RFID technology is used for tracking, identification, and data collection across various industries. Discover more about its applications, benefits, and future trends at pioneer-technology.com, where we provide in-depth analysis of cutting-edge technologies. Learn how Radio Frequency Identification is transforming sectors like retail, healthcare, and logistics.
1. What is RFID Technology?
RFID technology is a wireless communication method that uses radio waves to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. Pioneer-technology.com defines RFID as a system comprising RFID tags and RFID readers, working together to transmit and receive data.
- The technology allows for remote identification without a direct line of sight, making it useful in a wide range of applications, from inventory management to access control.
- RFID systems include tags, which contain information, and readers, which capture data from the tags using radio waves. The information gathered is then processed by a computer system.
1.1 What are the Key Components of an RFID System?
The essential components of an RFID system are tags, readers, and antennas.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| RFID Tag | Contains a microchip and antenna; stores and transmits data. |
| RFID Reader | Sends and receives radio waves; communicates with tags to retrieve data. |
| Antenna | Facilitates the transmission of radio waves between the reader and tag. |
| Software | Processes and manages the data collected by the RFID reader; integrates with systems. |
1.2 How Do RFID Tags Work?
RFID tags work by communicating with RFID readers via radio waves, transmitting stored information.
- When a reader emits a radio signal, the tag’s antenna picks up the signal and uses the energy to power the microchip.
- The microchip then modulates the signal and sends it back to the reader, which interprets the data.
1.3 What Are the Different Types of RFID Tags?
RFID tags come in two primary types: active and passive, each with unique characteristics.
Active RFID Tags: Have their own power source, such as a battery, allowing for longer read ranges and the ability to store more data.
Passive RFID Tags: Rely on the reader’s radio waves to power the tag and transmit data, resulting in shorter read ranges.
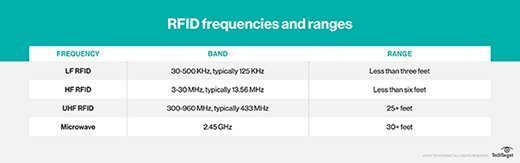
1.4 What are the Frequency Ranges Used in RFID Technology?
RFID technology operates on several frequency ranges, each suited for different applications and environments.
| Frequency Range | Typical Range | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Low Frequency | 30 kHz – 500 kHz | Animal tracking, access control |
| High Frequency | 3 MHz – 30 MHz | Library books, smart cards |
| Ultra-High Frequency | 300 MHz – 960 MHz | Supply chain management, retail inventory |
2. What Are the Primary Applications of RFID Technology?
RFID technology offers many applications across various industries, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and security. According to a study from ABI Research in February 2024, the RFID market is expected to reach $15 billion by 2027, driven by increased adoption in retail and healthcare.
- Inventory Management: RFID enables real-time tracking of inventory, reducing stockouts and improving supply chain efficiency.
- Asset Tracking: Companies can monitor the location and status of valuable assets, preventing loss and optimizing utilization.
- Access Control: RFID is used in security systems to grant or deny access to restricted areas, enhancing security.
- Retail: RFID improves inventory accuracy, reduces theft, and enhances the customer experience through faster checkout processes.
2.1 How Is RFID Used in Retail?
In retail, RFID enhances inventory management and the customer experience.
- RFID tags attached to clothing and other products allow retailers to track inventory in real-time, reducing stockouts and improving order accuracy.
- Self-checkout systems use RFID to quickly scan multiple items at once, improving checkout speed and reducing wait times for customers.
2.2 How Is RFID Used in Healthcare?
RFID technology enhances patient safety, asset tracking, and operational efficiency in healthcare settings.
- RFID tags track medical equipment, ensuring that vital resources are always available and easily located.
- Hospitals use RFID to monitor patient movement and ensure that patients receive the right medications and treatments.
2.3 How Is RFID Used in Supply Chain Management?
RFID technology provides real-time visibility into the location and status of goods as they move through the supply chain. According to a report by McKinsey in December 2023, companies that adopt RFID in their supply chains see a 20% reduction in inventory costs.
- RFID tags attached to pallets, containers, and individual items allow companies to track goods from the manufacturing facility to the distribution center and ultimately to the end customer.
- Real-time tracking improves efficiency, reduces delays, and minimizes the risk of theft or loss.
2.4 How Is RFID Used in Transportation and Logistics?
In transportation and logistics, RFID optimizes vehicle tracking, toll collection, and cargo management.
- RFID tags on vehicles enable automatic toll collection, reducing traffic congestion and improving the efficiency of toll roads.
- Logistics companies use RFID to track the location of cargo containers and manage inventory in warehouses and distribution centers.
2.5 How Is RFID Used in Agriculture?
RFID enhances livestock tracking, crop management, and supply chain visibility in agriculture.
- Farmers use RFID tags to track the location and health of livestock, improving management and preventing theft.
- RFID tags on crops enable tracking from the field to the consumer, ensuring food safety and traceability.
 RFID frequencies and ranges
RFID frequencies and ranges
3. What Are the Benefits of Using RFID Technology?
RFID technology offers many benefits, including increased efficiency, improved accuracy, and enhanced security. According to a study by the University of Arkansas in January 2022, retailers that implemented RFID saw a 16% reduction in out-of-stock items.
- Increased Efficiency: RFID automates data collection, reducing the need for manual processes and improving operational efficiency.
- Improved Accuracy: RFID eliminates errors associated with manual data entry, ensuring that data is accurate and reliable.
- Enhanced Security: RFID provides secure access control and tracking, preventing theft and unauthorized access.
- Real-Time Visibility: RFID offers real-time visibility into the location and status of assets, enabling better decision-making.
3.1 How Does RFID Improve Inventory Accuracy?
RFID improves inventory accuracy by automating the tracking and management of inventory items.
- RFID tags can be read quickly and accurately without requiring a direct line of sight, reducing the time and effort required to conduct inventory counts.
- Automated tracking reduces human error and ensures that inventory data is always up-to-date.
3.2 How Does RFID Enhance Security?
RFID enhances security through secure access control and real-time tracking of assets.
- RFID-enabled access control systems ensure that only authorized personnel can access restricted areas.
- Real-time tracking of assets helps prevent theft and unauthorized removal.
3.3 How Does RFID Increase Efficiency in Operations?
RFID increases operational efficiency by automating data collection and reducing manual processes.
- RFID tags can be read quickly and accurately, reducing the time required to track inventory, manage assets, and process transactions.
- Automated data collection reduces the need for manual data entry, freeing up staff to focus on higher-value tasks.
3.4 How Does RFID Reduce Costs?
RFID reduces costs by improving efficiency, reducing errors, and preventing losses.
- Improved inventory management reduces stockouts and overstocking, minimizing carrying costs and lost sales.
- Reduced errors and improved accuracy minimize the need for rework and corrections, saving time and money.
- Enhanced security and real-time tracking help prevent theft and loss, protecting valuable assets.
4. RFID vs. Barcodes: What are the Key Differences?
RFID and barcodes are both used for tracking and identification, but they have key differences.
| Feature | RFID | Barcodes |
|---|---|---|
| Read Range | Can be read from several feet away | Requires close proximity |
| Line of Sight | Does not require line of sight | Requires direct line of sight |
| Data Storage | Can store more data | Limited data storage |
| Data Read/Write | Can be read and written to | Read-only |
| Durability | More durable, less susceptible to damage | Easily damaged |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Real-Time Tracking | Provides real-time tracking | Requires manual scanning for updates |
| Automation | Supports automation and real-time updates | Requires manual intervention |
| Accuracy | Higher accuracy due to automated data collection | Susceptible to human error |
4.1 When Should You Use RFID Instead of Barcodes?
RFID is preferred over barcodes when real-time tracking, automation, and durability are required.
- RFID is ideal for applications such as inventory management, asset tracking, and access control, where real-time visibility and automated data collection are essential.
- RFID is also preferred in harsh environments where barcodes may be damaged or difficult to read.
4.2 When Should You Use Barcodes Instead of RFID?
Barcodes are preferred over RFID when cost is a major concern and real-time tracking is not required.
- Barcodes are ideal for applications such as retail point-of-sale, where the lower cost and simplicity of barcodes outweigh the benefits of RFID.
- Barcodes are also suitable for applications where items are scanned individually and real-time tracking is not necessary.
4.3 How Do RFID and Barcodes Work Together?
RFID and barcodes can work together to provide a comprehensive tracking solution.
- Some retailers use barcodes for point-of-sale transactions and RFID for inventory management, combining the benefits of both technologies.
- Barcodes can be used to identify individual items, while RFID provides real-time tracking and visibility across the supply chain.
5. What Are the Different Types of RFID Readers?
RFID readers come in various types, each designed for specific applications and environments.
- Fixed Readers: Installed in a fixed location, such as a doorway or conveyor belt, to monitor the movement of tagged items.
- Mobile Readers: Handheld devices used to scan RFID tags in a variety of locations, providing flexibility and portability.
- Integrated Readers: Embedded in devices such as printers or handheld computers, providing seamless RFID functionality.
5.1 What Are Fixed RFID Readers?
Fixed RFID readers are permanently installed in a specific location to monitor tagged items passing through.
- Fixed readers are commonly used in retail stores to track inventory, in warehouses to manage incoming and outgoing shipments, and in manufacturing plants to monitor the movement of parts and materials.
- These readers offer continuous monitoring and real-time data collection, improving efficiency and accuracy.
5.2 What Are Mobile RFID Readers?
Mobile RFID readers are portable devices used to scan RFID tags in various locations.
- Mobile readers are commonly used in retail stores for inventory counts, in warehouses for cycle counting, and in field service applications for asset tracking.
- These readers offer flexibility and portability, allowing users to collect data in a wide range of environments.
5.3 What Are Integrated RFID Readers?
Integrated RFID readers are embedded in other devices, such as printers or handheld computers, to provide seamless RFID functionality.
- Integrated readers are commonly used in point-of-sale systems to scan RFID-tagged items, in healthcare settings to track medical equipment, and in logistics applications to manage shipments.
- These readers offer convenience and efficiency, streamlining workflows and improving data collection.
6. What Are the Challenges of Implementing RFID Technology?
Implementing RFID technology can present several challenges that organizations must address.
- Cost: The initial cost of RFID tags and readers can be significant, especially for large-scale deployments.
- Interference: RFID signals can be affected by interference from other electronic devices or metal objects, reducing accuracy and reliability.
- Privacy Concerns: The use of RFID tags raises privacy concerns, as tags can be read without the knowledge or consent of the individual.
- Standardization: The lack of universal standards can create compatibility issues and limit interoperability between different RFID systems.
6.1 How Do You Address the Cost of RFID Implementation?
The cost of RFID implementation can be addressed through careful planning, pilot programs, and selecting the right RFID solution.
- Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to determine the potential return on investment and justify the upfront costs.
- Start with a pilot program to test the RFID solution in a limited area and refine the implementation strategy before scaling up.
- Select RFID tags and readers that are cost-effective and meet the specific requirements of your application.
6.2 How Do You Mitigate Interference in RFID Systems?
Interference in RFID systems can be mitigated through proper antenna placement, signal shielding, and frequency selection.
- Place RFID antennas in locations that minimize interference from metal objects or other electronic devices.
- Use signal shielding to block interference from external sources and improve the reliability of RFID readings.
- Select an RFID frequency that is less susceptible to interference in your specific environment.
6.3 How Do You Address Privacy Concerns with RFID?
Privacy concerns with RFID can be addressed through transparency, security measures, and compliance with privacy regulations.
- Inform customers and employees about the use of RFID technology and provide them with the option to remove or deactivate RFID tags.
- Implement security measures such as encryption and password protection to prevent unauthorized access to RFID data.
- Comply with relevant privacy regulations and industry best practices to protect the privacy of individuals.
7. What Are the Latest Trends in RFID Technology?
RFID technology is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging to enhance its capabilities and applications.
- Integration with IoT: RFID is increasingly being integrated with the Internet of Things (IoT) to provide real-time data and connectivity for smart devices and systems.
- Cloud-Based RFID: Cloud-based RFID solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and remote access to RFID data, enabling businesses to manage their operations more efficiently.
- RFID Sensors: RFID tags with integrated sensors can collect environmental data such as temperature, humidity, and pressure, providing valuable insights for various applications.
- Advanced Analytics: Advanced analytics tools are being used to analyze RFID data, providing insights into inventory levels, asset utilization, and supply chain performance.
7.1 How Is RFID Being Integrated with IoT?
RFID is being integrated with IoT to create smart, connected systems that provide real-time data and automation.
- RFID tags can be attached to objects and connected to IoT platforms, enabling them to communicate with other devices and systems.
- IoT-enabled RFID solutions can be used to track assets, monitor inventory levels, and automate processes in a variety of industries.
7.2 What Are the Benefits of Cloud-Based RFID?
Cloud-based RFID offers several benefits, including scalability, flexibility, and remote access to RFID data.
- Cloud-based RFID solutions can be easily scaled to accommodate changing business needs, providing the flexibility to add or remove RFID tags and readers as required.
- Cloud-based RFID data can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling businesses to manage their operations remotely.
7.3 How Are RFID Sensors Being Used?
RFID sensors are being used to collect environmental data such as temperature, humidity, and pressure.
- RFID sensors can be attached to objects or placed in specific locations to monitor environmental conditions and provide valuable insights for various applications.
- RFID sensors are commonly used in agriculture to monitor soil conditions, in healthcare to monitor patient vital signs, and in logistics to monitor the temperature of perishable goods.
8. What is the Future of RFID Technology?
The future of RFID technology looks promising, with ongoing innovations and increasing adoption across various industries. According to a report by Global Market Insights in March 2024, the RFID market is projected to grow to $25 billion by 2030, driven by increasing demand in retail, healthcare, and logistics.
- Wider Adoption: RFID technology is expected to be adopted more widely as costs decrease and benefits become more apparent.
- Advanced Applications: New applications for RFID technology will emerge, driven by innovations in sensors, analytics, and IoT integration.
- Enhanced Security: Security measures for RFID systems will be enhanced to address privacy concerns and prevent unauthorized access to data.
- Standardization: Efforts to standardize RFID technology will continue, improving compatibility and interoperability between different systems.
8.1 What New Applications Are Expected to Emerge for RFID?
New applications for RFID technology are expected to emerge in areas such as smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and personalized healthcare.
- RFID can be used in smart cities to track assets, monitor traffic flow, and manage waste collection.
- RFID can be used in autonomous vehicles to track the location of vehicles, monitor road conditions, and prevent collisions.
- RFID can be used in personalized healthcare to track patient medications, monitor vital signs, and improve patient outcomes.
8.2 How Will RFID Security Be Enhanced?
RFID security will be enhanced through the use of encryption, authentication, and access controls.
- Encryption will be used to protect RFID data from unauthorized access, ensuring that only authorized users can read and write data to RFID tags.
- Authentication protocols will be used to verify the identity of RFID readers and tags, preventing spoofing and unauthorized access.
- Access controls will be used to limit access to RFID data and functionality, ensuring that only authorized users can perform specific actions.
8.3 How Will RFID Standardization Improve?
RFID standardization will improve through the development of universal standards for RFID tags, readers, and protocols.
- Universal standards will ensure that RFID systems from different vendors can interoperate seamlessly, improving compatibility and reducing costs.
- Standardization efforts will focus on addressing issues such as frequency allocation, data formats, and security protocols.
9. RFID Security and Privacy Concerns: What You Need to Know
RFID technology is prone to security and privacy concerns, so RFID tag data can be read by anyone with a compatible reader. Tags can often be read after an item leaves a store or supply chain, and can also be read without a user’s knowledge using unauthorized readers. If a tag has a unique serial number, it can be associated with a consumer, raising a privacy concern.
- Data breaches: RFID data can be hacked and read by malicious actors, leading to potential data breaches.
- Unauthorized tracking: Individuals can be tracked without their consent using RFID tags, leading to privacy violations.
- Counterfeiting: RFID tags can be cloned or counterfeited, leading to fraudulent activities.
9.1 How to Protect Your Data from RFID Security Threats?
To mitigate RFID security threats, you can implement several security measures:
- Encryption: Encrypt RFID data to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Access controls: Implement access controls to restrict access to RFID data to authorized personnel only.
- Tag deactivation: Deactivate RFID tags when they are no longer needed to prevent unauthorized tracking.
- Faraday cages: Use Faraday cages to block RFID signals and prevent unauthorized reading.
9.2 What are the Privacy Implications of Using RFID Technology?
The privacy implications of using RFID technology are significant, as it can be used to track individuals without their knowledge or consent. This can lead to potential privacy violations and raise ethical concerns. It’s essential to be transparent about the use of RFID technology and obtain consent from individuals before tracking them.
10. RFID Standards and Regulations: Ensuring Compliance
RFID technology adheres to several guidelines and specifications, including ISO, EPCglobal, and IEC. Each radio frequency has associated standards, including ISO 14223 and ISO/IEC 18000-2 for LF RFID, ISO 15693 and ISO/IEC 14443 for HF RFID, and ISO 18000-6C for UHF RFID.
- Compliance with standards: Adhering to industry standards ensures interoperability and compatibility between different RFID systems.
- Regulatory requirements: Compliance with regulatory requirements, such as those set by the FCC, is essential for operating RFID systems legally.
- Data protection: Implementing data protection measures, such as encryption and access controls, is crucial for complying with privacy regulations.
For more information about RFID technology and its applications, visit pioneer-technology.com, where we provide in-depth analysis and the latest insights into cutting-edge technologies. Explore our articles and resources to stay informed about the transformative potential of RFID.
Ready to explore the future of technology? Visit pioneer-technology.com now and discover the latest insights and innovations. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to stay ahead in the world of technology. Our team of experts provides clear, accessible information to help you understand and leverage the power of RFID and other pioneering technologies. Address: 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States. Phone: +1 (650) 723-2300.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About RFID Technology
Q1: What is the difference between active and passive RFID tags?
Active RFID tags have their own power source (battery), allowing for longer read ranges, while passive RFID tags rely on the reader’s radio waves to power the tag and transmit data.
Q2: What are the primary frequency ranges used in RFID technology?
The primary frequency ranges are Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF), each suited for different applications and environments.
Q3: How does RFID technology improve inventory accuracy?
RFID automates the tracking and management of inventory items, reducing the time and effort required to conduct inventory counts and ensuring that data is always up-to-date.
Q4: What are the key differences between RFID and barcodes?
RFID can be read from a distance without a direct line of sight, store more data, and be read and written to, while barcodes require close proximity, direct line of sight, and are read-only.
Q5: What are the main challenges of implementing RFID technology?
The main challenges include the initial cost of RFID tags and readers, interference from electronic devices or metal objects, privacy concerns, and the lack of universal standards.
Q6: How is RFID technology being integrated with the Internet of Things (IoT)?
RFID is being integrated with IoT to create smart, connected systems that provide real-time data and automation, allowing objects to communicate with other devices and systems.
Q7: What are the benefits of cloud-based RFID?
Cloud-based RFID offers scalability, flexibility, and remote access to RFID data, enabling businesses to manage their operations more efficiently.
Q8: How are RFID sensors being used?
RFID sensors are used to collect environmental data such as temperature, humidity, and pressure, providing valuable insights for various applications.
Q9: What are the security and privacy concerns associated with RFID technology?
Security and privacy concerns include the potential for data breaches, unauthorized tracking, and counterfeiting, necessitating the implementation of security measures like encryption and access controls.
Q10: What is the future of RFID technology?
The future of RFID technology includes wider adoption, advanced applications, enhanced security measures, and improved standardization, driven by innovations in sensors, analytics, and IoT integration.
