Technology Advancement In Healthcare is revolutionizing patient care, improving diagnostics, and streamlining operations. Pioneer-technology.com offers insights into these cutting-edge technologies that are reshaping the medical landscape, providing accessible and in-depth analysis. Stay ahead of the curve with our expert coverage of digital health solutions, telehealth advancements, and AI-driven diagnostics, enhancing both patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.
Table of Contents
- What Are the Key Areas of Technology Advancement in Healthcare?
- How Is Artificial Intelligence (AI) Transforming Healthcare?
- What Role Does the Internet of Things (IoT) Play in Modern Healthcare?
- How Does Telehealth Enhance Healthcare Accessibility and Efficiency?
- What Innovations Are Occurring in Medical Imaging Technologies?
- How Is Robotics Being Integrated Into Healthcare Practices?
- What Are the Benefits of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) in Modern Healthcare?
- What Advancements Are Being Made in Personalized Medicine?
- How Is Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Being Used in Healthcare?
- What Are the Key Challenges and Considerations for Technology Implementation in Healthcare?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What Are the Key Areas of Technology Advancement in Healthcare?
Technology advancement in healthcare spans several critical areas including artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), telehealth, medical imaging, robotics, electronic health records (EHRs), personalized medicine, and virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR). These advancements collectively improve diagnostics, treatment, patient care, and operational efficiency.
Expanding on Key Areas of Technology in Healthcare:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI revolutionizes healthcare through machine learning algorithms that enhance diagnostics, personalize treatment plans, and improve drug discovery processes. AI tools can analyze vast amounts of medical data, identifying patterns and predicting outcomes with increasing accuracy.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT connects medical devices and sensors, enabling continuous monitoring of patients’ health metrics. This data-driven approach facilitates remote patient care, early detection of health issues, and personalized interventions.
- Telehealth: Telehealth expands healthcare access by enabling remote consultations, virtual check-ups, and remote monitoring. This technology is particularly beneficial for patients in rural areas or those with mobility issues, ensuring timely access to medical expertise.
- Medical Imaging: Advances in medical imaging technologies, such as MRI, CT scans, and ultrasound, provide clearer and more detailed images of the human body. These improvements allow for earlier and more accurate diagnoses, leading to better treatment outcomes.
- Robotics: Robotics are transforming surgical procedures with robotic-assisted surgery, which offers greater precision, minimal invasiveness, and faster recovery times. Robots also assist in rehabilitation, medication dispensing, and sanitation, improving overall efficiency and patient safety.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): EHRs streamline healthcare administration by digitizing patient records, making them easily accessible to healthcare providers. This enhances coordination of care, reduces medical errors, and improves overall efficiency.
- Personalized Medicine: Personalized medicine utilizes genetic and molecular data to tailor treatment plans to individual patients. This approach ensures that patients receive the most effective treatments based on their unique characteristics, improving outcomes and reducing adverse effects.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR are being used in healthcare for training, pain management, and rehabilitation. VR simulations provide immersive training environments for medical professionals, while AR enhances patient education and treatment adherence.
 Technology Advancement in Healthcare
Technology Advancement in Healthcare
2. How Is Artificial Intelligence (AI) Transforming Healthcare?
AI is transforming healthcare by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatment plans, automating administrative tasks, and accelerating drug discovery. AI algorithms analyze complex medical data, identifying patterns and insights that improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. According to research from Stanford University’s Department of Computer Science, AI-driven diagnostics can improve accuracy by up to 30% compared to traditional methods.
Expanding on the Roles of AI in Healthcare:
- Diagnostic Accuracy: AI algorithms analyze medical images, lab results, and patient history to detect diseases earlier and more accurately. Machine learning models can identify subtle anomalies that human doctors might miss, leading to faster diagnosis and treatment.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: AI uses patient-specific data to tailor treatment plans, ensuring that each patient receives the most effective interventions based on their unique needs. This personalized approach optimizes treatment outcomes and minimizes adverse effects.
- Automated Administrative Tasks: AI automates routine administrative tasks, such as scheduling appointments, processing insurance claims, and managing medical records. This frees up healthcare professionals to focus on patient care, improving overall efficiency.
- Drug Discovery: AI accelerates drug discovery by analyzing vast amounts of genomic and molecular data, identifying potential drug candidates, and predicting their efficacy. This reduces the time and cost associated with bringing new drugs to market.
- Predictive Analytics: AI uses predictive analytics to forecast patient health outcomes, identify at-risk populations, and optimize resource allocation. This proactive approach enables healthcare providers to intervene early, preventing complications and improving patient health.
- Robotic Surgery Enhancement: AI algorithms can enhance the capabilities of robotic surgery systems, providing surgeons with real-time feedback, improved precision, and enhanced visualization. This results in less invasive procedures, shorter recovery times, and better patient outcomes.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: AI-powered remote patient monitoring systems track patients’ health metrics from their homes, enabling early detection of health issues and timely interventions. This approach improves patient outcomes, reduces hospital readmissions, and lowers healthcare costs.
- Mental Health Support: AI chatbots and virtual assistants provide mental health support to patients, offering immediate access to counseling, stress management techniques, and personalized advice. This improves mental health outcomes, reduces stigma, and enhances access to care.
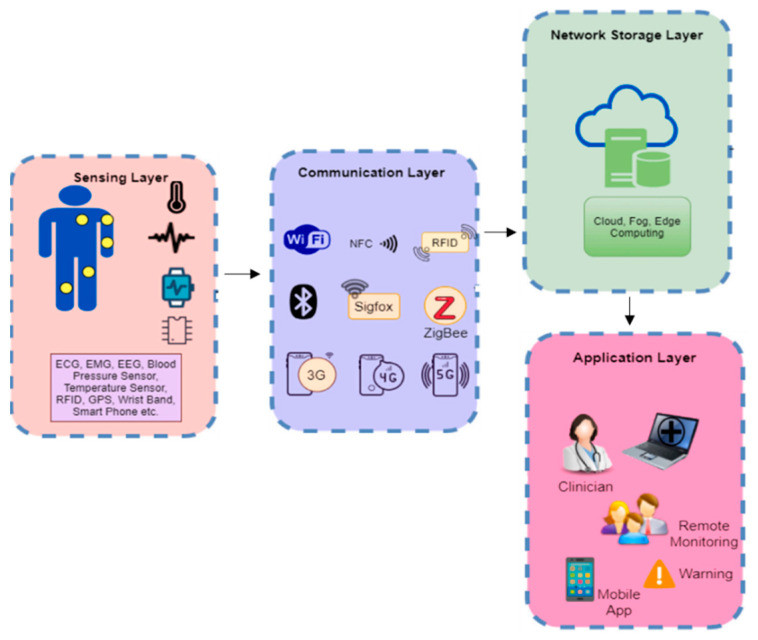
3. What Role Does the Internet of Things (IoT) Play in Modern Healthcare?
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects medical devices and sensors, enabling real-time monitoring of patients’ health data, improving remote patient care, and enhancing the efficiency of healthcare operations. According to a report by McKinsey, the IoT in healthcare is expected to generate over $1 trillion in economic value by 2025 through improved patient outcomes and reduced costs.
Expanding on the IoT’s Impact in Healthcare:
- Real-Time Monitoring: IoT devices continuously monitor vital signs, activity levels, and other health metrics, providing real-time data to healthcare providers. This enables early detection of health issues and timely interventions.
- Remote Patient Care: IoT-enabled remote monitoring allows patients to receive care from the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for hospital visits and improving access to care for those in rural areas or with mobility issues.
- Medication Management: Smart pill dispensers and wearable sensors ensure patients take their medications as prescribed, improving adherence and treatment outcomes. These devices track medication usage and remind patients to take their pills at the correct times.
- Chronic Disease Management: IoT devices help patients manage chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and asthma by monitoring key health metrics and providing personalized feedback. This empowers patients to take control of their health and reduces the need for frequent hospital visits.
- Asset Tracking: IoT sensors track the location and status of medical equipment, ensuring that it is available when and where it is needed. This reduces equipment downtime, improves efficiency, and lowers costs.
- Hygiene Monitoring: IoT sensors monitor hand hygiene compliance in healthcare facilities, reducing the spread of infections and improving patient safety. These systems track handwashing frequency and provide feedback to healthcare workers, promoting better hygiene practices.
- Smart Hospitals: IoT technologies create smart hospitals that optimize resource allocation, improve patient flow, and enhance the overall patient experience. These hospitals use data-driven insights to streamline operations, reduce wait times, and improve patient satisfaction.
- Emergency Response: IoT sensors detect falls, seizures, and other medical emergencies, automatically alerting emergency services and healthcare providers. This ensures that patients receive timely assistance, improving outcomes and saving lives.
 Internet of Things (IoT) in Healthcare
Internet of Things (IoT) in Healthcare
4. How Does Telehealth Enhance Healthcare Accessibility and Efficiency?
Telehealth enhances healthcare accessibility and efficiency by enabling remote consultations, virtual check-ups, and remote monitoring, reducing the need for in-person visits and expanding access to care for patients in underserved areas. According to the American Telemedicine Association, telehealth services have increased by over 50% in recent years, demonstrating their growing importance in modern healthcare.
Expanding on Telehealth’s Benefits in Healthcare:
- Remote Consultations: Telehealth allows patients to consult with doctors and specialists remotely, eliminating the need to travel to medical facilities. This is particularly beneficial for patients in rural areas or those with mobility issues.
- Virtual Check-Ups: Telehealth enables virtual check-ups, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health progress and adjust treatment plans as needed. This improves patient outcomes and reduces the need for frequent in-person visits.
- Remote Monitoring: Telehealth facilitates remote monitoring of patients’ vital signs and other health metrics, enabling early detection of health issues and timely interventions. This reduces hospital readmissions and improves overall patient health.
- Specialist Access: Telehealth expands access to specialists, allowing patients to consult with experts regardless of their location. This is particularly important for patients with rare or complex conditions who may not have access to specialists in their local area.
- Mental Health Support: Telehealth provides virtual mental health support, offering counseling, therapy, and psychiatric evaluations remotely. This improves access to mental healthcare, reduces stigma, and enhances patient outcomes.
- Chronic Disease Management: Telehealth programs help patients manage chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and asthma by providing remote monitoring, education, and support. This improves patient adherence to treatment plans and reduces the need for hospital visits.
- Post-Operative Care: Telehealth enables remote post-operative care, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patients’ recovery progress and provide guidance from their homes. This reduces the risk of complications, improves patient satisfaction, and lowers healthcare costs.
- Emergency Consultations: Telehealth provides emergency consultations, allowing healthcare providers to assess patients’ conditions and provide immediate guidance in urgent situations. This improves outcomes, reduces wait times, and saves lives.
5. What Innovations Are Occurring in Medical Imaging Technologies?
Innovations in medical imaging technologies include advancements in MRI, CT scans, PET scans, and ultrasound, providing higher resolution images, faster scanning times, and reduced radiation exposure. These improvements enhance diagnostic accuracy, enable earlier detection of diseases, and improve treatment planning. A study published in the journal Radiology highlighted that advanced imaging techniques can detect tumors at earlier stages, improving survival rates by up to 20%.
Expanding on Medical Imaging Innovations:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Advances in MRI technology include higher field strengths, improved image resolution, and faster scanning times. This allows for more detailed and accurate imaging of soft tissues, improving diagnosis of neurological and musculoskeletal conditions.
- Computed Tomography (CT Scans): Innovations in CT scanning technology include reduced radiation exposure, faster scanning speeds, and improved image quality. Dual-energy CT scans provide additional diagnostic information, improving detection of tumors and other abnormalities.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET Scans): Advances in PET scanning technology include improved detector sensitivity, reduced scanning times, and enhanced image resolution. PET scans are used to detect cancer, assess brain function, and monitor treatment response.
- Ultrasound: Innovations in ultrasound technology include higher frequency transducers, improved image processing, and enhanced portability. Ultrasound is used to image a wide range of tissues and organs, including the heart, liver, and blood vessels.
- Molecular Imaging: Molecular imaging technologies, such as SPECT and PET, allow for the visualization of biological processes at the molecular level. This improves early detection of diseases, enhances treatment planning, and monitors treatment response.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Imaging: AI algorithms are used to enhance medical images, improve diagnostic accuracy, and automate image analysis. AI can detect subtle anomalies that human doctors might miss, leading to faster diagnosis and treatment.
- 3D Printing: 3D printing is used to create patient-specific anatomical models, allowing surgeons to plan complex procedures and improve outcomes. These models provide a tactile representation of the patient’s anatomy, enhancing surgical precision and reducing the risk of complications.
- Contrast Agents: Advances in contrast agents improve the visibility of tissues and organs in medical images, enhancing diagnostic accuracy. New contrast agents are designed to target specific molecules or cells, providing additional diagnostic information.
6. How Is Robotics Being Integrated Into Healthcare Practices?
Robotics are being integrated into healthcare practices through robotic-assisted surgery, rehabilitation robots, medication dispensing robots, and sanitation robots, improving precision, reducing invasiveness, and enhancing efficiency. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the healthcare robotics market is projected to reach $17 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures and improved patient outcomes.
Expanding on the Applications of Robotics in Healthcare:
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Robotic-assisted surgery provides surgeons with enhanced precision, dexterity, and control, allowing for minimally invasive procedures with smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, and faster recovery times.
- Rehabilitation Robots: Rehabilitation robots assist patients with physical therapy, helping them regain mobility and function after injury or surgery. These robots provide personalized exercises and monitor patients’ progress, improving rehabilitation outcomes.
- Medication Dispensing Robots: Medication dispensing robots automate the process of dispensing medications, reducing errors, improving efficiency, and enhancing patient safety. These robots track medication inventory, verify prescriptions, and ensure that patients receive the correct medications at the correct times.
- Sanitation Robots: Sanitation robots clean and disinfect healthcare facilities, reducing the spread of infections and improving patient safety. These robots use UV light and other advanced technologies to eliminate pathogens, creating a safer environment for patients and healthcare workers.
- Telepresence Robots: Telepresence robots allow doctors and specialists to interact with patients remotely, improving access to care for those in rural areas or with mobility issues. These robots provide real-time audio and video communication, enabling virtual consultations and examinations.
- Exoskeletons: Exoskeletons provide support and assistance to patients with mobility impairments, enabling them to walk, stand, and perform other activities. These devices are used in rehabilitation, long-term care, and everyday life, improving patients’ quality of life.
- Surgical Training: Robots are used to train surgeons, providing realistic simulations and feedback to improve their skills and techniques. These robots allow surgeons to practice complex procedures in a safe environment, enhancing their proficiency and reducing the risk of errors.
- Pharmacy Automation: Robots are used to automate pharmacy tasks, such as filling prescriptions, managing inventory, and compounding medications. This improves efficiency, reduces errors, and enhances patient safety.
7. What Are the Benefits of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) in Modern Healthcare?
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) in modern healthcare offer numerous benefits including improved care coordination, reduced medical errors, enhanced efficiency, and better data analysis. According to the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC), over 90% of U.S. hospitals have adopted EHRs, demonstrating their widespread adoption and impact on healthcare delivery.
Expanding on the Advantages of EHRs in Healthcare:
- Improved Care Coordination: EHRs provide a centralized repository of patient information, allowing healthcare providers to access and share data seamlessly. This improves care coordination, reduces duplication of services, and enhances patient outcomes.
- Reduced Medical Errors: EHRs reduce medical errors by providing alerts and reminders, verifying prescriptions, and ensuring that healthcare providers have access to accurate and up-to-date information. This improves patient safety and reduces the risk of adverse events.
- Enhanced Efficiency: EHRs streamline administrative tasks, automate workflows, and improve communication among healthcare providers. This reduces paperwork, saves time, and enhances overall efficiency.
- Better Data Analysis: EHRs generate valuable data that can be used to analyze trends, identify at-risk populations, and improve healthcare quality. This data-driven approach enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions and optimize resource allocation.
- Patient Engagement: EHRs provide patients with access to their medical records, allowing them to review their health information, communicate with their healthcare providers, and participate in their care. This improves patient engagement and empowers them to take control of their health.
- Clinical Decision Support: EHRs integrate clinical decision support tools, providing healthcare providers with evidence-based guidelines, alerts, and recommendations to improve patient care. This helps healthcare providers make informed decisions and deliver the best possible care.
- Billing and Coding Accuracy: EHRs improve billing and coding accuracy by automating the process of generating claims, verifying codes, and ensuring compliance with regulations. This reduces errors, speeds up reimbursement, and enhances financial performance.
- Public Health Reporting: EHRs facilitate public health reporting, allowing healthcare providers to submit data to public health agencies for surveillance, prevention, and response efforts. This improves public health outcomes and protects the population from infectious diseases and other threats.
8. What Advancements Are Being Made in Personalized Medicine?
Advancements in personalized medicine include the use of genetic testing, biomarkers, and targeted therapies to tailor treatment plans to individual patients, improving outcomes and reducing adverse effects. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), personalized medicine has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by providing more effective and targeted treatments for a wide range of conditions.
Expanding on Personalized Medicine Advancements:
- Genetic Testing: Genetic testing identifies genetic variations that influence an individual’s risk of disease, response to medications, and other health-related traits. This information is used to personalize treatment plans and prevent disease.
- Biomarkers: Biomarkers are measurable indicators of disease or physiological state that are used to monitor treatment response, predict prognosis, and diagnose disease. Personalized medicine uses biomarkers to tailor treatment plans and optimize outcomes.
- Targeted Therapies: Targeted therapies are drugs that target specific molecules or pathways involved in disease, improving efficacy and reducing side effects. These therapies are designed to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and other conditions.
- Pharmacogenomics: Pharmacogenomics studies how genes affect an individual’s response to drugs, allowing healthcare providers to select the most effective medications and dosages based on their genetic makeup. This reduces adverse drug reactions and improves treatment outcomes.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy harnesses the power of the immune system to fight cancer and other diseases. Personalized medicine uses biomarkers to identify patients who are most likely to respond to immunotherapy, improving efficacy and reducing side effects.
- Gene Editing: Gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR, allow for precise modification of genes to treat genetic diseases. This approach has the potential to cure inherited disorders and improve patient outcomes.
- Liquid Biopsies: Liquid biopsies analyze circulating tumor cells, DNA, and other biomarkers in the blood, providing a non-invasive way to monitor cancer progression, detect recurrence, and guide treatment decisions.
- Data Analytics: Data analytics are used to integrate and analyze large amounts of patient data, including genetic information, medical history, and lifestyle factors, to personalize treatment plans and improve outcomes.
9. How Is Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Being Used in Healthcare?
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are being used in healthcare for surgical training, pain management, rehabilitation, and patient education, providing immersive experiences and enhancing outcomes. According to a report by Grand View Research, the VR and AR in healthcare market is projected to reach $11.4 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand for innovative training and treatment solutions.
Expanding on the Applications of VR and AR in Healthcare:
- Surgical Training: VR simulations provide realistic training environments for surgeons, allowing them to practice complex procedures and improve their skills and techniques. This reduces the risk of errors and enhances surgical precision.
- Pain Management: VR is used to distract patients from pain, reducing the need for medication and improving comfort. VR experiences transport patients to calming environments, reducing anxiety and alleviating pain.
- Rehabilitation: AR and VR are used in rehabilitation to help patients regain mobility, improve balance, and enhance cognitive function. These technologies provide personalized exercises and monitor patients’ progress, improving rehabilitation outcomes.
- Patient Education: AR enhances patient education by providing interactive visualizations of anatomy, disease processes, and treatment options. This improves patient understanding and empowers them to make informed decisions about their care.
- Mental Health Therapy: VR provides immersive environments for mental health therapy, allowing patients to confront phobias, manage anxiety, and process trauma in a safe and controlled setting.
- Medical Device Training: AR is used to train healthcare providers on the operation and maintenance of medical devices, improving their skills and reducing the risk of errors. This ensures that healthcare providers are proficient in using advanced technologies.
- Surgical Planning: VR is used to create 3D models of patients’ anatomy, allowing surgeons to plan complex procedures and improve outcomes. These models provide a detailed visualization of the surgical site, enhancing precision and reducing the risk of complications.
- Remote Collaboration: AR facilitates remote collaboration among healthcare providers, allowing them to share real-time images and data, provide guidance, and consult on complex cases. This improves access to expertise and enhances patient care.
10. What Are the Key Challenges and Considerations for Technology Implementation in Healthcare?
The key challenges and considerations for technology implementation in healthcare include data security and privacy, interoperability, cost, user training, regulatory compliance, and ethical concerns. Addressing these challenges is essential for successful technology integration and improved patient outcomes. Pioneer-technology.com provides comprehensive insights into these challenges, helping healthcare professionals navigate the complexities of technology adoption.
Expanding on the Key Challenges:
- Data Security and Privacy: Protecting patient data from unauthorized access and cyber threats is a critical challenge. Implementing robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention strategies, is essential.
- Interoperability: Ensuring that different healthcare systems can communicate and share data seamlessly is a major challenge. Adopting standardized data formats and APIs is necessary to achieve interoperability and improve care coordination.
- Cost: The high cost of implementing and maintaining new technologies can be a barrier for many healthcare organizations. Conducting thorough cost-benefit analyses and exploring funding options is crucial for successful technology adoption.
- User Training: Providing adequate training to healthcare professionals on how to use new technologies is essential for ensuring their effective adoption and utilization. Investing in comprehensive training programs can improve user satisfaction and enhance patient outcomes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Complying with healthcare regulations, such as HIPAA and GDPR, is a critical consideration for technology implementation. Implementing policies and procedures to ensure compliance is essential for avoiding penalties and protecting patient privacy.
- Ethical Concerns: Addressing ethical concerns related to AI, data analytics, and other technologies is necessary for ensuring responsible innovation in healthcare. Developing ethical guidelines and involving patients in decision-making can help mitigate these concerns.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating new technologies with existing healthcare systems can be complex and time-consuming. Planning for seamless integration and conducting thorough testing is essential for minimizing disruption and maximizing benefits.
- Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of healthcare data is essential for effective technology implementation. Implementing data governance policies and validation procedures can improve data quality and enhance decision-making.
By visiting pioneer-technology.com, you can discover more about the latest healthcare technology trends, gain in-depth insights into emerging challenges, and find effective solutions to enhance your healthcare practices. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to stay informed and ahead in the rapidly evolving world of healthcare technology.
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How is technology helping in healthcare?
A: Technology helps in healthcare by improving diagnostics, personalizing treatment plans, streamlining administrative tasks, enabling remote patient monitoring, and enhancing surgical precision.
Q: What are the latest technology trends in healthcare?
A: The latest technology trends in healthcare include AI-driven diagnostics, IoT-enabled remote monitoring, telehealth advancements, personalized medicine, and the use of VR and AR for training and therapy.
Q: What is the impact of technology on healthcare quality?
A: Technology improves healthcare quality by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, reducing medical errors, improving care coordination, and providing patients with access to more effective and targeted treatments.
Q: How is AI used in healthcare today?
A: AI is used in healthcare today for analyzing medical images, predicting patient outcomes, automating administrative tasks, accelerating drug discovery, and providing mental health support.
Q: What is the role of the Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare?
A: The IoT connects medical devices and sensors, enabling real-time monitoring of patients’ health data, improving remote patient care, and enhancing the efficiency of healthcare operations.
Q: How does telehealth improve access to healthcare?
A: Telehealth improves access to healthcare by enabling remote consultations, virtual check-ups, and remote monitoring, reducing the need for in-person visits and expanding access to care for patients in underserved areas.
Q: What are the benefits of using electronic health records (EHRs)?
A: The benefits of using EHRs include improved care coordination, reduced medical errors, enhanced efficiency, better data analysis, and increased patient engagement.
Q: How is personalized medicine transforming healthcare?
A: Personalized medicine is transforming healthcare by tailoring treatment plans to individual patients based on their genetic makeup, biomarkers, and other factors, improving outcomes and reducing adverse effects.
Q: What is the role of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) in healthcare?
A: VR and AR are used in healthcare for surgical training, pain management, rehabilitation, patient education, and mental health therapy, providing immersive experiences and enhancing outcomes.
Q: What are the key challenges in implementing technology in healthcare?
A: The key challenges in implementing technology in healthcare include data security and privacy, interoperability, cost, user training, regulatory compliance, and ethical concerns.