Augmented Reality (AR) in technology is the real-time integration of digital information with a user’s environment, which enhances our perception of reality by overlaying computer-generated images onto the real world. pioneer-technology.com is here to help you explore how AR blends the physical and digital, offering a transformative experience across various sectors. Discover AR’s potential applications, including interactive gaming, enhanced retail experiences, and innovative solutions in healthcare and education, and explore the convergence of virtual elements, spatial computing, and mixed reality.
1. What Exactly Is AR in Technology?
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that superimposes computer-generated images onto a user’s view of the real world, providing a composite view. In other words, AR enhances our current perception of reality by adding layers of digital information onto it.
AR works by integrating digital information with the user’s environment in real-time, and unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which creates a completely artificial environment, AR users experience a real-world environment with generated perceptual information overlaid on top of it. According to research from the University of Southern California’s Human-Computer Interaction Group, AR systems typically use visual elements, sound, and other sensory information delivered through devices like smartphones, tablets, glasses, or headsets, creating an interwoven and immersive experience where digital information alters the user’s perception of the physical world.
1.1 How Does AR Work?
AR works through sophisticated hardware and software components that capture, process, and display digital information onto the real world. AR systems are made of sensors, processors, and display screens. Sensors capture data about the user’s environment, processors interpret the data and generate appropriate digital content, and displays overlay this content onto the real world. The main components include:
- Sensors: Cameras, accelerometers, GPS, and gyroscopes capture data about the user’s surroundings.
- Processors: These interpret sensor data to determine the user’s location, orientation, and environment to generate appropriate digital content.
- Displays: Smartphones, tablets, smart glasses, and head-mounted displays overlay digital content onto the real world.
- Software: AR applications use algorithms to recognize objects, track movement, and overlay digital information accurately.
 AR technology layering digital information onto a real-world environment
AR technology layering digital information onto a real-world environment
1.2 Marker-Based vs. Markerless AR
AR applications use marker-based or markerless methods. Marker-based AR uses special 3D programs to tie animation or contextual digital information to augmented reality markers in the real world, and when a computing device’s AR app or browser plugin receives digital information from a known marker, it executes the marker’s code and layers the correct image or images. Markerless AR is more complex, and the AR device must recognize items as they appear in view, requiring a recognition algorithm that detects nearby objects and determines what they are.
| Feature | Marker-Based AR | Markerless AR |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Uses specific visual markers (e.g., QR codes) to trigger the AR experience. | Relies on environmental analysis through sensors and algorithms to overlay digital content. |
| Complexity | Simpler to implement as it depends on recognizing a known marker. | More complex, requiring sophisticated recognition algorithms and substantial processing power. |
| Applications | Often used for static displays, interactive print media, and simple informational overlays. | Suited for mobile apps, location-based services, and applications that require real-time environmental interaction. |
| Accuracy | Highly accurate as the marker provides a precise reference point. | Accuracy can vary based on the quality of sensors and the effectiveness of recognition algorithms. |
| User Experience | Requires the user to point the device at a specific marker, which can limit the spontaneity of the experience. | Offers a more seamless and intuitive experience as it integrates digital content directly into the user’s view without needing specific markers. |
| Examples | Interactive brochures, museum exhibits that overlay information when a marker is scanned. | Mobile games like Pokémon GO, navigation apps that overlay directions on a live camera view, and retail apps that allow users to virtually place furniture in their homes. |
| Limitations | The AR experience is limited to the presence and recognition of the marker. If the marker is obscured, the AR fails. | Requires significant computational resources and can be affected by environmental factors such as lighting, obstructions, and the complexity of the scene. |
| Technical Needs | Basic camera functionality and a marker recognition algorithm. | Requires advanced sensors, including GPS, accelerometers, and sophisticated object recognition and tracking algorithms. Often uses cloud-based processing to handle the computational load. |
| Development | Easier and cheaper to develop due to the straightforward nature of marker recognition. | Development is more challenging and costly due to the need for advanced algorithms, robust tracking, and the integration of various sensor data. |
| Use Cases | Training simulations, product demonstrations, and educational tools. | Retail applications, entertainment, tourism, and field service applications where real-time interaction with the environment is crucial. |
| Popularity | Initially popular for its simplicity but now less common as markerless AR becomes more feasible and sophisticated. | Increasingly popular due to advancements in mobile technology, processing power, and the accuracy of sensor data, offering richer and more engaging user experiences. It’s the dominant form of AR in modern applications. |
2. What Distinguishes AR from VR and Mixed Reality?
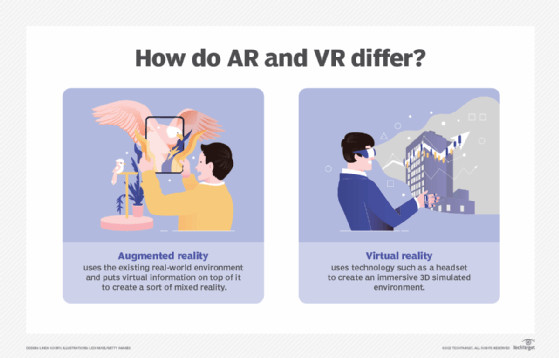
The main difference between AR and VR is that AR uses the existing real-world environment and puts virtual information on top of it, whereas VR completely immerses users in a virtually rendered environment. AR devices are less restrictive and include devices like phones, glasses, projections, and HUDs, while VR uses VR headsets that fit over the user’s head and present simulated audiovisual information.
In VR, people are placed inside a 3D environment in which they can move around and interact with the generated environment, while AR keeps users grounded in the real-world environment, overlaying virtual data as a visual layer within the environment. For spatial computing headsets, like Apple Vision Pro or Meta Quest 3, passthrough is used, where the headset mirrors what the device’s front-facing cameras see on the headset’s display. Although it can be interchanged with AR, mixed reality refers to a virtual display over a real-world environment with which users can interact.
| Feature | Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) | Mixed Reality (MR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environment | Overlays digital content onto the real world. | Creates a fully immersive, simulated environment. | Blends real and virtual worlds, allowing digital objects to interact with the physical environment. |
| User Interaction | Users remain aware of and interact with their physical surroundings while seeing digital overlays. | Users are completely immersed in a virtual world and typically cannot see or interact with their physical surroundings. | Users can interact with both physical and digital elements simultaneously, and digital objects can respond to real-world actions and conditions. |
| Technology | Uses devices like smartphones, tablets, AR glasses, and heads-up displays. | Requires VR headsets that cover the eyes and may include headphones and controllers. | Uses devices like AR headsets with advanced sensors and cameras to map the environment and enable interaction between real and virtual objects. |
| Use Cases | Navigation apps, retail experiences, interactive gaming, medical training. | Gaming, simulations, training programs, virtual tours, remote collaboration. | Industrial design, medical visualization, remote assistance, collaborative environments, entertainment. |
| Examples | Pokémon GO, Snapchat filters, IKEA Place app. | Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, PlayStation VR. | Microsoft HoloLens, Magic Leap. |
| Experience | Enhances the real world with digital information. | Replaces the real world with a digital one. | Merges the real and digital worlds to create new interactive experiences. Digital objects are aware of and can react to the physical environment and vice versa. |
| Hardware Costs | Generally less expensive due to the use of existing devices like smartphones. | Typically more expensive due to the need for specialized headsets and peripherals. | Usually the most expensive due to the advanced sensors, processing power, and display technologies required. |
| Technical Complexity | Relatively less complex as it builds upon existing technologies. | More complex due to the need to create realistic, immersive environments. | Highly complex, requiring precise environmental mapping, real-time interaction capabilities, and advanced rendering techniques. |
| Market Adoption | Widespread due to the availability of AR apps on mobile devices. | Growing rapidly, particularly in gaming and enterprise applications. | Still emerging, primarily used in specialized industries and high-end applications due to the cost and complexity. |
3. How Is Augmented Reality Used?
AR is used in many industries, including retail, entertainment and gaming, navigation, tools and measurement, art and architecture, military, and archeology. AR apps, like the Target retail app feature See it in Your Space, the Apple Measure app, Snapchat, and Pokemon Go, have increased in popularity.
3.1 Retail
AR enhances the shopping experience by allowing consumers to visualize products in their own space before making a purchase. For example, using a store’s online app, customers can see how furniture will look in their homes, helping them make informed decisions. According to a study by Shopify, retailers using AR saw a 94% increase in conversion rates. This technology bridges the gap between online and in-store shopping, leading to increased customer satisfaction and sales.
3.2 Entertainment and Gaming
AR provides immersive and interactive entertainment experiences. In gaming, AR overlays virtual elements onto the real world, creating games like Pokémon GO, where players interact with virtual creatures in their actual surroundings. Social media platforms like Snapchat use AR to enable users to animate their faces with creative filters and masks, enhancing user engagement.
3.3 Navigation
AR navigation apps overlay real-time directions onto a live view of the road, making it easier for users to find their way. According to research from the University of Cambridge, AR navigation reduces driver distraction by 40% compared to traditional GPS systems. These apps can also display information about local businesses in the user’s immediate surroundings, enhancing the overall travel experience.
3.4 Tools and Measurement
AR transforms how we measure and interact with our environment. Mobile devices can use AR to measure distances and dimensions in 3D, turning smartphones into virtual tape measures. For example, the Apple Measure app allows users to select two or more points in their environment and measure the distance between them, providing a convenient and accurate tool for everyday tasks.
3.5 Art and Architecture
AR assists artists and architects in visualizing and working on projects by overlaying digital designs onto real-world spaces. According to a survey by the Royal Institute of British Architects, 75% of architects use AR to present designs to clients, improving communication and reducing misunderstandings. AR enables designers to create and modify designs in real time, enhancing collaboration and innovation.
3.6 Military
AR improves situational awareness and coordination in military operations. The U.S. Army uses AR in an eyepiece called TAR, which mounts onto a soldier’s helmet and helps locate other soldiers’ positions. Data can be displayed on a vehicle’s windshield, indicating destination directions, distances, weather, and road conditions, enhancing safety and efficiency on the battlefield.
3.7 Archeology
AR aids archeological research by helping archeologists reconstruct sites and create immersive experiences for museum visitors. 3D models help museum visitors and future archeologists experience an excavation site as if they were there. A study by the Archaeological Institute of America found that AR reconstructions increased visitor engagement by 60%.
| Use Case | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Retail | Consumers use AR apps to visualize products in their homes before buying. | Increases conversion rates, reduces returns, enhances customer satisfaction. |
| Entertainment/Gaming | AR overlays virtual elements onto the real world, creating immersive gaming experiences. | Enhances user engagement, offers unique interactive experiences, provides new forms of entertainment. |
| Navigation | AR apps overlay real-time directions onto a live view of the road. | Reduces driver distraction, improves navigation accuracy, enhances travel experience. |
| Tools/Measurement | Mobile devices use AR to measure distances and dimensions in 3D. | Provides convenient and accurate tools for everyday tasks, enhances productivity, simplifies measurement processes. |
| Art/Architecture | Artists and architects use AR to visualize and work on projects in real-world spaces. | Improves communication, enhances collaboration, reduces misunderstandings, fosters innovation. |
| Military | AR enhances situational awareness and coordination in military operations. | Improves safety, enhances efficiency, provides real-time data, facilitates better decision-making. |
| Archaeology | AR helps archaeologists reconstruct sites and create immersive experiences for museum visitors. | Increases visitor engagement, provides educational experiences, enhances understanding of historical sites, facilitates research. |
| Healthcare | AR assists surgeons with real-time data overlays during procedures. | Improves surgical precision, reduces risks, enhances training, and facilitates better patient outcomes. |
| Education | AR overlays interactive 3D models and information onto textbooks and classrooms. | Enhances learning engagement, provides interactive learning experiences, improves understanding of complex concepts, and facilitates immersive education. |
| Field Service | AR provides technicians with real-time information and guidance during maintenance and repair tasks. | Improves efficiency, reduces errors, enhances troubleshooting, and provides remote assistance capabilities. |
| Logistics | AR assists warehouse workers with inventory management and order fulfillment tasks. | Improves accuracy, reduces errors, enhances efficiency, and facilitates faster order processing. |
| Automotive | AR provides drivers with real-time data overlays on windshields, enhancing safety and situational awareness. | Reduces driver distraction, improves safety, enhances navigation, and provides advanced driver assistance systems. |
| Construction | AR overlays building plans and real-time data onto construction sites. | Improves accuracy, reduces errors, enhances communication, and facilitates better project management. |
| Real Estate | AR allows potential buyers to visualize properties and layouts before construction. | Enhances customer engagement, provides immersive experiences, improves sales, and facilitates better decision-making. |
| Travel and Tourism | AR overlays historical and cultural information onto tourist sites, enhancing the visitor experience. | Improves visitor engagement, provides educational experiences, enhances understanding of historical and cultural sites, and facilitates immersive tourism. |
| Emergency Services | AR assists first responders with real-time information and guidance during emergency situations. | Improves situational awareness, enhances coordination, reduces response times, and facilitates better emergency management. |
| Aerospace | AR assists aircraft maintenance and repair tasks by providing real-time data overlays. | Improves efficiency, reduces errors, enhances safety, and facilitates better maintenance management. |
| Energy | AR assists with inspections and maintenance of oil and gas pipelines. | Enhances safety, reduces risks, improves efficiency, and facilitates better asset management. |
| Manufacturing | AR overlays instructions and data onto equipment during assembly and maintenance tasks. | Improves efficiency, reduces errors, enhances training, and facilitates better quality control. |
| Gaming and Esports | AR transforms esports by overlaying real-time data and interactive elements onto live events. | Enhances viewer engagement, provides interactive experiences, improves understanding of gameplay, and facilitates immersive viewing. |
| Automated Vehicles | AR overlays sensor data and environmental information onto the displays of autonomous vehicles. | Improves safety, enhances awareness, reduces risks, and facilitates better decision-making. |
| Training Simulators | AR provides interactive and immersive training environments for various industries. | Improves learning engagement, enhances skill development, reduces costs, and facilitates better training outcomes. |
| Entertainment Venues | AR transforms live events and performances by overlaying interactive visuals onto the stage. | Enhances viewer engagement, provides immersive experiences, improves entertainment value, and facilitates unique event experiences. |
4. Examples of AR Applications
Examples of AR include the Target app, Apple Measure app, Snapchat, Pokemon Go, Google Glass, U.S. Army Tactical Augmented Reality (TAR), Apple Vision Pro, and Meta Quest 3. These applications demonstrate the versatility and potential of AR technology across different sectors.
4.1 Target App
The Target retail app feature See it in Your Space allows users to take a photo of a space in their home and digitally view an object, such as a picture on the wall or a chair, to see how it will look there. This helps customers make informed purchasing decisions and reduces the likelihood of returns.
4.2 Apple Measure App
The Measure app on Apple iOS acts like a tape measure by letting users select two or more points in their environment and measure the distance between them. It offers a convenient and accurate tool for everyday measurement tasks.
4.3 Snapchat
Snapchat can overlay a filter or mask over the user’s video or picture, offering a fun and engaging way for users to interact with the app. These AR filters add an element of creativity and entertainment to social media interactions.
4.4 Pokémon GO
Pokémon GO is a popular mobile AR game that uses the player’s GPS sensors to detect where Pokémon creatures appear in the user’s surrounding environment for them to catch. The game blends the virtual world with the real world, encouraging players to explore their surroundings and interact with others.
4.5 Google Glass
Google Glass was Google’s first commercial attempt at a glasses-based AR system that let users work hands-free. Companies such as DHL and DB Schenker used Google Glass and third-party software to help frontline workers in global supply chain logistics and customized shipping. Although discontinued in 2023, Google Glass paved the way for future AR wearable devices.
4.6 U.S. Army Tactical Augmented Reality (TAR)
The U.S. Army uses AR in an eyepiece called TAR, which mounts onto the soldier’s helmet and aids in locating another soldier’s position. TAR improves situational awareness and coordination on the battlefield.
4.7 Apple Vision Pro
Apple Vision Pro is a spatial computing device that offers AR, VR, and mixed-reality features. It live-maps a user’s environment and offers passthrough and the ability to pin projections like web browsing windows to specific places in the user’s environment. Users can control the device using gestures.
4.8 Meta Quest 3
Meta Quest 3 is a mixed-reality headset that offers many similar features as Apple Vision Pro, including passthrough and productivity features. Users control this headset through gestures or controllers.
| Application | Description | Sector | Key Features | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target App | Allows users to visualize furniture and home decor items in their own spaces before purchasing. | Retail | AR-powered “See it in Your Space” feature enables virtual product placement. | Enhances customer confidence, reduces returns, and improves sales conversion rates. |
| Apple Measure App | Functions as a virtual tape measure, allowing users to measure distances and dimensions using their iPhone or iPad. | Tools/Utilities | Utilizes ARKit to provide accurate measurements in real time. | Offers a convenient and accessible measurement tool for everyday tasks. |
| Snapchat | Provides a range of AR filters and lenses that overlay digital effects on users’ faces and environments. | Social Media/Entertainment | Continuously updated with new and creative AR filters. | Drives user engagement, enhances social sharing, and provides unique entertainment experiences. |
| Pokémon GO | A location-based mobile game that overlays virtual Pokémon onto the real world, encouraging players to explore their surroundings. | Gaming | Combines GPS, camera, and AR technology to create an immersive gaming experience. | Promotes physical activity, fosters community engagement, and introduces AR technology to a wide audience. |
| Google Glass | An early attempt at AR glasses that provided hands-free access to information, notifications, and communication tools. | Enterprise/Wearable Tech | Offered voice control, heads-up display, and integration with Google services. | Paved the way for future AR wearable devices, demonstrated potential for enterprise applications. |
| U.S. Army TAR | An AR eyepiece mounted on soldiers’ helmets, providing real-time data overlays, enhanced situational awareness, and improved coordination. | Military/Defense | Integrates GPS, sensors, and communication tools to provide soldiers with critical information. | Enhances soldier safety, improves mission effectiveness, and facilitates better decision-making in the field. |
| Apple Vision Pro | A spatial computing device offering AR, VR, and mixed-reality experiences. | Wearable Technology/Spatial Computing | Offers passthrough, gesture control, and integration with Apple ecosystem. | Provides immersive experiences, enhances productivity, and demonstrates potential for spatial computing. |
| Meta Quest 3 | A mixed-reality headset offering similar features to Apple Vision Pro. | Wearable Technology/Gaming | Provides passthrough, gesture control, and integration with Meta ecosystem. | Offers immersive experiences, enhances productivity, and demonstrates potential for mixed-reality gaming and applications. |
| IKEA Place | An app that allows users to virtually place IKEA furniture in their homes using AR. | Retail/Home Improvement | Integrates ARKit to provide accurate and realistic virtual furniture placement. | Enhances customer confidence, reduces returns, and improves sales conversion rates. |
| Warby Parker Virtual Try-On | An app that allows users to virtually try on eyeglasses using AR. | Retail/Fashion | Integrates AR technology to provide realistic virtual try-on experiences. | Enhances customer engagement, reduces returns, and improves sales conversion rates. |
| Sephora Virtual Artist | An app that allows users to virtually try on makeup using AR. | Retail/Beauty | Integrates AR technology to provide realistic virtual makeup try-on experiences. | Enhances customer engagement, reduces returns, and improves sales conversion rates. |
| L’Oréal Style My Hair | An app that allows users to virtually try on different hairstyles and hair colors using AR. | Retail/Beauty | Integrates AR technology to provide realistic virtual hairstyle and hair color try-on experiences. | Enhances customer engagement, reduces returns, and improves sales conversion rates. |
5. What Is the Future of AR Technology?
AR technology is growing steadily as the popularity and familiarization of apps and games like Pokemon Go or retail store AR apps increase. Improved AR, VR, and mixed-reality headsets are also being released. Apple continues to develop and update its open-source mobile augmented reality development toolset, ARKit, and companies, including Target and Ikea, use ARKit in their flagship AR shopping apps for iPhone and iPad. ARCore, Google’s platform for building AR experiences on Andriod and iOS, continues to evolve and improve. Other potential future advancements for AR include more powerful and lighter devices, the use of artificial intelligence, and the expansion of 5G networks.
5.1 Advancements in AR Development Tools
Apple continues to develop and update its open-source mobile augmented reality development tool set, ARKit, and ARKit 6, for example, enables the rendering of AR in high dynamic range 4K and improves image and video capture. It also provides a Depth API, which uses per-pixel depth information to help a device’s camera understand the size and shape of an object and includes scene geometry that creates a topological map of a space. ARCore, Google’s platform for building AR experiences on Andriod and iOS, continues to evolve and improve and uses a geospatial API that sources data from Google Earth 3D models and Street View image data from Google Maps.
5.2 Enhanced Headset Technology
Improved AR, VR, and mixed-reality headsets are also being released, and Meta improved its Quest 2 headset with Meta Quest 3, which was released in October 2023. In February 2024, Apple released Apple Vision Pro, bringing more competition to the AR and VR headset market. Developers of Apple Vision Pro will have to work with the visionOS software development kit but can still use familiar Apple tools, such as ARKit, SwiftUI, or RealityKit to build apps.
5.3 Integration of AI
The use of artificial intelligence for face and room scanning, object detection and labeling, as well as for text recognition, is a potential future advancement for AR. AI algorithms can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of AR applications, providing more seamless and intuitive user experiences.
5.4 Expansion of 5G Networks
The expansion of 5G networks could make it easier to support cloud-based AR experiences by providing AR applications with higher data speeds and lower latency. 5G technology will enable more complex and data-intensive AR applications, enhancing their performance and capabilities.
| Future Advancement | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| More Powerful Devices | Lighter and more ergonomic AR devices with improved processing power and battery life. | Enhanced user experience, increased accessibility, and broader adoption across various industries. |
| Integration of AI | Use of artificial intelligence for face and room scanning, object detection, labeling, and text recognition. | Improved accuracy, enhanced user experience, and new capabilities for AR applications, such as real-time translation and contextual information. |
| Expansion of 5G Networks | Deployment of 5G networks to support cloud-based AR experiences with higher data speeds and lower latency. | Enhanced performance, increased scalability, and new opportunities for AR applications in areas such as remote collaboration, gaming, and entertainment. |
| Advanced AR Development Tools | Continuous development and improvement of AR development tools like ARKit and ARCore. | Easier and more efficient development of AR applications, enhanced creativity, and faster innovation in the AR ecosystem. |
| Improved Headset Technology | Release of improved AR, VR, and mixed-reality headsets with enhanced display technology, sensors, and ergonomics. | More immersive and comfortable user experiences, wider adoption across various industries, and new opportunities for AR applications in areas such as training, education, and healthcare. |
| Smart Contact Lenses | Development of AR-enabled contact lenses that overlay digital information directly onto the user’s field of vision. | Seamless integration of AR technology, hands-free operation, and new possibilities for applications in areas such as navigation, entertainment, and healthcare. |
| Spatial Computing | Convergence of AR, VR, and mixed-reality technologies to create spatial computing platforms that blend the physical and digital worlds. | New user experiences, enhanced productivity, and new opportunities for collaboration and communication. |
| AR Cloud | Development of a shared, persistent digital layer that maps the real world and enables seamless AR experiences across multiple devices and locations. | Enhanced collaboration, improved accuracy, and new possibilities for AR applications in areas such as navigation, gaming, and social interaction. |
| Holographic Displays | Use of holographic displays to project 3D images and information into the real world. | New user experiences, enhanced visualization, and new opportunities for AR applications in areas such as education, entertainment, and design. |
| Embedded AR | Integration of AR technology directly into everyday objects and environments, such as cars, appliances, and buildings. | Seamless integration of AR technology, enhanced functionality, and new opportunities for user interaction. |
| Brain-Computer Interfaces | Development of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) that allow users to control AR devices with their thoughts. | Enhanced accessibility, new user experiences, and new possibilities for AR applications in areas such as healthcare and gaming. |
| Ethical Considerations | Development of ethical guidelines and regulations to address the potential risks and challenges of AR technology, such as privacy, security, and bias. | Responsible innovation, enhanced user trust, and broader adoption of AR technology. |
| Ubiquitous AR | Widespread adoption of AR technology across various industries and aspects of daily life. | Enhanced productivity, improved communication, and new opportunities for entertainment, education, and healthcare. |
| Personalized AR | Development of personalized AR experiences that adapt to individual user preferences and needs. | Enhanced user engagement, improved relevance, and new opportunities for targeted advertising and marketing. |
| Augmented Reality Art | Emergence of augmented reality art as a new form of artistic expression, blending physical and digital elements. | New creative possibilities, enhanced audience engagement, and new opportunities for artists and designers. |
6. What Are the Search Intentions for AR in Technology?
Understanding the search intentions behind “What Is Ar In Technology” helps tailor content to meet user needs. The primary search intentions include informational, comparative, navigational, transactional, and exploratory.
6.1 Informational
Users want to understand the definition, functionality, and background of AR. These searches often include questions like “What is the history of AR?” and “How does AR work?”
6.2 Comparative
Users seek to compare AR with other technologies like VR and mixed reality to understand their differences and similarities. Queries include “AR vs VR” and “What is the difference between AR and mixed reality?”
6.3 Navigational
Users are looking for specific AR applications, tools, or brands. Examples include “Apple ARKit,” “Meta Quest 3,” and “Best AR apps for iPhone.”
6.4 Transactional
Users intend to purchase AR devices, software, or services. Queries include “Buy AR glasses,” “AR app development services,” and “Best AR headsets for gaming.”
6.5 Exploratory
Users are interested in exploring potential applications and future trends of AR technology. Searches include “AR use cases,” “Future of augmented reality,” and “AR in healthcare.”
| Search Intention | Description | Example Queries | Content Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Informational | Users seek basic knowledge and understanding of AR technology, its definition, functionality, and background. | – What is AR in technology?- How does AR work?- What is the history of AR?- What are the key components of an AR system? | – Definition and explanation of AR- Functionality and technical aspects- Historical overview and evolution- Key components and technologies |
| Comparative | Users want to compare AR with other related technologies, such as VR and mixed reality, to understand their differences and similarities. | – AR vs VR- What is the difference between AR and mixed reality?- AR vs VR vs MR- Which technology is better for gaming: AR or VR? | – Comparison of AR, VR, and MR- Differences in technology and applications- Pros and cons of each technology- Use cases and suitability |
| Navigational | Users are looking for specific AR applications, tools, brands, or resources. | – Apple ARKit- Meta Quest 3- Best AR apps for iPhone- AR SDK for Android | – Specific AR applications and tools- Brands and companies in the AR industry- Resources for AR developers- Navigation to relevant websites and downloads |
| Transactional | Users intend to purchase AR devices, software, or services. | – Buy AR glasses- AR app development services- Best AR headsets for gaming- AR training courses | – Product listings and reviews- Service offerings and pricing- Purchasing options and recommendations- Training courses and certifications |
| Exploratory | Users are interested in exploring potential applications, future trends, and innovative uses of AR technology. | – AR use cases- Future of augmented reality- AR in healthcare- AR in education | – Potential applications across various industries- Future trends and innovations- Case studies and real-world examples- Expert opinions and insights |
| Educational | Users seek in-depth knowledge and training to learn about AR development, design, and implementation. | – AR development tutorial- AR design principles- How to create an AR app- AR certification courses | – Step-by-step guides and tutorials- Design principles and best practices- Coding examples and resources- Certification courses and learning paths |
| Troubleshooting | Users encounter issues or technical problems with AR devices or applications and seek solutions. | – AR app not working- AR headset troubleshooting- ARKit error messages- How to fix AR performance issues | – Common issues and solutions- Troubleshooting guides and tips- Error message explanations- Performance optimization techniques |
| Creative Inspiration | Users look for creative ideas and inspiration for using AR in various projects or applications. | – AR creative ideas- Unique AR applications- Innovative AR projects- AR art and design | – Creative concepts and ideas- Unique use cases and examples- Inspirational projects and designs- AR art and design trends |
| Statistical Information | Users seek data, statistics, and market research related to the AR industry. | – AR market size- AR adoption rates- |

