With multiple parties involved, determining responsibility in the event of an error or a security breach is more complex. This ambiguity can slow down problem resolution and lead to prolonged downtime or unresolved customer concerns.
- Hidden Costs: In addition to API subscription fees, there may be hidden costs for compliance or technical adjustments. These can add up over time, potentially negating the cost-saving benefits of open banking.
- Dependency Risk: By outsourcing core financial functions to third-party providers, businesses are subject to their control to a certain extent. Changes in service availability or terms of use may require abrupt changes to the operations that rely on these services, which can be costly and time-consuming.
- Market Uncertainties: Open banking is still a developing field, subject to changes in technology and public opinion. These unpredictable factors can impact long-term strategies, making secure planning difficult.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Despite efforts to secure the systems, potential gaps in data protection and security protocols may be exploited. The impact of a data breach or other security compromise can extend beyond financial losses, damaging reputation, undermining customer trust, and potentially leading to legal consequences.
The potential of open banking to enhance customer service and unlock new revenue streams also carries risks. Businesses should proceed with caution when adopting this technology, implementing rigorous measures to protect security and privacy. Approaching this field thoughtfully, strategically, and with the right risk-mitigation measures can yield many benefits.
At pioneer-technology.com, we acknowledge these challenges and provide comprehensive guides on navigating them. Stay informed, stay secure, and stay ahead with our expert analysis.
7. FAQ
Q1: What exactly is open banking technology?
Open banking technology allows third-party developers to access a bank’s financial data securely through APIs, enabling innovation and competition in financial services.
Q2: How does open banking enhance financial services?
Open banking allows for the creation of personalized financial products, improved payment processes, and real-time fraud detection, enhancing the overall customer experience and efficiency.
Q3: What are the main benefits of using open banking?
The primary benefits include data-driven decision-making, operational flexibility, streamlined payment processes, enhanced security measures, and customer customization.
Q4: Who are the key players in the open banking ecosystem?
Key players include individual customers, financial institutions, FinTech companies, SMEs, regulatory authorities, e-commerce businesses, accounting platforms, and software developers.
Q5: What security measures are in place to protect data in open banking?
Open banking employs stringent data protection measures, including standardized protocols, secure APIs, and compliance with financial regulations to ensure data security.
Q6: How do open banking APIs facilitate data sharing between banks and third parties?
Open banking APIs provide a secure and standardized method for banks to share financial data with authorized third-party providers, enabling the development of new financial services.
Q7: What are some examples of real-world applications of open banking?
Examples include payment initiation services, account aggregation, automated budgeting, instant loans and credit scoring, automated invoice reconciliation, and personalized marketing.
Q8: What challenges do businesses face when implementing open banking solutions?
Challenges include inconsistent service quality, integration problems, limited standardization, regulatory hurdles, accountability gaps, hidden costs, dependency risk, and potential security vulnerabilities.
Q9: How can businesses overcome integration challenges in open banking?
Businesses can overcome integration challenges by utilizing expert advice, adhering to standardized protocols, and staying updated with regulatory changes.
Q10: How does open banking drive innovation in the financial sector?
Open banking fosters innovation by enabling collaboration between financial institutions and technology companies, leading to the creation of new and improved financial services.
Want to stay ahead of the curve and learn more about these innovative technologies? Visit pioneer-technology.com for more in-depth articles, expert analyses, and the latest trends in open banking and beyond. Don’t just keep up with the future of finance—pioneer it with us. Contact us at Address: 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States. Phone: +1 (650) 723-2300 or visit our Website: pioneer-technology.com.

