Is Ai A Part Of Technology? Yes, artificial intelligence (AI) is undoubtedly a core component of modern technology, revolutionizing industries and reshaping our daily lives, and pioneer-technology.com is here to explain how. AI’s integration into various systems enhances automation, improves decision-making, and opens new avenues for innovation. Stay ahead of the curve with our analysis, case studies, and expert insights at pioneer-technology.com.
1. What Defines AI Within The Realm of Technology?
AI, or artificial intelligence, is indeed a pivotal part of modern technology. It’s essentially about creating computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence.
AI is a broad field encompassing various technologies designed to mimic human cognitive functions. According to research from Stanford University’s Department of Computer Science, AI systems leverage algorithms and models to analyze data, learn from patterns, and make decisions or predictions.
1.1 How Does AI Work?
AI systems function by processing vast quantities of labeled training data. These systems analyze the data to identify correlations and patterns, which are then utilized to forecast future outcomes.
For instance, consider an AI chatbot: by being exposed to numerous text examples, it can learn to produce realistic human-like conversations. Similarly, an image recognition tool can learn to recognize and describe objects within images by examining millions of examples. Generative AI techniques, rapidly evolving in recent years, can now produce realistic text, images, music, and various other forms of media.
1.2 What Cognitive Skills Are Used?
Programming AI systems involves focusing on several cognitive skills:
- Learning: Acquiring information and rules for its use.
- Reasoning: Using rules to reach conclusions, whether definite or probable.
- Problem-solving: Formulating problems, generating solutions, and evaluating them.
- Perception: Gathering and interpreting sensory inputs through vision, sound, and touch.
- Language understanding: Processing and understanding written and spoken language.
1.3 What Programming Languages Are Used in AI Development?
While no single programming language is exclusively used in AI, Python, R, Java, C++, and Julia are popular choices among AI developers. These languages provide the necessary tools and libraries for writing and training machine learning algorithms.
2. What Is The Significance Of AI In Today’s World?
AI is significant because it has the potential to transform how we live, work, and interact with the world around us. It is reshaping industries, automating tasks, and providing new opportunities for innovation.
AI has found effective application in business, automating tasks traditionally performed by humans, including customer service, lead generation, fraud detection, and quality control. According to a McKinsey report, businesses that have embraced AI have seen significant improvements in efficiency and productivity.
2.1 How Does AI Improve Efficiency and Accuracy?
In various fields, AI can execute tasks more efficiently and accurately than humans. It excels at repetitive, detail-oriented tasks, such as analyzing large volumes of legal documents to ensure relevant fields are correctly filled.
2.2 What Insights Does AI Provide?
AI’s ability to process massive data sets allows enterprises to gain insights into their operations that might otherwise go unnoticed. As noted in a Harvard Business Review article, AI algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies in data that humans may miss.
2.3 How Is Generative AI Being Used?
The rapidly expanding array of generative AI tools is becoming increasingly important in fields ranging from education to marketing to product design. These tools can generate realistic text, images, and other media, opening up new possibilities for content creation and innovation.
2.4 What New Business Opportunities Does AI Create?
Advancements in AI techniques have not only fueled an explosion in efficiency but also paved the way for entirely new business opportunities for some larger enterprises. Prior to the current wave of AI, it would have been hard to imagine using computer software to connect riders to taxis on demand, yet Uber has become a Fortune 500 company by doing just that.
2.5 What Companies Are Using AI?
AI has become central to many of today’s largest and most successful companies, including Alphabet, Apple, Microsoft, and Meta, which use AI to improve their operations and outpace competitors. At Alphabet subsidiary Google, for example, AI is central to its eponymous search engine, and self-driving car company Waymo began as an Alphabet division. The Google Brain research lab also invented the transformer architecture that underpins recent NLP breakthroughs such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT.
3. What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of AI?
AI technologies, particularly deep learning models such as artificial neural networks, can process vast amounts of data much faster and make predictions more accurately than humans. However, AI also has disadvantages, including high costs and potential biases.
According to a study by PwC, AI could contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030. However, it’s crucial to understand both its advantages and disadvantages to harness its potential effectively.
3.1 What Are The Advantages of AI?
- Efficiency and Speed: AI systems can process large volumes of data much faster than humans.
- Accuracy: AI can make predictions and decisions with greater accuracy.
- Automation: AI can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers for more creative and strategic activities.
- Data Analysis: AI can analyze vast data sets to uncover insights and patterns that humans may miss.
- Innovation: AI can enable new products, services, and business models.
3.2 What Are The Disadvantages of AI?
- High Costs: Processing the large amounts of data AI requires is expensive.
- Job Displacement: AI can lead to job loss if organizations replace human workers with machines.
- Security Vulnerabilities: AI systems are susceptible to a wide range of cyberthreats.
- Environmental Impact: The data centers and network infrastructures that underpin the operations of AI models consume large amounts of energy and water.
- Legal Issues: AI raises complex questions around privacy and legal liability.
 Chart comparing AI, machine learning and deep learning in terms of data volumes, outputs, processes and management.
Chart comparing AI, machine learning and deep learning in terms of data volumes, outputs, processes and management.
AI, machine learning and deep learning illustrated.
4. What Are Strong AI And Weak AI?
AI can be categorized into two main types: narrow (or weak) AI and general (or strong) AI. Understanding the differences between these types is essential for setting realistic expectations and goals.
AI is further divided into two categories, weak AI, also known as Narrow AI, and Strong AI, also known as Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
4.1 What Is Weak AI?
Narrow AI is designed and trained for a specific task. For example, a voice assistant like Siri can understand and respond to voice commands, but it cannot perform tasks outside of its programming.
4.2 What Is Strong AI?
General AI, on the other hand, possesses the ability to understand, learn, and implement knowledge across various domains, much like a human. This type of AI can perform any intellectual task that a human being can.
4.3 Can AGI Be Created?
The question of whether AGI can be created remains hotly debated among AI experts. Even today’s most advanced AI technologies, such as ChatGPT and other highly capable LLMs, do not demonstrate cognitive abilities on par with humans and cannot generalize across diverse situations. ChatGPT, for example, is designed for natural language generation, and it is not capable of going beyond its original programming to perform tasks such as complex mathematical reasoning.
5. What Are The 4 Types Of AI?
AI can be categorized into four types, starting with task-specific intelligent systems in wide use today and progressing to sentient systems, which do not yet exist. Knowing these categories helps in understanding the current state and future possibilities of AI.
5.1 What Is Type 1: Reactive Machines?
These AI systems have no memory and are task-specific. An example is Deep Blue, the IBM chess program that beat Russian chess grandmaster Garry Kasparov in the 1990s. Deep Blue was able to identify pieces on a chessboard and make predictions, but because it had no memory, it could not use past experiences to inform future ones.
5.2 What Is Type 2: Limited Memory?
These AI systems have memory, so they can use past experiences to inform future decisions. Some of the decision-making functions in self-driving cars are designed this way.
5.3 What Is Type 3: Theory Of Mind?
Theory of mind is a psychology term. When applied to AI, it refers to a system capable of understanding emotions. This type of AI can infer human intentions and predict behavior, a necessary skill for AI systems to become integral members of historically human teams.
5.4 What Is Type 4: Self-Awareness?
In this category, AI systems have a sense of self, which gives them consciousness. Machines with self-awareness understand their own current state. This type of AI does not yet exist.
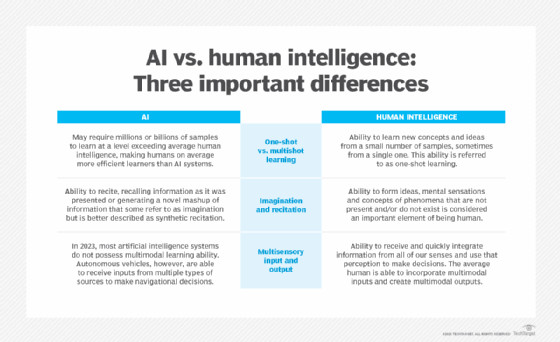 Chart highlighting how artificial and human intelligence differ in the areas of learning, imagination and multisensory processing.
Chart highlighting how artificial and human intelligence differ in the areas of learning, imagination and multisensory processing.
AI vs human intelligence: key differences.
6. What Are Examples Of AI Technology And How Is It Used Today?
AI technologies enhance existing tools’ functionalities and automate various tasks and processes, affecting numerous aspects of everyday life. Understanding these examples provides insight into AI’s widespread impact.
6.1 How Is AI Used In Automation?
AI enhances automation technologies by expanding the range, complexity, and number of tasks that can be automated. An example is robotic process automation (RPA), which automates repetitive, rules-based data processing tasks traditionally performed by humans. Because AI helps RPA bots adapt to new data and dynamically respond to process changes, integrating AI and machine learning capabilities enables RPA to manage more complex workflows.
6.2 How Is AI Used In Machine Learning?
Machine learning is the science of teaching computers to learn from data and make decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, uses sophisticated neural networks to perform what is essentially an advanced form of predictive analytics.
- Supervised Learning: Trains models on labeled data sets, enabling them to accurately recognize patterns, predict outcomes, or classify new data.
- Unsupervised Learning: Trains models to sort through unlabeled data sets to find underlying relationships or clusters.
- Reinforcement Learning: Takes a different approach, in which models learn to make decisions by acting as agents and receiving feedback on their actions.
6.3 How Is AI Used In Computer Vision?
Computer vision is a field of AI that focuses on teaching machines how to interpret the visual world. By analyzing visual information such as camera images and videos using deep learning models, computer vision systems can learn to identify and classify objects and make decisions based on those analyses. The primary aim of computer vision is to replicate or improve on the human visual system using AI algorithms.
6.4 How Is AI Used In Natural Language Processing?
NLP refers to the processing of human language by computer programs. NLP algorithms can interpret and interact with human language, performing tasks such as translation, speech recognition, and sentiment analysis. One of the oldest and best-known examples of NLP is spam detection, which looks at the subject line and text of an email and decides whether it is junk.
6.5 How Is AI Used In Robotics?
Robotics is a field of engineering that focuses on the design, manufacturing, and operation of robots: automated machines that replicate and replace human actions, particularly those that are difficult, dangerous, or tedious for humans to perform.
6.6 How Is AI Used In Autonomous Vehicles?
Autonomous vehicles, more colloquially known as self-driving cars, can sense and navigate their surrounding environment with minimal or no human input. These vehicles rely on a combination of technologies, including radar, GPS, and a range of AI and machine learning algorithms.
6.7 How Is AI Used In Generative AI?
The term generative AI refers to machine learning systems that can generate new data from text prompts — most commonly text and images, but also audio, video, software code, and even genetic sequences and protein structures.
7. What Are The Applications Of AI Across Various Sectors?
AI is transforming numerous sectors by automating tasks, improving decision-making, and enabling new innovations. Examining these applications provides a glimpse into AI’s transformative power.
7.1 How Is AI Used In Healthcare?
AI is applied to a range of tasks in the healthcare domain, with the overarching goals of improving patient outcomes and reducing systemic costs. One major application is the use of machine learning models trained on large medical data sets to assist healthcare professionals in making better and faster diagnoses.
7.2 How Is AI Used In Business?
AI is increasingly integrated into various business functions and industries, aiming to improve efficiency, customer experience, strategic planning, and decision-making. For example, machine learning models power many of today’s data analytics and customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, helping companies understand how to best serve customers through personalizing offerings and delivering better-tailored marketing.
7.3 How Is AI Used In Education?
AI has a number of potential applications in education technology. It can automate aspects of grading processes, giving educators more time for other tasks. AI tools can also assess students’ performance and adapt to their individual needs, facilitating more personalized learning experiences that enable students to work at their own pace. AI tutors could also provide additional support to students, ensuring they stay on track.
7.4 How Is AI Used In Finance And Banking?
Banks and other financial organizations use AI to improve their decision-making for tasks such as granting loans, setting credit limits, and identifying investment opportunities. In addition, algorithmic trading powered by advanced AI and machine learning has transformed financial markets, executing trades at speeds and efficiencies far surpassing what human traders could do manually.
7.5 How Is AI Used In Law?
AI is changing the legal sector by automating labor-intensive tasks such as document review and discovery response, which can be tedious and time-consuming for attorneys and paralegals. Law firms today use AI and machine learning for a variety of tasks, including analytics and predictive AI to analyze data and case law, computer vision to classify and extract information from documents, and NLP to interpret and respond to discovery requests.
7.6 How Is AI Used In Entertainment And Media?
The entertainment and media business uses AI techniques in targeted advertising, content recommendations, distribution, and fraud detection. The technology enables companies to personalize audience members’ experiences and optimize delivery of content.
7.7 How Is AI Used In Journalism?
In journalism, AI can streamline workflows by automating routine tasks, such as data entry and proofreading. Investigative journalists and data journalists also use AI to find and research stories by sifting through large data sets using machine learning models, thereby uncovering trends and hidden connections that would be time-consuming to identify manually.
7.8 How Is AI Used In Software Development And IT?
AI is used to automate many processes in software development, DevOps, and IT. For example, AIOps tools enable predictive maintenance of IT environments by analyzing system data to forecast potential issues before they occur, and AI-powered monitoring tools can help flag potential anomalies in real-time based on historical system data.
7.9 How Is AI Used In Security?
AI and machine learning are prominent buzzwords in security vendor marketing, so buyers should take a cautious approach. Still, AI is indeed a useful technology in multiple aspects of cybersecurity, including anomaly detection, reducing false positives, and conducting behavioral threat analytics.
7.10 How Is AI Used In Manufacturing?
Manufacturing has been at the forefront of incorporating robots into workflows, with recent advancements focusing on collaborative robots, or cobots. Unlike traditional industrial robots, which were programmed to perform single tasks and operated separately from human workers, cobots are smaller, more versatile, and designed to work alongside humans.
7.11 How Is AI Used In Transportation?
In addition to AI’s fundamental role in operating autonomous vehicles, AI technologies are used in automotive transportation to manage traffic, reduce congestion, and enhance road safety. In air travel, AI can predict flight delays by analyzing data points such as weather and air traffic conditions. In overseas shipping, AI can enhance safety and efficiency by optimizing routes and automatically monitoring vessel conditions.
8. What Is Augmented Intelligence And How Does It Differ From AI?
Augmented intelligence refers to machine systems that support humans, distinguishing them from fully autonomous systems. Understanding this concept clarifies the role of AI as a tool to enhance human capabilities.
AI is often associated with popular culture which leads to unrealistic expectations about the impact on our daily routines.
8.1 What Is Augmented Intelligence?
The term augmented intelligence distinguishes machine systems that support humans from the fully autonomous systems found in science fiction.
8.2 What Is The Focus Of Augmented Intelligence?
Augmented intelligence focuses on using AI to enhance human capabilities rather than replace them. This involves creating systems that assist humans in decision-making, problem-solving, and creative tasks.
9. What Are The Ethical Considerations For AI Usage?
Ethical considerations in AI use are crucial due to the potential for bias, misuse, and privacy concerns. Addressing these challenges ensures that AI is developed and used responsibly.
AI systems reinforce what they have already learned, meaning that these algorithms are highly dependent on the data they are trained on. Because a human being selects that training data, the potential for bias is inherent and must be monitored closely.
9.1 What Ethical Challenges Does AI Present?
- Bias: Due to improperly trained algorithms and human prejudices or oversights.
- Misuse: Of generative AI to produce deepfakes, phishing scams, and other harmful content.
- Legal Concerns: Including AI libel and copyright issues.
- Job Displacement: Due to the increasing use of AI to automate workplace tasks.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Particularly in fields such as banking, healthcare, and legal that deal with sensitive personal data.
 components of responsible AI use.
components of responsible AI use.
Responsible AI components.
9.2 What Is Responsible AI?
Responsible AI refers to the development and implementation of safe, compliant, and socially beneficial AI systems. It is driven by concerns about algorithmic bias, lack of transparency, and unintended consequences. Integrating responsible AI principles into business strategies helps organizations mitigate risk and foster public trust.
9.3 Why Is Explainability Important In AI?
Explainability, or the ability to understand how an AI system makes decisions, is a growing area of interest in AI research. Lack of explainability presents a potential stumbling block to using AI in industries with strict regulatory compliance requirements. For example, fair lending laws require U.S. financial institutions to explain their credit-issuing decisions to loan and credit card applicants.
10. What Governance And Regulations Exist For AI?
AI governance and regulations are evolving to address ethical concerns and ensure responsible use. Understanding the current regulatory landscape is essential for compliance and ethical AI development.
Despite potential risks, there are currently few regulations governing the use of AI tools, and many existing laws apply to AI indirectly rather than explicitly.
10.1 What Regulations Exist In The EU?
The European Union has been proactive in addressing AI governance. The EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) already imposes strict limits on how enterprises can use consumer data, affecting the training and functionality of many consumer-facing AI applications. In addition, the EU AI Act, which aims to establish a comprehensive regulatory framework for AI development and deployment, went into effect in August 2024.
10.2 What Regulations Exist In The US?
While the U.S. is making progress, the country still lacks dedicated federal legislation akin to the EU’s AI Act. Policymakers have yet to issue comprehensive AI legislation, and existing federal-level regulations focus on specific use cases and risk management, complemented by state initiatives. The White House Office of Science and Technology Policy published a “Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights” in October 2022, providing guidance for businesses on how to implement ethical AI systems.
10.3 What Challenges Exist In Regulating AI?
Crafting laws to regulate AI will not be easy, partly because AI comprises a variety of technologies used for different purposes, and partly because regulations can stifle AI progress and development, sparking industry backlash. The rapid evolution of AI technologies is another obstacle to forming meaningful regulations, as is AI’s lack of transparency, which makes it difficult to understand how algorithms arrive at their results. Moreover, technology breakthroughs and novel applications such as ChatGPT and Dall-E can quickly render existing laws obsolete.
The four types of AI.
FAQ: Is AI A Part Of Technology?
1. What is the definition of artificial intelligence (AI) in technology?
Artificial intelligence (AI) in technology refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems, enabling them to perform tasks that typically require human intellect.
2. How does machine learning relate to AI as a part of technology?
Machine learning is a subset of AI. It involves teaching computers to learn from data and make decisions without explicit programming, making it a core technique within the broader field of AI.
3. What are the primary applications of AI in various industries?
AI is applied across industries such as healthcare for diagnostics, business for automation, finance for fraud detection, and transportation for autonomous vehicles, enhancing efficiency and innovation.
4. What are the advantages of integrating AI into technological systems?
Integrating AI into technological systems offers advantages such as increased efficiency, improved accuracy, automation of tasks, enhanced data analysis, and the potential for new business opportunities.
5. What are the potential disadvantages of using AI in technology?
Disadvantages of using AI in technology include high costs, potential job displacement, security vulnerabilities, environmental impacts, and legal and ethical issues related to privacy and bias.
6. How do the concepts of strong AI and weak AI differ within the technological landscape?
Strong AI refers to general intelligence that can understand, learn, and implement knowledge across various domains like a human, while weak AI is designed for specific tasks and lacks broader cognitive abilities.
7. What are some examples of AI technologies used in everyday life?
Examples of AI technologies in everyday life include virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, computer vision in self-driving cars, natural language processing in chatbots, and recommendation systems in e-commerce.
8. What ethical concerns are associated with AI technology?
Ethical concerns associated with AI technology include potential bias in algorithms, misuse of generative AI, legal issues such as copyright, job displacement, and data privacy concerns.
9. How is AI governance and regulation being addressed globally?
AI governance and regulation are being addressed through initiatives like the EU AI Act, which aims to establish a comprehensive regulatory framework, and various guidelines and policies in the U.S. to ensure responsible AI development and deployment.
10. What role does augmented intelligence play in contrast to full AI automation?
Augmented intelligence focuses on using AI to enhance human capabilities rather than replace them, creating systems that assist humans in decision-making, problem-solving, and creative tasks.
AI is undeniably a transformative part of technology, driving innovation and efficiency across various sectors. To stay informed about the latest advancements, expert insights, and future trends in AI, visit pioneer-technology.com. Discover detailed analysis, case studies, and practical solutions to help you navigate the complexities of AI and leverage its potential for your business or personal growth. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to explore the cutting edge of technology—explore pioneer-technology.com today!
Address: 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States. Phone: +1 (650) 723-2300. Website: pioneer-technology.com.
