Technology is undoubtedly changing the job market, but it’s not necessarily destroying jobs entirely; instead, it’s reshaping them. Pioneer-technology.com is dedicated to exploring these shifts, offering insights and strategies to adapt and thrive in this evolving landscape. By understanding the nuanced relationship between technological advancements and employment, we can harness new opportunities and prepare for the future of work. Let’s dive in to explore new employment trends and technological unemployment.
1. What Evidence Shows Technology’s Impact on Job Loss?
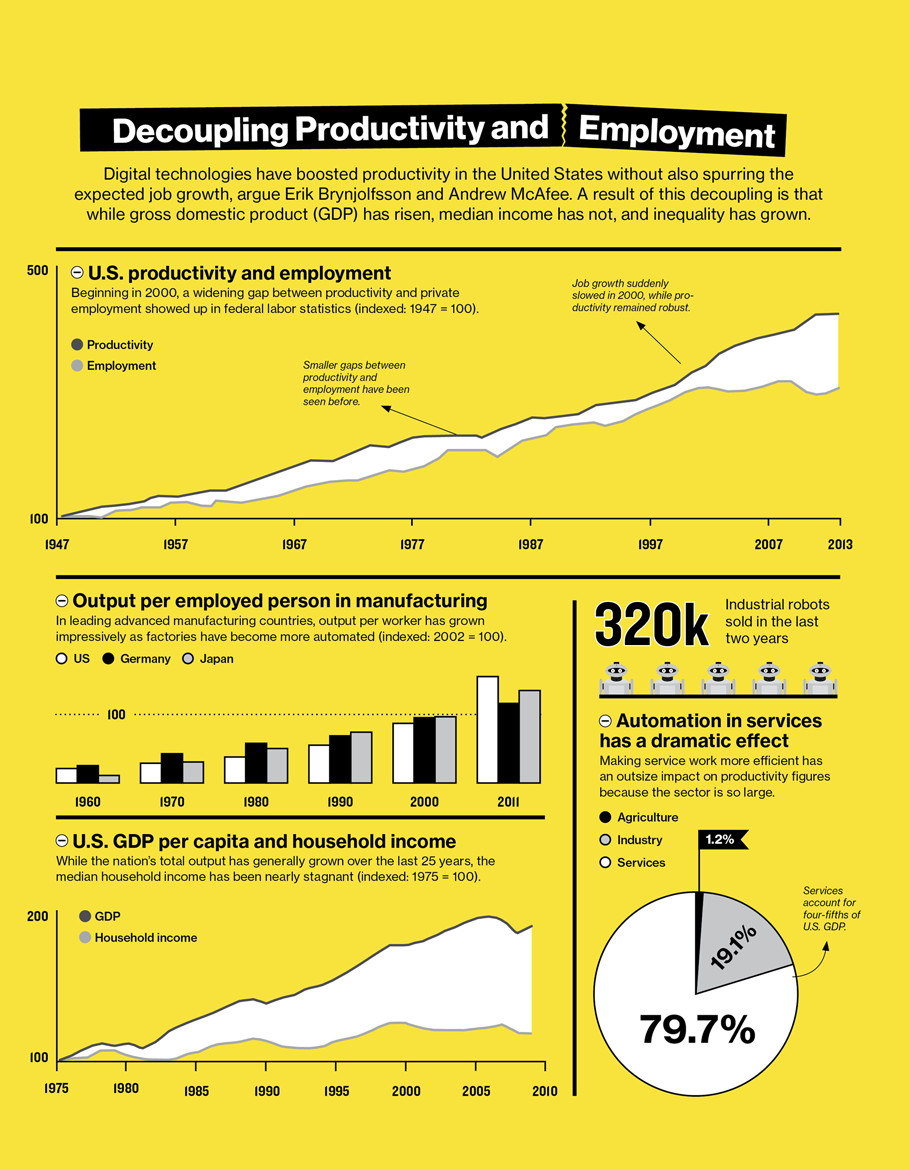
Evidence suggests a notable shift in the job market where productivity increases without a corresponding rise in employment. According to research from MIT’s Center for Digital Business at the Sloan School of Management, the “great decoupling” illustrates this trend, where productivity and employment tracked together until around 2000, after which productivity continued to rise while employment stagnated. This decoupling indicates that technological advancements are enhancing productivity but not necessarily creating more jobs.
This phenomenon is further supported by data showing median income failing to keep pace with GDP growth, highlighting an economic paradox where technological progress isn’t benefiting the average worker as it once did. Brynjolfsson and McAfee, who introduced the idea of the “great decoupling,” argue that technology drives both increased productivity and job displacement.
2. Which Sectors Are Most Affected by Technology-Driven Job Displacement?
Manufacturing, clerical work, and professional services are significantly impacted by technology-driven job displacement. Automation and robotics have reduced the need for human labor in manufacturing plants, with fewer people employed in these roles compared to previous decades. The rise of digital processes, AI, big data, and improved analytics is automating routine tasks in clerical work and professional services, leading to the disappearance of traditional white-collar jobs in sectors such as post offices and customer service.
For example, modern automotive plants use machines for welding and painting that humans previously performed. Startups are designing robots for warehouse tasks, and the rise of self-driving cars suggests automation’s potential in transportation. These technological shifts are reshaping job landscapes across various industries.
3. Is Technology the Only Factor Contributing to Job Losses?
No, technology is not the only factor contributing to job losses; other elements like globalization, economic policies, and educational disparities also play significant roles. Globalization leads to the outsourcing of jobs to countries with lower labor costs. Economic policies can influence job creation and retention through regulations, tax incentives, and trade agreements. Educational disparities result in a skills gap, where workers lack the necessary training and education to adapt to new job requirements, exacerbating the impact of technology on employment.
These factors combined create a complex landscape where technology accelerates job displacement, while other forces compound the challenges workers face. Understanding these multiple influences is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate job losses.
4. How Does Automation Affect Different Skill Levels Differently?
Automation disproportionately affects workers in routine and manual labor roles, while increasing demand for those with advanced technical and creative skills. Jobs involving repetitive tasks, such as data entry, assembly line work, and basic customer service, are easily automated. This shift increases the demand for roles requiring skills in software development, data analysis, AI, and creative problem-solving.
The result is a widening skills gap, where many workers lack the education and training needed for these new, high-demand roles. This gap exacerbates inequality and makes it more challenging for displaced workers to transition to new careers.
5. What Are the Potential Long-Term Effects of Technology on the Job Market?
The long-term effects of technology on the job market could include a significant restructuring of work, with a greater emphasis on specialized skills and adaptability. As technology continues to advance, more jobs will require skills in technology, data analysis, and creative problem-solving. This shift may lead to the creation of new types of jobs that do not currently exist, as well as the obsolescence of many traditional roles.
Economically, there could be increased income inequality if the benefits of technological progress are not evenly distributed. Socially, there may be challenges related to unemployment, job satisfaction, and the need for continuous learning and adaptation. pioneer-technology.com aims to provide insights and resources to help individuals and businesses navigate these long-term changes.
6. What Government Policies Can Help Mitigate Technology-Induced Job Losses?
 Robotic arm sorting packages in a warehouse, symbolizing automation's impact on jobs
Robotic arm sorting packages in a warehouse, symbolizing automation's impact on jobs
Government policies can play a crucial role in mitigating technology-induced job losses through investments in education and training, social safety nets, and incentives for innovation. Initiatives that focus on STEM education, vocational training, and lifelong learning can help workers acquire the skills needed for emerging jobs. Social safety nets, such as unemployment benefits and universal basic income, can provide a cushion for displaced workers while they seek retraining or new employment.
Incentives for innovation can encourage the creation of new industries and jobs, offsetting some of the losses from automation. Additionally, policies that promote equitable distribution of wealth and reduce income inequality can help ensure that the benefits of technological progress are shared by all members of society.
7. How Can Individuals Prepare for a Changing Job Market?
Individuals can prepare for a changing job market by focusing on continuous learning, developing in-demand skills, and cultivating adaptability. Pursuing education and training in STEM fields, data analytics, and creative problem-solving can open doors to new opportunities. It is also important to stay informed about emerging technologies and industry trends, and to be willing to learn new skills throughout one’s career.
Adaptability, or the ability to quickly adjust to new situations and learn new skills, is a critical attribute in a rapidly evolving job market. Networking, seeking mentorship, and participating in industry events can also help individuals stay connected and informed about new opportunities.
8. What Role Do Businesses Play in Addressing Technology-Related Job Displacement?
Businesses play a key role in addressing technology-related job displacement by investing in workforce development, promoting upskilling initiatives, and fostering a culture of innovation. Companies can partner with educational institutions to create training programs that equip workers with the skills needed for new roles. Upskilling initiatives, which provide existing employees with opportunities to learn new skills and advance in their careers, can help mitigate job losses due to automation.
Fostering a culture of innovation can lead to the creation of new products, services, and business models, generating new employment opportunities. Businesses can also play a role in advocating for policies that support workforce development and economic growth.
9. Are There Any Industries Where Technology Creates More Jobs Than It Destroys?
Yes, certain industries, particularly those centered around technology development and innovation, often experience job creation exceeding job destruction. The tech industry itself, including software development, data science, AI, and cloud computing, is a significant source of new jobs. Additionally, the growth of the green energy sector, driven by technological advancements in renewable energy and sustainable practices, is creating numerous jobs in areas such as solar panel installation, wind turbine maintenance, and energy efficiency consulting.
Healthcare technology is another area experiencing job growth, with new roles emerging in telemedicine, health data analytics, and medical device innovation. These industries demonstrate how technology can drive job creation in specific sectors, even as it displaces workers in others.
10. How Can pioneer-technology.com Help Navigate These Changes?
pioneer-technology.com can help you navigate these changes by providing you with up-to-date information, detailed analysis, and expert opinions on emerging technologies and their impact on the job market. Our articles and resources are designed to help you stay informed about new trends, understand the skills needed for future jobs, and prepare for the changes ahead. We offer practical advice on how to upskill, reskill, and adapt to new career paths.
By exploring pioneer-technology.com, you can gain a deeper understanding of the forces shaping the future of work and develop strategies to thrive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
11. How Is The Rise Of Artificial Intelligence Affecting Job Security?
The rise of artificial intelligence is affecting job security by automating tasks previously performed by humans and creating new roles that require AI-related skills. According to a 2023 report by the World Economic Forum, AI could displace 85 million jobs globally by 2025, while also creating 97 million new jobs. This indicates a significant shift in job roles and skill requirements.
AI excels at tasks such as data analysis, customer service, and repetitive manual work, leading to job losses in these areas. Conversely, AI is driving demand for experts in machine learning, AI ethics, and AI implementation. The long-term impact will depend on how quickly and effectively workers can adapt to these changing skill requirements.
11.1. Which Roles Are Most Vulnerable To AI Automation?
Data entry clerks, customer service representatives, and factory workers are among the roles most vulnerable to AI automation. AI systems can handle large volumes of data entry with greater accuracy and speed, reducing the need for human clerks. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are increasingly used in customer service, handling routine inquiries and resolving basic issues.
In manufacturing, robots and automated systems are replacing human workers in assembly lines and other repetitive tasks. These trends suggest that jobs involving repetitive tasks, data processing, and basic customer interactions are at high risk of being automated.
11.2. What New Job Opportunities Are Emerging Due To AI?
Emerging job opportunities due to AI include roles in AI development, data science, AI ethics, and AI implementation. AI developers are needed to create and maintain AI systems, while data scientists analyze large datasets to train and improve AI models. AI ethicists ensure AI systems are used responsibly and ethically, addressing issues such as bias and privacy.
AI implementation specialists help organizations integrate AI technologies into their operations and workflows. These roles require a combination of technical expertise, analytical skills, and ethical awareness, reflecting the multidisciplinary nature of AI.
12. What Is The Impact Of Remote Work Technologies On Traditional Employment?
Remote work technologies such as video conferencing, collaboration tools, and cloud computing are impacting traditional employment by enabling companies to hire talent globally and reducing the need for physical office spaces. A study by Stanford University found that remote work could increase productivity by up to 13% due to reduced commuting time and fewer distractions. This shift is causing companies to rethink their real estate strategies and consider more flexible work arrangements.
The rise of remote work is also influencing job markets, as location becomes less of a barrier to employment. This can lead to increased competition for jobs and the potential for wage adjustments as companies tap into global talent pools.
12.1. How Do Video Conferencing Tools Affect Business Travel?
Video conferencing tools, such as Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet, are affecting business travel by providing a cost-effective alternative for meetings, conferences, and training sessions. Companies can save on travel expenses, accommodation costs, and employee time by conducting virtual meetings instead of in-person gatherings.
While video conferencing cannot completely replace face-to-face interactions, it offers a viable solution for many business communication needs. This trend is reshaping the business travel industry and driving demand for high-quality video conferencing equipment and services.
12.2. In What Ways Does Cloud Computing Support Remote Work?
Cloud computing supports remote work by providing access to data, applications, and IT resources from anywhere with an internet connection. Services such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) allow employees to collaborate on projects, share files, and access company resources without being physically present in the office.
Cloud-based productivity suites like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace offer tools for document creation, email, and project management, further enabling remote work. This infrastructure is essential for maintaining productivity and ensuring business continuity in a remote work environment.
13. How Does The Gig Economy Influence Long-Term Career Stability?
The gig economy, characterized by short-term contracts and freelance work, influences long-term career stability by offering flexibility and autonomy while also posing challenges related to income security and benefits. A study by McKinsey found that up to 162 million people in Europe and the United States engage in some form of independent work. The gig economy can provide opportunities for individuals to pursue diverse projects, develop a broad range of skills, and control their work schedules.
However, gig workers often lack the job security and benefits associated with traditional employment, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. This can lead to financial instability and difficulty planning for the future.
13.1. What Are The Advantages Of Participating In The Gig Economy?
Advantages of participating in the gig economy include flexibility, autonomy, and the ability to pursue diverse projects. Gig workers can often set their own hours, choose their projects, and work from anywhere with an internet connection. This can be particularly appealing to individuals seeking work-life balance or those with specialized skills that are in high demand.
The gig economy also offers opportunities for individuals to experiment with different career paths and develop a portfolio of diverse experiences. This can enhance their marketability and provide a competitive edge in the job market.
13.2. What Are The Drawbacks Of Relying On Gig Work For Income?
Drawbacks of relying on gig work for income include income instability, lack of benefits, and limited career advancement opportunities. Gig workers often experience fluctuations in income, making it difficult to budget and plan for the future. They typically do not receive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off, which can create financial risks.
Gig work may also offer limited opportunities for career advancement, as it often involves short-term projects rather than long-term employment relationships. This can make it challenging for gig workers to build a stable career path and achieve their long-term professional goals.
14. How Is E-Learning Impacting Traditional Education Systems?
E-learning is impacting traditional education systems by providing accessible, flexible, and personalized learning experiences. A report by Research and Markets projects the e-learning market to reach $325 billion by 2025. E-learning platforms offer a wide range of courses, from academic subjects to vocational skills, allowing individuals to learn at their own pace and on their own schedule.
This is challenging the traditional model of classroom-based instruction and creating new opportunities for lifelong learning. E-learning also allows for personalized learning experiences, as students can focus on areas where they need the most support and access resources tailored to their learning styles.
14.1. What Are The Benefits Of Online Learning Platforms?
Benefits of online learning platforms include accessibility, flexibility, and personalized learning experiences. Online learning platforms make education accessible to individuals who may not have access to traditional educational institutions due to geographical barriers, financial constraints, or time limitations.
The flexibility of online learning allows students to study at their own pace and on their own schedule, making it easier to balance education with other commitments. Personalized learning experiences enable students to focus on areas where they need the most support and access resources tailored to their learning styles.
14.2. How Does Gamification Enhance Online Learning Engagement?
Gamification enhances online learning engagement by incorporating game-like elements such as points, badges, leaderboards, and challenges into the learning process. These elements can make learning more fun and motivating, increasing student participation and retention. Gamification can also provide immediate feedback on student progress, helping them stay engaged and track their achievements.
By incorporating game-like elements, online learning platforms can create a more immersive and interactive learning experience, enhancing student engagement and improving learning outcomes.
15. What Are The Ethical Considerations Surrounding Automation and Job Displacement?
Ethical considerations surrounding automation and job displacement include ensuring fairness, equity, and social responsibility in the implementation of new technologies. As automation displaces workers, it is essential to provide them with opportunities for retraining, upskilling, and support to transition to new careers. Companies and governments have a responsibility to mitigate the negative impacts of automation on workers and communities.
It is also important to address issues of bias and discrimination in AI systems, ensuring that they are used fairly and equitably. Transparency and accountability in the development and deployment of AI technologies are crucial for building trust and ensuring that they are used for the benefit of society.
15.1. How Can Businesses Ethically Implement Automation?
Businesses can ethically implement automation by prioritizing workforce development, providing retraining opportunities, and ensuring transparency in their automation strategies. Companies should invest in training programs to help workers acquire the skills needed for new roles created by automation.
They should also provide support for displaced workers, such as severance packages, career counseling, and job placement assistance. Transparency in automation strategies is essential for building trust with employees and stakeholders, ensuring that they understand the reasons for automation and the steps being taken to mitigate its impact.
15.2. What Role Should Governments Play In Addressing Automation’s Ethical Challenges?
Governments should play a key role in addressing automation’s ethical challenges by implementing policies that support workforce development, providing social safety nets, and regulating the use of AI technologies. Policies that promote STEM education, vocational training, and lifelong learning can help workers acquire the skills needed for emerging jobs.
Social safety nets, such as unemployment benefits and universal basic income, can provide a cushion for displaced workers while they seek retraining or new employment. Governments should also regulate the use of AI technologies to ensure fairness, equity, and transparency, addressing issues such as bias, discrimination, and privacy.
16. What Are The Psychological Impacts Of Job Insecurity Due To Technological Advancements?
The psychological impacts of job insecurity due to technological advancements can include increased stress, anxiety, and depression among workers. According to a study by the American Psychological Association, job insecurity is associated with higher rates of stress-related health problems, such as cardiovascular disease and mental health disorders. Workers who fear losing their jobs to automation may experience chronic stress, leading to burnout, reduced job satisfaction, and decreased productivity.
These psychological impacts can affect not only individual workers but also their families and communities, creating a ripple effect of negative consequences. Addressing these psychological impacts requires a multifaceted approach, including providing mental health support, promoting work-life balance, and fostering a sense of job security and stability.
16.1. How Can Employers Support Employees Facing Job Insecurity?
Employers can support employees facing job insecurity by providing clear communication, offering retraining opportunities, and promoting a culture of support and resilience. Clear and transparent communication about the company’s plans for automation can help alleviate anxiety and uncertainty among employees.
Offering retraining opportunities can equip workers with the skills needed for new roles, enhancing their job security and career prospects. Promoting a culture of support and resilience can help employees cope with stress and uncertainty, fostering a sense of belonging and shared purpose.
16.2. What Resources Are Available For Workers Coping With Job-Related Stress?
Resources available for workers coping with job-related stress include employee assistance programs (EAPs), mental health counseling, and stress management workshops. EAPs provide confidential counseling and support services to employees facing personal or work-related challenges. Mental health counseling can help workers address issues such as anxiety, depression, and burnout.
Stress management workshops can teach employees techniques for managing stress, improving resilience, and promoting work-life balance. Additionally, online resources, such as websites and apps, can provide information and tools for coping with job-related stress.
17. How Do Cultural Attitudes Toward Technology Influence Job Market Dynamics?
Cultural attitudes toward technology significantly influence job market dynamics by shaping adoption rates, innovation, and workforce readiness. Cultures that embrace technological change and prioritize STEM education tend to adapt more quickly to new job requirements and create innovative industries. According to the National Science Foundation, countries with strong investments in research and development often see greater economic growth and job creation in technology-related fields.
Conversely, cultures that are resistant to change or lack access to education and training may struggle to adapt to the changing job market, leading to job losses and economic disparities. Cultural attitudes also influence the types of jobs that are valued and pursued, shaping the skills and talent available in the workforce.
17.1. How Does Emphasis On STEM Education Affect Job Creation?
Emphasis on STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) education significantly affects job creation by preparing workers for high-demand roles in technology-related fields. STEM education equips students with the skills and knowledge needed to innovate, problem-solve, and adapt to new technologies.
This can lead to the creation of new industries, products, and services, generating employment opportunities. Countries with strong STEM education systems often see greater economic growth and job creation in technology sectors. Additionally, STEM skills are increasingly valuable in a wide range of industries, making workers with STEM backgrounds highly sought after in the job market.
17.2. How Do Different Countries Approach Retraining Displaced Workers?
Different countries approach retraining displaced workers through various strategies, including government-funded programs, industry partnerships, and individual initiatives. Germany, for example, has a well-established apprenticeship system that provides workers with on-the-job training and skills development.
Singapore offers a SkillsFuture initiative that provides individuals with lifelong learning opportunities and funding for training courses. The United States has a mix of federal and state programs aimed at retraining displaced workers, but these programs often face challenges related to funding, coordination, and effectiveness.
18. What Are The Global Implications Of Technology-Driven Job Displacement?
The global implications of technology-driven job displacement include shifts in economic power, increased income inequality, and the need for international cooperation to address workforce challenges. As technology reshapes job markets, countries that adapt quickly and invest in workforce development may gain a competitive advantage in the global economy.
Conversely, countries that struggle to adapt may face job losses, economic stagnation, and increased social unrest. Technology-driven job displacement can also exacerbate income inequality, as those with the skills and resources to adapt to new job requirements may thrive, while those without these advantages may fall behind. International cooperation is needed to address these challenges, sharing best practices, coordinating policies, and providing support to countries in need.
18.1. How Can Developing Countries Prepare For Automation?
Developing countries can prepare for automation by investing in education, infrastructure, and entrepreneurship. Investing in education, particularly STEM education, can help build a skilled workforce capable of adapting to new technologies. Improving infrastructure, such as internet access and transportation networks, can facilitate the adoption of new technologies and create new business opportunities.
Promoting entrepreneurship can encourage the creation of new businesses and jobs, offsetting some of the job losses from automation. Additionally, developing countries can learn from the experiences of developed countries, adapting successful strategies and avoiding costly mistakes.
18.2. What Role Do International Organizations Play In Addressing Global Job Displacement?
International organizations, such as the United Nations, the World Bank, and the International Labour Organization (ILO), play a key role in addressing global job displacement by providing research, technical assistance, and policy recommendations to member states. These organizations conduct research on the impacts of technology on the job market, identifying trends and challenges.
They provide technical assistance to countries in developing and implementing policies to promote workforce development, social protection, and economic growth. They also facilitate dialogue and cooperation among countries, sharing best practices and coordinating efforts to address global challenges.
19. How Does Ageism Affect Older Workers Facing Technological Changes?
Ageism affects older workers facing technological changes by creating barriers to retraining, job opportunities, and career advancement. Older workers may face stereotypes that they are less adaptable, less tech-savvy, and less willing to learn new skills. This can make it difficult for them to access retraining programs, secure new jobs, and advance in their careers.
According to the AARP, ageism is a pervasive problem in the workplace, with many older workers experiencing discrimination based on their age. Addressing ageism requires challenging stereotypes, promoting diversity and inclusion, and providing older workers with equal opportunities for training and employment.
19.1. What Support Systems Can Help Older Workers Adapt To New Technologies?
Support systems that can help older workers adapt to new technologies include mentorship programs, targeted training courses, and flexible work arrangements. Mentorship programs can pair older workers with younger colleagues who can provide guidance and support in learning new technologies.
Targeted training courses can be designed to meet the specific needs and learning styles of older workers, addressing common challenges and building confidence. Flexible work arrangements, such as part-time work and telecommuting, can allow older workers to balance their work and personal lives while adapting to new technologies.
19.2. How Can Employers Create Age-Inclusive Workplaces?
Employers can create age-inclusive workplaces by challenging ageist stereotypes, promoting diversity and inclusion, and providing equal opportunities for training and employment. Companies can conduct awareness campaigns to educate employees about ageism and its negative impacts.
They can implement policies that promote diversity and inclusion, ensuring that older workers are represented in all areas of the organization. They can also provide equal opportunities for training and employment, regardless of age, and support older workers in adapting to new technologies.
20. What Emerging Technologies Could Create New Job Categories In The Future?
Emerging technologies that could create new job categories in the future include quantum computing, biotechnology, and nanotechnology. Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize fields such as cryptography, drug discovery, and materials science, creating new roles for quantum computer engineers, quantum algorithm developers, and quantum cybersecurity experts.
Biotechnology is driving innovation in healthcare, agriculture, and environmental science, creating new jobs for bioengineers, genetic counselors, and biomanufacturing specialists. Nanotechnology is enabling the development of new materials and devices with unique properties, creating new roles for nanotechnologists, nanomaterials scientists, and nanomanufacturing technicians.
20.1. How Might Quantum Computing Reshape The Tech Industry?
Quantum computing is expected to reshape the tech industry by enabling new types of computations that are impossible for classical computers. This could lead to breakthroughs in fields such as cryptography, optimization, and machine learning. Quantum computers could be used to develop unbreakable encryption algorithms, design more efficient supply chains, and create more powerful AI systems.
The development of quantum computing will require a new generation of tech professionals with expertise in quantum physics, computer science, and mathematics. This could create significant job opportunities in the tech industry, as companies race to develop and deploy quantum computing technologies.
20.2. What Skills Will Be Needed To Work In The Biotechnology Sector?
Skills needed to work in the biotechnology sector include expertise in biology, chemistry, genetics, and engineering. Bioengineers design and develop new medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and agricultural products. Genetic counselors provide guidance to individuals and families about genetic risks and testing options.
Biomanufacturing specialists oversee the production of biological products, ensuring quality and safety. Additionally, skills in data analysis, project management, and regulatory compliance are increasingly valuable in the biotechnology sector.
Navigating the complexities of technological change requires staying informed and proactive. Visit pioneer-technology.com today to explore the latest articles, gain valuable insights, and equip yourself with the knowledge to thrive in the ever-evolving world of technology. Don’t just adapt—lead the way. Explore innovative solutions, understand job market trends, and discover how to leverage technology for career advancement and economic prosperity at pioneer-technology.com. Stay ahead with future employment trends and technology evolution. Our address is 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States and our phone number is +1 (650) 723-2300.
FAQ: Technology and Job Displacement
Q1: Is technology really destroying jobs, or is it just changing them?
Technology is primarily reshaping jobs rather than outright destroying them, yet this shift necessitates adaptation and new skills.
Q2: Which jobs are most at risk from automation?
Repetitive, manual labor roles, such as data entry and assembly line work, are most at risk.
Q3: What new job opportunities are being created by technology?
Emerging roles in AI development, data science, and renewable energy are on the rise.
Q4: How can I prepare for the changing job market?
Focus on continuous learning, especially in STEM fields, and develop adaptability.
Q5: What role should governments play in addressing technology-induced job losses?
Governments should invest in education, training, and social safety nets.
Q6: Can businesses help mitigate job displacement?
Yes, by investing in workforce development and upskilling initiatives.
Q7: Are there industries where technology creates more jobs than it destroys?
The tech industry itself and the green energy sector are examples of this.
Q8: How can pioneer-technology.com help me navigate these changes?
We provide up-to-date information, analysis, and expert opinions on emerging technologies.
Q9: What are the ethical considerations of automation?
Fairness, equity, and social responsibility in implementing new technologies are crucial.
Q10: How can older workers adapt to technological changes?
Through mentorship programs, targeted training courses, and flexible work arrangements.

