Augmented Reality (AR) in technology seamlessly blends digital information with your real-world environment in real-time, offering a unique and immersive experience. At pioneer-technology.com, we’re dedicated to unraveling the complexities of cutting-edge technologies like AR, providing you with clear, insightful, and actionable information. Explore the convergence of the digital and physical realms and discover how AR is transforming industries and everyday life with digital overlays, computer-generated perceptual information, and sensory information.
1. Understanding Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality (AR) enhances the real world by overlaying computer-generated perceptual information on top of it. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which creates entirely artificial environments, AR enriches the user’s actual surroundings with digital content.
What is Augmented Reality?
AR augments reality by adding layers of digital information to the user’s perception. According to a 2023 study by the University of California, Berkeley, AR enhances user experiences by providing contextual and interactive information in real-time.
How Does AR Work?
AR systems utilize hardware components such as processors, sensors, displays, and input devices. Mobile devices like smartphones and tablets are commonly used due to their built-in hardware, including cameras, accelerometers, GPS instruments, and compasses. GPS is used to pinpoint the user’s location, while the compass detects device orientation, enabling AR applications to overlay digital content accurately.
 Smartphone augmented reality
Smartphone augmented reality
Marker-Based vs. Markerless AR
AR applications use either marker-based or markerless methods. Marker-based AR uses special 3D programs that tie animation or contextual digital information into the computer program to an augmented reality marker in the real world. Markerless AR is more complex, relying on recognition algorithms to detect nearby objects and overlay images within the user’s environment.
2. The History and Evolution of AR
The term “augmented reality” was coined in 1990 by Thomas Caudell, a Boeing Computer Services employee. One of the first commercial applications of AR technology was the yellow first-down marker in televised football games in 1998.
Who Coined the Term Augmented Reality?
Thomas Caudell, then at Boeing Computer Services, coined the term in 1990.
Early Applications of AR
The yellow first-down marker in televised football games was one of the first commercial applications.
AR Today
Today, smartphone games, mixed-reality headsets, and heads-up displays (HUDs) in car windshields are well-known consumer AR products. AR technology is also used in healthcare, public safety, gas and oil, tourism, and marketing.
3. AR vs. VR vs. MR
It’s important to differentiate Augmented Reality (AR) from Virtual Reality (VR) and Mixed Reality (MR) to understand each technology’s unique capabilities and applications.
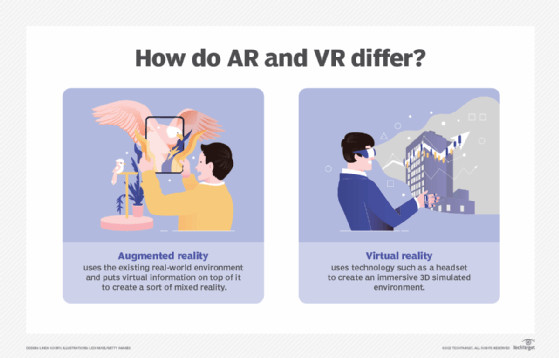
What is the Difference Between AR and VR?
AR enhances the real world by overlaying virtual information on top of it, while VR immerses users in a completely virtual environment. VR is primarily experienced through a headset with sight and sound, whereas AR uses devices like phones, glasses, projections, and HUDs.
What is Mixed Reality (MR)?
Mixed Reality (MR) refers to a virtual display over a real-world environment with which users can interact. For example, Apple Vision Pro can project a virtual keyboard that the wearer can use to type. The key difference between MR and AR is the user’s ability to interact with the digital display.
 Apple Vision Pro
Apple Vision Pro
Spatial Computing and Passthrough
Spatial computing headsets like Apple Vision Pro or Meta Quest 3 use a technique called “passthrough.” This mirrors what the device’s front-facing cameras see on the headset’s display, blending the real and virtual worlds.
4. Key Components of AR Technology
AR technology integrates various components to deliver immersive and interactive experiences.
Hardware Components
AR systems require processors, sensors (cameras, accelerometers, GPS), displays, and input devices. Mobile devices are commonly used due to their integrated hardware.
Software and Algorithms
AR software uses algorithms for object recognition, gesture recognition, and spatial mapping. Machine vision enhances the accuracy and responsiveness of AR applications.
Display Technologies
AR uses various display technologies, including smartphone screens, smart glasses, and heads-up displays (HUDs). These displays present digital information overlaid on the real world.
5. Top AR Use Cases Across Industries
AR is transforming industries by providing innovative solutions and enhancing user experiences.
Retail
Consumers can use AR apps to visualize products in their homes before buying. The Target app’s “See it in Your Space” feature lets users take a photo of a space and digitally view objects to see how they look.
Entertainment and Gaming
AR is used to overlay video games in the real world and animate faces on social media. Pokemon Go is a popular mobile AR game that uses GPS sensors to detect and display Pokemon creatures in the user’s environment.
Navigation
AR can overlay routes over live views of roads and display information about local businesses.
Tools and Measurement
Mobile devices use AR to measure 3D points in the user’s environment. The Apple Measure app acts like a tape measure, allowing users to select points and measure distances.
Art and Architecture
AR helps artists visualize and work on projects, providing new ways to create and interact with art.
Military
AR displays data on vehicle windshields, indicating directions, distances, weather, and road conditions. The U.S. Army uses AR in an eyepiece called TAR to locate soldiers’ positions.
Archaeology
AR aids archaeological research by helping reconstruct sites. 3D models help museum visitors experience excavation sites as if they were there.
6. Real-World Examples of Augmented Reality
Several applications showcase the versatility and impact of AR technology.
Retail Applications
- Target App: The “See it in Your Space” feature lets users visualize furniture and décor in their homes.
- IKEA Place: Allows users to virtually place IKEA furniture in their homes to see how it fits.
Gaming Applications
- Pokemon Go: Uses GPS and AR to overlay Pokemon characters in the real world.
- Snapchat Filters: Overlays filters and masks on users’ faces in real-time.
Industrial Applications
- Boeing: Uses AR to assist technicians in assembling complex wiring harnesses.
- DHL and DB Schenker: Employed Google Glass for frontline workers in supply chain logistics.
Medical Applications
- AccuVein: Uses AR to project vein patterns onto the skin, helping healthcare professionals locate veins easily.
- Surgical Navigation: AR provides surgeons with real-time data and guidance during procedures.
7. Hardware and Software Platforms for AR Development
Developing AR applications requires specific hardware and software platforms.
AR Hardware
- Smartphones and Tablets: Mobile devices are the most accessible AR platforms due to their built-in hardware.
- Smart Glasses: Devices like Google Glass and Microsoft HoloLens provide hands-free AR experiences.
- Headsets: Mixed-reality headsets like Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest 3 offer advanced AR capabilities.
AR Software Platforms
- ARKit (Apple): A set of tools for developing AR experiences on iOS devices. ARKit 6 enables high dynamic range 4K rendering and improves image and video capture.
- ARCore (Google): A platform for building AR experiences on Android and iOS. ARCore uses a geospatial API that sources data from Google Earth 3D models and Street View images.
- Unity: A cross-platform game engine that supports AR development.
- Vuforia: An AR software development kit (SDK) for creating AR applications.
8. The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in AR
Artificial Intelligence (AI) enhances AR by improving object recognition, spatial understanding, and user interaction.
Object Recognition
AI algorithms enable AR devices to recognize and understand objects in the environment.
Spatial Understanding
AI helps AR systems create detailed spatial maps, improving the accuracy of digital overlays.
User Interaction
AI facilitates more natural and intuitive user interactions with AR applications.
9. Challenges and Limitations of AR Technology
Despite its potential, AR faces several challenges and limitations.
Technical Challenges
- Processing Power: AR applications can be computationally intensive, requiring powerful hardware.
- Battery Life: AR devices often consume significant battery power.
- Display Limitations: Current display technologies have limitations in terms of resolution, field of view, and brightness.
Social and Ethical Concerns
- Privacy: AR devices can collect and process personal data, raising privacy concerns.
- Social Acceptance: The use of AR devices in public spaces may face social resistance.
- Digital Divide: Access to AR technology may be limited by cost and availability.
10. The Future of AR Technology: Trends and Predictions
The future of AR is promising, with several trends and predictions shaping its development.
Advancements in Hardware
- More Powerful and Lighter Devices: Future AR devices will be more powerful and lighter, offering improved performance and comfort.
- Improved Displays: Advances in display technology will lead to higher resolution, wider field of view, and brighter displays.
Integration with 5G and Cloud Computing
- 5G Networks: The expansion of 5G networks will support cloud-based AR experiences by providing higher data speeds and lower latency.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing will enable AR applications to offload processing tasks, improving performance and reducing the hardware requirements of AR devices.
Expansion of AR in Various Industries
- Healthcare: AR will play a greater role in surgical navigation, medical training, and patient care.
- Education: AR will enhance learning experiences by providing interactive and immersive content.
- Manufacturing: AR will improve efficiency and accuracy in manufacturing processes.
11. Exploring AR Development Platforms
Diving into AR development means understanding the platforms that bring these visions to life. Whether you’re aiming to create immersive games or practical applications, the right platform can make all the difference. Let’s explore some key players in the AR development space.
ARKit: Apple’s AR Framework
ARKit is Apple’s dedicated framework for creating augmented reality experiences on iOS devices. It’s known for its ease of use and robust features, making it a favorite among developers targeting the Apple ecosystem.
Key Features of ARKit
- Scene Understanding: ARKit excels at understanding the environment, allowing developers to create experiences that interact seamlessly with the real world.
- Motion Tracking: Precise motion tracking capabilities ensure that virtual objects stay anchored in place, even as the user moves around.
- Rendering: With advanced rendering capabilities, ARKit enables the creation of visually stunning AR experiences that blend seamlessly with the real world.
ARCore: Google’s AR Platform
ARCore is Google’s answer to ARKit, providing developers with the tools they need to create augmented reality experiences on Android devices. With its focus on accessibility and cross-platform compatibility, ARCore has become a popular choice for reaching a wide audience.
Key Features of ARCore
- Cross-Platform Support: ARCore supports both Android and iOS, making it easy to create AR experiences that work on a variety of devices.
- Cloud Anchors: ARCore’s Cloud Anchors feature allows users to share AR experiences with others, creating collaborative and engaging interactions.
- Augmented Images: With Augmented Images, developers can trigger AR experiences based on real-world images, opening up a world of possibilities for interactive storytelling and marketing.
Unity: The Versatile Game Engine
While not strictly an AR platform, Unity is a versatile game engine that supports AR development through plugins and extensions. With its intuitive interface and extensive asset store, Unity is a popular choice for creating immersive AR games and applications.
Key Features of Unity
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Unity supports a wide range of platforms, including iOS, Android, and desktop, making it easy to reach a broad audience with your AR creations.
- Asset Store: Unity’s Asset Store is a treasure trove of pre-built assets, plugins, and tools that can accelerate the AR development process.
- Visual Scripting: With visual scripting tools like Bolt, Unity allows developers to create complex AR interactions without writing a single line of code.
12. How Augmented Reality is Being Used
AR, has rapidly evolved from a futuristic concept to a practical tool with diverse applications.
AR in Retail: Enhancing the Shopping Experience
AR is revolutionizing the retail industry by enhancing the shopping experience for consumers.
- Virtual Try-On: AR enables customers to virtually try on clothing, accessories, and makeup before making a purchase.
- Product Visualization: AR allows shoppers to visualize furniture and home decor items in their living spaces, helping them make informed decisions.
- Interactive Catalogs: AR-powered catalogs bring products to life with interactive 3D models and augmented reality experiences.
AR in Healthcare: Transforming Patient Care
AR is transforming healthcare by improving patient care and enhancing medical training.
- Surgical Assistance: AR provides surgeons with real-time guidance and visualization during complex procedures, improving precision and reducing errors.
- Medical Training: AR simulations allow medical students to practice procedures in a safe and controlled environment, enhancing their skills and confidence.
- Patient Education: AR apps help patients understand medical conditions and treatment options through interactive visualizations and augmented reality experiences.
AR in Education: Engaging Students in New Ways
AR is revolutionizing education by engaging students in new and exciting ways.
- Interactive Textbooks: AR-enhanced textbooks bring learning materials to life with interactive 3D models and augmented reality experiences.
- Virtual Field Trips: AR allows students to explore historical sites, museums, and natural wonders from the comfort of their classroom, providing immersive and engaging learning experiences.
- Gamified Learning: AR games and simulations make learning fun and engaging, helping students master complex concepts and skills.
AR in Manufacturing: Streamlining Processes and Improving Efficiency
AR is streamlining processes and improving efficiency in the manufacturing industry.
- Assembly Assistance: AR provides workers with step-by-step instructions and visual guidance during assembly tasks, reducing errors and improving productivity.
- Remote Maintenance: AR enables remote experts to provide real-time assistance and troubleshooting to on-site technicians, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Quality Control: AR overlays provide inspectors with visual cues and annotations, making it easier to identify defects and ensure product quality.
13. Augmented Reality: Statistics Defining the Present and Future
As augmented reality becomes more integrated into our daily lives, understanding its statistical impact helps us grasp its current standing and future trajectory.
Market Size and Growth:
The global augmented reality (AR) market was valued at USD 35.37 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow from USD 48.47 billion in 2024 to USD 341.60 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 27.5% during the forecast period. This demonstrates the rapidly increasing adoption of AR technologies across various sectors.
Consumer Adoption Rates:
A recent survey indicates that nearly 60% of consumers are already aware of AR technology, and about 35% have used AR applications at least once. This highlights a growing familiarity and willingness among the general population to engage with AR experiences.
Industry-Specific Impacts:
- Retail: Retailers using AR have reported a 40% increase in click-through rates and a 25% uplift in conversion rates. This showcases AR’s effectiveness in enhancing the shopping experience and driving sales.
- Healthcare: Hospitals employing AR for surgical procedures have seen a 30% reduction in surgery time and a 20% decrease in post-operative complications. AR’s precision and real-time guidance are significantly improving medical outcomes.
- Education: Schools that integrate AR into their curricula have observed a 45% improvement in student engagement and a 35% increase in knowledge retention. AR’s interactive and immersive nature is transforming educational practices.
Investment Trends:
Venture capital investments in AR startups have surged by 50% year-over-year, reaching a total of USD 4 billion in the last year. This substantial financial backing underscores the immense potential that investors see in AR technology.
Forecasts and Predictions:
By 2025, it is estimated that over 70% of enterprises will be using AR in some form, whether for training, customer engagement, or product development. Furthermore, analysts predict that AR-enabled devices will outsell VR devices by a ratio of 3:1, emphasizing AR’s broader appeal and utility.
Usage in Marketing and Advertising:
Brands using AR in their marketing campaigns have experienced a 70% higher engagement rate compared to traditional methods. AR ads also see a dwell time that is twice as long as standard video ads, indicating that consumers are more interested and spend more time interacting with AR content.
14. AR and Mobile Technology
Augmented Reality (AR) has found a natural ally in mobile technology, creating a dynamic synergy that has revolutionized various aspects of our daily lives.
Accessibility and Convenience:
Mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, are ubiquitous, making AR technology highly accessible to a broad audience. The convenience of having AR capabilities on devices that people already own has significantly accelerated its adoption.
Integration of Sensors:
Mobile devices are equipped with a variety of sensors, including cameras, GPS, accelerometers, and gyroscopes, which are essential for AR functionality. These sensors enable AR apps to understand the user’s environment, track movement, and overlay digital content accurately.
AR Apps and Ecosystems:
The proliferation of AR apps on platforms like the App Store (iOS) and Google Play Store (Android) has fueled the growth of AR. These apps offer a wide range of experiences, from gaming and entertainment to education and productivity.
Mobile AR for Retail:
Retailers have leveraged mobile AR to enhance the shopping experience for consumers. AR apps allow customers to virtually try on clothes, visualize furniture in their homes, and access product information in an interactive way.
Mobile AR in Education:
Educational institutions are using mobile AR to create engaging and immersive learning experiences. AR apps can bring textbooks to life, provide interactive simulations, and enable virtual field trips.
Challenges and Considerations:
Despite the benefits, mobile AR also faces challenges. Processing power, battery life, and display limitations on mobile devices can impact the performance and quality of AR experiences.
15. Augmented Reality in the Automotive Industry
Augmented Reality (AR) is making significant inroads into the automotive industry, transforming how vehicles are designed, manufactured, sold, and maintained.
Design and Prototyping:
AR is being used to visualize and evaluate vehicle designs in real-time. Designers can overlay virtual models onto physical prototypes, allowing them to assess aesthetics, ergonomics, and functionality.
Manufacturing and Assembly:
AR provides workers with step-by-step instructions and visual guidance during assembly tasks. AR-enabled tools project information onto the vehicle, ensuring that components are installed correctly and efficiently.
Sales and Marketing:
AR enhances the car-buying experience by allowing customers to visualize vehicles in their driveways or customize them with different features. AR apps provide interactive tours of vehicle interiors and highlight key selling points.
Navigation and Driver Assistance:
AR is integrated into heads-up displays (HUDs) to provide drivers with real-time navigation and safety information. AR overlays can highlight points of interest, warn of potential hazards, and provide lane guidance.
Maintenance and Repair:
AR assists mechanics with diagnosing and repairing vehicles. AR apps overlay diagnostic information onto the engine, guiding mechanics through complex repair procedures.
Challenges and Considerations:
Implementing AR in the automotive industry requires careful consideration of safety, reliability, and user experience. AR systems must be designed to minimize distractions and provide accurate information in real-time.
16. The Impact of AR on Training and Development
Augmented Reality (AR) is revolutionizing training and development across various industries, offering immersive, interactive, and cost-effective solutions.
Enhanced Learning Experiences:
AR creates engaging learning experiences by overlaying digital content onto the real world. Trainees can interact with virtual objects, explore complex systems, and practice skills in a safe and controlled environment.
Real-Time Guidance and Feedback:
AR provides trainees with real-time guidance and feedback during training exercises. AR apps overlay instructions onto equipment, highlight critical steps, and provide performance metrics.
Remote Collaboration:
AR enables remote experts to provide training and support to on-site workers. AR-enabled tools allow experts to see what trainees are seeing and provide real-time assistance.
Cost-Effective Solutions:
AR reduces the cost of training by eliminating the need for physical equipment, travel expenses, and instructor fees. AR simulations can be created quickly and easily, allowing organizations to adapt to changing training needs.
Applications Across Industries:
- Manufacturing: AR is used to train workers on assembly tasks, machine operation, and quality control procedures.
- Healthcare: AR is used to train medical students on surgical procedures, anatomy, and patient care.
- Aerospace: AR is used to train technicians on aircraft maintenance, repair, and inspection procedures.
17. Security and Privacy in Augmented Reality
As Augmented Reality (AR) becomes more pervasive, addressing security and privacy concerns is essential to ensure user safety and trust.
Data Collection and Usage:
AR apps collect and process a wide range of data, including location, camera data, user interactions, and personal information. It is crucial to implement transparent data collection practices and obtain user consent.
Authentication and Authorization:
AR systems must implement robust authentication and authorization mechanisms to protect user accounts and prevent unauthorized access. Multi-factor authentication, biometric authentication, and secure password policies are essential.
Privacy-Preserving Techniques:
Techniques such as differential privacy, homomorphic encryption, and federated learning can be used to protect user privacy while still enabling AR functionality.
Security Vulnerabilities:
AR systems are vulnerable to a variety of security threats, including spoofing, tampering, eavesdropping, and denial-of-service attacks. Regular security audits, penetration testing, and vulnerability assessments are necessary.
Ethical Considerations:
AR developers and organizations must consider the ethical implications of AR technology, including potential bias, discrimination, and manipulation.
Regulations and Compliance:
Organizations must comply with relevant data protection regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA.
18. AR Applications in Cultural Heritage and Tourism
Augmented Reality (AR) is transforming cultural heritage and tourism, offering new ways for visitors to engage with historical sites, artifacts, and cultural experiences.
Interactive Site Visits:
AR apps overlay digital content onto historical sites, providing visitors with information about the site’s history, architecture, and significance. Visitors can use their smartphones or tablets to explore the site in an interactive way.
Virtual Reconstructions:
AR can reconstruct historical sites and artifacts that have been damaged or destroyed. Visitors can use AR apps to see what these sites and artifacts looked like in their original state.
Augmented Museum Exhibits:
AR enhances museum exhibits by overlaying digital content onto artifacts. Visitors can use AR apps to access additional information, view 3D models, and interact with exhibits in new ways.
Personalized Tours:
AR apps can provide personalized tours that cater to visitors’ interests and preferences. Visitors can select the topics they want to learn about and receive customized content.
Remote Access:
AR allows people to experience cultural heritage sites and artifacts remotely. AR apps can provide virtual tours of sites and museums, allowing people to explore these places from the comfort of their homes.
19. Integrating AR with IoT (Internet of Things)
The integration of Augmented Reality (AR) with the Internet of Things (IoT) is creating new possibilities for enhancing productivity, efficiency, and user experiences across various industries.
Real-Time Data Visualization:
AR can overlay real-time data from IoT devices onto the physical world. For example, AR can display temperature, pressure, and flow rate data from sensors in a factory.
Remote Monitoring and Control:
AR enables remote operators to monitor and control IoT devices. Operators can use AR apps to view data, adjust settings, and perform maintenance tasks from anywhere in the world.
Predictive Maintenance:
AR can predict equipment failures based on data from IoT sensors. AR apps can alert maintenance technicians to potential problems and provide guidance on how to fix them.
Smart Environments:
AR can create smart environments by connecting IoT devices with AR applications. For example, AR can be used to control lighting, temperature, and security systems in a building.
Applications Across Industries:
- Manufacturing: AR and IoT can improve efficiency and productivity in manufacturing processes.
- Healthcare: AR and IoT can enhance patient care and improve medical outcomes.
- Retail: AR and IoT can create personalized shopping experiences.
20. Ethical Considerations in the Use of Augmented Reality
As Augmented Reality (AR) technology becomes more sophisticated and integrated into our daily lives, it is crucial to address the ethical considerations surrounding its use.
Privacy and Data Collection:
AR apps collect and process a wide range of data, including location, camera data, user interactions, and personal information. It is essential to implement transparent data collection practices and obtain user consent.
Bias and Discrimination:
AR algorithms can perpetuate bias and discrimination if they are trained on biased data. AR developers must ensure that their algorithms are fair and equitable.
Manipulation and Deception:
AR can be used to manipulate and deceive people. For example, AR can be used to create fake news or propaganda. It is important to develop safeguards to prevent AR from being used for malicious purposes.
Addiction and Mental Health:
Excessive use of AR can lead to addiction and mental health problems. It is important to promote responsible use of AR and provide resources for people who are struggling with addiction.
Accessibility:
AR technology should be accessible to people with disabilities. AR developers should design their apps with accessibility in mind.
Transparency and Accountability:
AR developers and organizations should be transparent about how they are using AR technology and be accountable for the consequences of their actions.
As you can see, AR is revolutionizing numerous industries, from retail and healthcare to education and manufacturing. Stay ahead of the curve by visiting pioneer-technology.com for the latest updates, in-depth analyses, and expert insights into the world of augmented reality and other groundbreaking technologies.
Ready to explore the endless possibilities of AR and other cutting-edge technologies? Visit pioneer-technology.com today and unlock a world of innovation! For more information, reach out to us at 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States, or call +1 (650) 723-2300.
FAQ: Augmented Reality (AR)
1. What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
Augmented Reality (AR) enhances the real world by overlaying computer-generated images on top of it.
2. How does AR differ from Virtual Reality (VR)?
AR enhances the real world, while VR creates a completely virtual environment.
3. What are the main components of an AR system?
Processors, sensors, displays, and input devices are the main components.
4. What are some common uses of AR in retail?
Virtual try-ons and visualizing products in a space are common uses.
5. How is AR being used in the healthcare industry?
AR is used for surgical assistance, medical training, and patient education.
6. What is ARKit?
ARKit is Apple’s platform for building AR experiences on iOS devices.
7. What is ARCore?
ARCore is Google’s platform for building AR experiences on Android and iOS.
8. What are the challenges of developing AR applications?
Processing power, battery life, and display limitations are challenges.
9. How is AR being used in the automotive industry?
AR assists in design, manufacturing, sales, and navigation.
10. What ethical considerations should be considered in AR development?
Privacy, bias, and the potential for manipulation should be considered.
