Near-field communication (NFC) technology enables seamless wireless communication between devices, and understanding how it works can unlock a world of possibilities. At pioneer-technology.com, we’re dedicated to exploring cutting-edge technologies, and we’re here to provide you with a comprehensive overview of NFC, its functionality, and its myriad applications. Discover how NFC simplifies transactions, enhances security, and revolutionizes data exchange, paving the way for contactless interactions.
1. What is NFC Technology and How Does It Work?
NFC technology is a short-range wireless communication technology that enables two devices to exchange data when they are within a few centimeters of each other. An NFC system consists of two main components: an NFC tag or chip and an NFC reader.
Answer: NFC, or Near Field Communication, enables devices to communicate wirelessly over short distances, typically a few centimeters. It’s a technology that allows for contactless data exchange, powering mobile payments, data sharing, and access control systems.
Expanding on NFC Technology
NFC operates on the principle of inductive coupling, using magnetic fields to transmit data. This close-proximity requirement significantly enhances security, as the risk of interception is drastically reduced. The technology is governed by the ISO/IEC 18092 standard, ensuring interoperability and security across different devices and applications.
NFC technology has three primary modes of operation:
- Card Emulation: This mode allows an NFC-enabled device, like a smartphone, to act as a contactless credit card, enabling mobile payments at compatible point-of-sale (POS) terminals.
- Reader/Writer: In this mode, an NFC device can read information stored on NFC tags, such as URLs, contact details, or product information.
- Peer-to-Peer: This mode allows two NFC-enabled devices to exchange data directly, facilitating file transfers, contact sharing, or even gaming interactions.
NFC’s versatility makes it an ideal solution for various applications, from secure payments and access control to interactive advertising and data sharing. Its ease of use and inherent security features have contributed to its growing adoption across industries.
2. What are the Key Components of an NFC System?
An NFC system requires two primary components to facilitate communication: the NFC tag or chip and the NFC reader. The NFC tag, often a passive device, contains the data to be transmitted. The NFC reader, typically an active device like a smartphone or payment terminal, generates an electromagnetic field that powers the NFC tag and initiates the data transfer.
Answer: An NFC system primarily comprises two key components: an NFC tag or chip, which stores data, and an NFC reader, which initiates data transfer by generating an electromagnetic field.
Expanding on Key Components of an NFC System
Let’s delve deeper into the roles and characteristics of each component:
- NFC Tag/Chip: These are small, often passive devices that store information. Passive tags do not require a power source of their own; instead, they draw power from the electromagnetic field generated by the NFC reader. NFC tags come in various forms, including stickers, cards, and embedded chips.
- NFC Reader: This device generates an electromagnetic field that energizes the passive NFC tag, allowing it to transmit its stored data. NFC readers are commonly found in smartphones, payment terminals, and access control systems. They decode the data received from the NFC tag and perform the appropriate action, such as processing a payment or granting access.
According to research from Stanford University’s Department of Computer Science, the efficiency and reliability of data transfer in an NFC system depend significantly on the quality and design of both the NFC tag and the NFC reader. High-quality components ensure seamless communication and minimize the risk of errors or security breaches.
 Close-up of an NFC chip on a circuit board
Close-up of an NFC chip on a circuit board
An NFC chip, the brain of the tag, manages data storage and processing for smooth data exchange.
3. What are the Different Types of NFC Tags?
NFC tags come in various types, each with unique characteristics and capabilities. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right tag for a specific application.
Answer: There are five main types of NFC tags: Type 1, Type 2, Type 3, Type 4, and Type 5, each offering different memory capacities and speeds for various applications.
Expanding on Different Types of NFC Tags
Here’s a more detailed look at the different NFC tag types:
| Tag Type | Memory Capacity | Communication Speed (Kbps) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | 96 bytes to 2KB | 106 | Basic URLs, short messages, simple tasks |
| Type 2 | 48 bytes to 144 bytes | 106 | Event ticketing, URL redirection, low-value transactions |
| Type 3 | 1KB to 9KB | 212 or 424 | E-money, membership cards, electronic IDs, applications requiring more data storage |
| Type 4 | 4KB to 32KB | 106, 212, or 424 | Payment and e-ticketing, larger data storage, faster speeds |
| Type 5 | 192 bytes to 3584 bytes | 106 | Library inventory management, healthcare, ticketing, specialized applications |
- Type 1 Tags: These are the most basic and cost-effective tags, suitable for simple applications like storing URLs or short messages.
- Type 2 Tags: These tags offer slightly more memory than Type 1 tags and are commonly used for event ticketing and low-value transactions.
- Type 3 Tags: With significantly larger memory capacities, Type 3 tags are ideal for applications requiring more data storage, such as e-money and membership cards.
- Type 4 Tags: These are versatile and powerful tags, capable of handling large amounts of data and supporting faster communication speeds, making them suitable for payment and e-ticketing applications.
- Type 5 Tags: These tags are often used in specialized applications like library inventory management and healthcare, where specific data storage and speed requirements are needed.
The choice of NFC tag type depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the amount of data to be stored, the required communication speed, and the overall cost considerations.
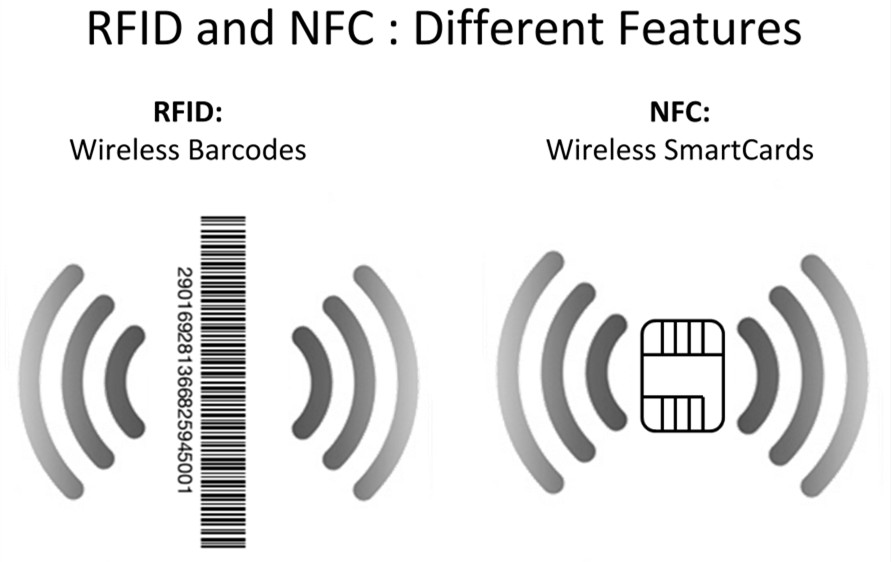
4. How Does NFC Compare to Other Wireless Communication Technologies Like Bluetooth and RFID?
While NFC shares similarities with other wireless communication technologies like Bluetooth and RFID, it also has distinct differences that make it suitable for specific applications.
Answer: NFC differs from Bluetooth and RFID in range, communication method, and applications. NFC has a shorter range than Bluetooth, enabling more secure transactions. Unlike RFID, NFC supports two-way communication, making it ideal for interactive applications.
Expanding on Comparisons
Let’s compare NFC with Bluetooth and RFID in more detail:
| Feature | NFC | Bluetooth | RFID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Up to 4 cm | Up to 100 meters | Up to several meters |
| Communication | Two-way | Two-way | One-way |
| Power Consumption | Low (passive tags require no power) | Moderate | Low (passive tags require no power) |
| Use Cases | Mobile payments, access control, data sharing | Audio streaming, file transfer, device pairing | Inventory tracking, supply chain management |
| Security | High (due to short range) | Moderate | Low |
- Range: NFC has a very short range (up to 4 cm), making it ideal for secure transactions and close-proximity interactions. Bluetooth has a much longer range (up to 100 meters), suitable for audio streaming and file transfers. RFID can operate over a range of several meters, making it useful for inventory tracking.
- Communication: NFC supports two-way communication, allowing devices to both read and write data. Bluetooth also supports two-way communication, while RFID typically involves one-way communication from the tag to the reader.
- Power Consumption: NFC tags can be passive, requiring no power source of their own. Bluetooth devices consume more power, while RFID tags can also be passive.
- Use Cases: NFC is commonly used for mobile payments, access control, and data sharing. Bluetooth is popular for audio streaming, file transfer, and device pairing. RFID is widely used for inventory tracking and supply chain management.
- Security: NFC’s short range enhances security, as the risk of interception is minimized. Bluetooth’s longer range makes it more vulnerable to eavesdropping, while RFID systems can also be susceptible to security breaches.
NFC’s unique combination of short range, two-way communication, and low power consumption makes it a compelling choice for applications requiring secure and convenient close-proximity interactions.
5. What are the Advantages of Using NFC Technology?
NFC technology offers numerous advantages over other wireless communication methods, making it a valuable tool for businesses and consumers alike.
Answer: NFC offers instant connectivity, wireless exchange, robust security, no need for network connectivity, and convenience at an affordable cost, all contributing to a reduced carbon footprint.
Expanding on Advantages of NFC Technology
Here are some key benefits of using NFC technology:
- Instant Connection: NFC devices connect instantly for data exchange when brought close together, streamlining transactions and interactions.
- Wireless Exchange: NFC-enabled devices communicate wirelessly without the need for external power sources, enhancing convenience and portability.
- Secure Technology: NFC data exchange occurs only between devices in close proximity, protecting transactions from remote hacking and ensuring secure communication.
- No Network Connectivity Required: NFC tags can work without WiFi, 4G, or LTE connectivity, enabling payments, data transfers, and access control even when offline.
- Convenient and Affordable: NFC tags are an easy and affordable technology that can help in digital transformation, improving customer and employee experiences.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: NFC is an eco-friendly solution that can minimize the carbon footprint of businesses by reducing the use of plastic access cards.
A study by the NFC Forum found that NFC technology can significantly improve the efficiency and convenience of various processes, leading to increased customer satisfaction and reduced operational costs.
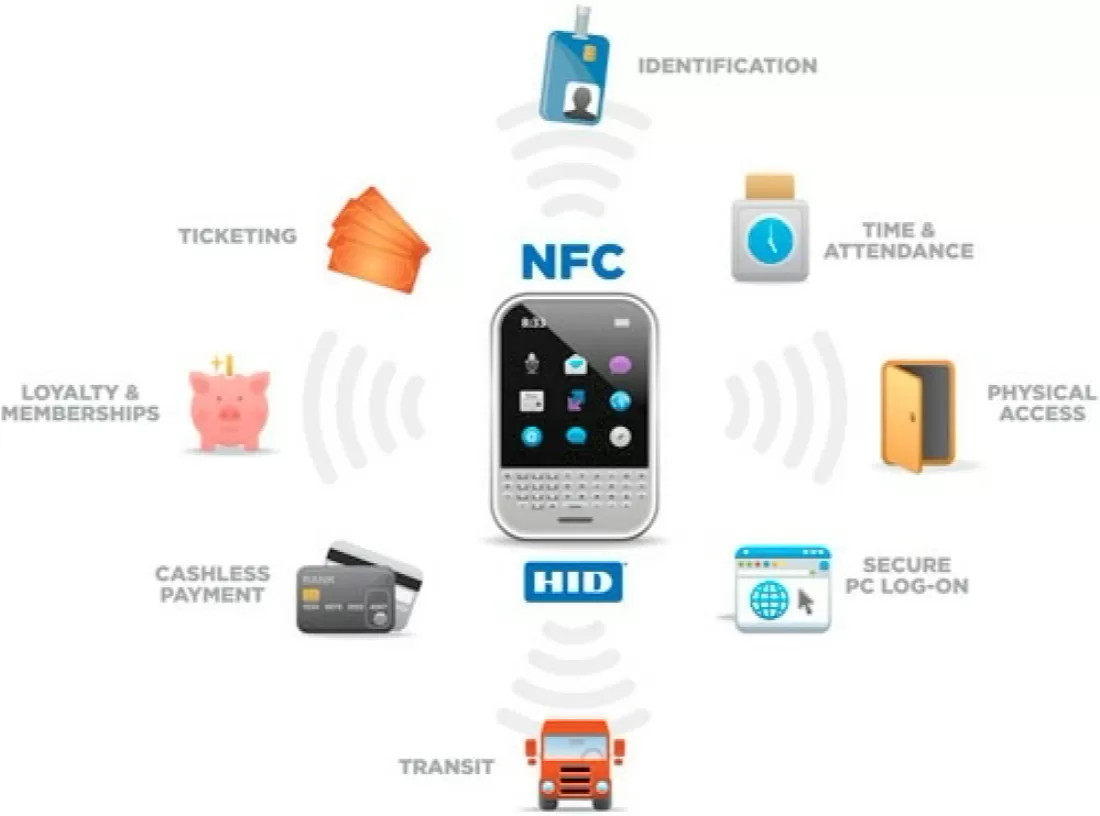
6. What are Some Common Applications of NFC Technology in Everyday Life?
NFC technology has found its way into numerous applications in our daily lives, enhancing convenience, security, and efficiency.
Answer: NFC is commonly used for contactless payments, ticketing, identification and access control, product status and maintenance, and even tracking in sports events.
Expanding on Common Applications of NFC Technology
Here are some examples of how NFC is used in everyday life:
- Contactless Payments: NFC-enabled smartphones and wearables allow users to make secure and convenient payments at compatible POS terminals.
- Ticketing: NFC technology is used for digital ticketing in public transportation, concerts, and events, providing a seamless and efficient entry experience.
- Identification and Access Control: NFC can be used to identify team members and control access to secure areas, eliminating the need for physical access cards.
- Product Status and Maintenance: NFC tags can be integrated into products to provide information on their status, maintenance requirements, and authenticity.
- Checkpoint and Player Tracking in Sports Events: NFC technology can revolutionize orienteering and other sports events by providing an efficient and accurate way to track participants’ progress and verify checkpoints.
- Trail Completion and Summit Confirmation: NFC tags and companion mobile applications can be used to create a verifiable repository of completed trails and summits, motivating younger generations to explore the outdoors.
These are just a few examples of the many ways NFC technology is transforming our daily lives, making tasks easier, faster, and more secure.
 A woman using her smartphone to make a contactless payment
A woman using her smartphone to make a contactless payment
NFC technology simplifies transactions and enhances convenience with contactless payments via smartphones.
7. How Secure is NFC Technology, and What Measures are in Place to Protect Against Fraud?
Security is a top priority when it comes to NFC technology, and several measures are in place to protect against fraud and unauthorized access.
Answer: NFC payments are highly secure due to tokenization and encryption, protecting against unauthorized access. The short communication range also minimizes the risk of interception.
Expanding on Security Measures
Here are some of the security measures implemented in NFC systems:
- Tokenization: Sensitive card details are replaced with a unique token, which is used for transactions instead of the actual card number. This prevents fraudsters from gaining access to the cardholder’s financial information.
- Encryption: Data transmitted between the NFC device and the payment terminal is encrypted, making it difficult for hackers to intercept and decipher the information.
- Proximity Limitation: NFC’s short communication range (typically a few centimeters) significantly reduces the risk of eavesdropping, as hackers would need to be in very close proximity to intercept the data.
- Secure Element: Many NFC-enabled devices use a secure element, a dedicated hardware chip that stores sensitive data and performs cryptographic operations, providing an additional layer of security.
- PIN and Biometric Authentication: For higher-value transactions, users may be required to enter a PIN or use biometric authentication (such as fingerprint scanning or facial recognition) to authorize the payment.
According to a report by Visa, NFC payments are significantly more secure than traditional magnetic stripe card transactions, with fraud rates being substantially lower.
8. What is the Role of NFC in Mobile Payments, and How Does it Enhance the Payment Experience?
NFC technology plays a crucial role in mobile payments, enabling secure and convenient contactless transactions.
Answer: NFC enhances the payment experience by enabling quick, secure, and contactless transactions, eliminating the need for physical cards and streamlining the payment process.
Expanding on Role of NFC in Mobile Payments
Here’s how NFC enhances the mobile payment experience:
- Speed and Convenience: NFC payments are quick and easy, requiring only a tap of the device on the payment terminal.
- Security: NFC payments are more secure than traditional card transactions, thanks to tokenization, encryption, and proximity limitations.
- Contactless: NFC eliminates the need for physical cards, reducing the risk of loss or theft and providing a more hygienic payment option.
- Integration with Mobile Wallets: NFC seamlessly integrates with popular mobile wallets like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay, allowing users to store multiple cards on their smartphones and make payments with a single tap.
- Rewards and Loyalty Programs: NFC can be used to automatically apply rewards and loyalty points to purchases, enhancing the customer experience and driving repeat business.
A survey by Statista found that the number of NFC mobile payment users is expected to reach over 2 billion by 2025, highlighting the growing popularity and adoption of this technology.
 Multiple Google Pay screens
Multiple Google Pay screens
Google Pay is an all-in-one NFC-enabled payments app, offering a seamless and secure payment experience.
9. How are Businesses Using NFC Technology to Improve Customer Experience and Streamline Operations?
Businesses across various industries are leveraging NFC technology to enhance customer experience, streamline operations, and gain a competitive edge.
Answer: Businesses use NFC for contactless payments, ticketing, access control, product authentication, and targeted marketing, enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency.
Expanding on Business Applications of NFC
Here are some examples of how businesses are using NFC technology:
- Retail: NFC-enabled POS systems allow for faster and more secure payments, reducing checkout times and improving customer satisfaction.
- Hospitality: Hotels use NFC keycards for room access, streamlining the check-in process and enhancing security.
- Transportation: Public transportation agencies use NFC ticketing systems to provide a seamless and efficient travel experience for commuters.
- Healthcare: NFC tags can be used to track medical equipment, monitor patients’ vital signs, and authenticate medications, improving patient safety and operational efficiency.
- Manufacturing: NFC tags can be integrated into products to provide information on their origin, manufacturing date, and maintenance requirements, enhancing product transparency and customer trust.
- Marketing: NFC tags can be used to deliver targeted marketing messages to customers’ smartphones, providing personalized offers and promotions.
According to a study by Accenture, businesses that adopt NFC technology can experience significant improvements in customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and revenue growth.
10. What are the Future Trends and Emerging Applications of NFC Technology?
NFC technology is constantly evolving, with new trends and emerging applications on the horizon.
Answer: Future trends include enhanced security, integration with IoT devices, expanded use in healthcare, and innovative applications in retail and marketing.
Expanding on Future Trends
Here are some of the future trends and emerging applications of NFC technology:
- Enhanced Security: Researchers are working on developing more secure NFC protocols and encryption methods to further protect against fraud and unauthorized access.
- Integration with IoT Devices: NFC is being integrated into a wide range of IoT devices, such as smart home appliances, wearable devices, and connected cars, enabling seamless communication and control.
- Expanded Use in Healthcare: NFC is expected to play an increasingly important role in healthcare, enabling remote patient monitoring, medication adherence tracking, and secure access to medical records.
- Innovative Applications in Retail and Marketing: NFC is being used to create interactive shopping experiences, deliver personalized offers, and track customer behavior in retail environments.
- Checkpoint and Player Tracking in Sports Events: NFC technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach orienteering, a sport that is still heavily reliant on expensive tracking and navigation systems.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global NFC market is projected to reach $47.8 billion by 2026, driven by the increasing adoption of NFC technology across various industries and the emergence of new and innovative applications.
NFC technology is poised to play an even greater role in our lives in the years to come, transforming the way we interact with the world around us.
Are you ready to explore the endless possibilities of NFC technology? Visit pioneer-technology.com to discover the latest articles, in-depth analyses, and cutting-edge innovations in the world of technology. Stay ahead of the curve and unlock the potential of NFC to transform your business, enhance your customer experience, and simplify your life. Contact us at 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States or call +1 (650) 723-2300 to learn more.
FAQs About NFC Technology
1. How Close Do You Have to Be For NFC to Work Effectively?
NFC operates effectively within a radius of approximately 4 inches (10 centimeters). Devices must be within this range for a successful connection. This close proximity enhances the security and precision of NFC interactions.
2. Which is Better: RFID or NFC for Specific Applications?
NFC and RFID serve different purposes. NFC is ideal for applications requiring secure, two-way communication over short distances, such as mobile payments. RFID is better suited for asset tracking and inventory management over longer distances.
3. How Can I Increase the NFC Range for Enhanced Connectivity?
NFC is designed for short-range communication, and increasing the range is not possible. For longer-range wireless communication, technologies like Bluetooth or RFID are more suitable.
4. Are NFC Payments Considered Secure Compared to Other Payment Methods?
NFC payments are highly secure due to tokenization and encryption technologies. These methods protect your financial information from unauthorized access, making NFC a secure payment option.
5. What are the Primary Benefits of Using NFC Payments in Retail and E-commerce?
NFC payments offer convenience, speed, and security. They eliminate the need to carry physical cards, reduce transaction times, and provide a contactless payment option that is highly secure.
6. How Does NFC Technology Work with Existing Infrastructure in Retail Environments?
NFC is compatible with existing POS systems, requiring minimal upgrades. This makes it easy for businesses to adopt NFC payments without significant investments in new infrastructure.
7. What Security Protocols are in Place to Protect NFC-Enabled Devices from Hacking?
NFC-enabled devices use encryption, tokenization, and secure elements to protect against hacking. These protocols ensure that sensitive data is securely stored and transmitted during NFC transactions.
8. How Does NFC Integrate with IoT Devices for Smart Home Automation?
NFC allows seamless integration with IoT devices, enabling quick pairing and data exchange. This makes it easy to control smart home devices, automate tasks, and enhance the overall smart home experience.
9. Can NFC Be Used for Access Control in Office Buildings and Secure Facilities?
NFC is widely used for access control, replacing traditional keycards with NFC-enabled smartphones or wearables. This provides a secure and convenient way to manage access to buildings and facilities.
10. What Are the Current Limitations of NFC Technology and How Can They Be Overcome?
One limitation is the short communication range, which can sometimes be inconvenient. Future developments aim to improve the range and enhance the overall user experience.
 A person using an NFC-enabled smartphone to scan a product in a store
A person using an NFC-enabled smartphone to scan a product in a store
NFC-enabled smartphones offer a convenient and secure way to scan products and access information.

