Is Technology Impacting Our Intelligence? Yes, technology significantly impacts our intelligence, both negatively and positively, and at pioneer-technology.com, we are committed to providing you with a detailed exploration of how digital tools affect our cognitive abilities. Explore the nuances of cognitive enhancement, digital literacy, and adaptive learning to stay informed about the evolution of human intellect in the digital age.
1. What Are the Multifaceted Impacts of Technology on Intelligence?
Technology impacts our intelligence in many ways. Digital technology significantly influences both brain function and behavior, with studies showing the potential for both positive and negative outcomes. Let’s dive into how exactly that happens.
- Cognitive Enhancement: Technology offers tools that can improve memory, attention, and problem-solving skills.
- Digital Distraction: Excessive technology use can lead to attention deficits, reduced emotional intelligence, and addiction.
1.1 Can Technology Use Lead to Cognitive Decline?
Yes, extensive screen time and technology use have been linked to cognitive decline. Emerging scientific evidence suggests that while technology offers numerous benefits, overuse can lead to several detrimental effects on brain function and behavior. Let’s see how:
- Attention-Deficit Symptoms: Frequent digital technology use has been associated with heightened symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found a significant correlation between increased digital media use and ADHD symptoms in adolescents.
- Impaired Emotional and Social Intelligence: Spending excessive time with digital media reduces opportunities for face-to-face interactions, which are critical for developing emotional and social intelligence. Research from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) demonstrated that preteens who were restricted from screen-based media for five days showed significant improvements in recognizing nonverbal emotional and social cues.
- Technology Addiction: Pathological internet use shares features with substance-use disorders, including preoccupation, mood changes, tolerance, withdrawal, and functional impairment. The global prevalence of internet addiction is estimated at around 6%, with higher rates in certain regions.
- Social Isolation: Paradoxically, social media use is linked to social isolation, which is associated with poor health outcomes and increased mortality. A study in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine found that young adults who use social media for more than two hours a day are twice as likely to report feeling socially isolated.
- Impaired Brain Development: Increased screen time, especially in very young children, has been associated with poorer language development and executive functioning. Research has shown that children aged 8 to 12 who spend more time on screens have decreased brain connectivity in regions controlling word recognition, language, and cognitive control.
- Disrupted Sleep: Screen exposure disrupts sleep, which can negatively affect cognition and behavior. The blue light emitted from computer and phone screens interferes with circadian rhythms, leading to reduced sleep quality and shorter sleep duration.
1.2 How Can Technology Enhance Cognitive Abilities?
Technology is not all bad. Various apps, video games, and online tools can benefit brain health and enhance cognitive abilities. Functional imaging scans have shown that internet-naive older adults who learn to search online exhibit significant increases in brain neural activity during simulated internet searches. Several key areas can be improved:
- Memory: Certain computer programs and video games may improve memory function. A study in Neurobiology of Aging found that computerized brain-training exercises improved delayed memory in older adults without dementia.
- Multitasking Skills: Specific video games can enhance multitasking skills. Research from the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) demonstrated that training with the video game NeuroRacer improved multitasking abilities in older adults, even exceeding the performance of untrained individuals in their twenties.
- Fluid Intelligence: Training programs, such as the n-back task, have been shown to improve working memory and fluid intelligence. A study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences found that working-memory training led to significant improvements in fluid intelligence.
- Mental Health Interventions: Some apps and digital tools offer mental health interventions, providing self-management, monitoring, skills training, and other interventions that may improve mood and behavior.
1.3 Which Technologies Provide Mental Exercise?
Searching the internet can serve as a form of mental exercise that strengthens neural circuits. Our team’s functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) research tracking neural activity during simulated internet searches suggests that simply searching online may represent a form of mental exercise that can strengthen neural circuits. Let’s see a breakdown:
Internet Searching
- Neural Activation: Internet searching activates brain regions controlling decision-making, complex reasoning, and vision.
- Cognitive Benefits: Regular internet searching may delay cognitive decline and improve overall brain health.
Cognitive Training Games
- Targeted Skills: These games can improve global cognition, memory (immediate, delayed, and working), attention, and learning abilities.
- Examples: Dakim Brain Fitness is one program that has shown potential benefits.
Specific Video Games
- Multitasking: Racecar video games with distracting road signs can enhance multitasking skills.
- Working Memory and Fluid Intelligence: N-back task training games improve working memory and fluid intelligence.
- Visual Attention: Action video games enhance visual attention, reaction time, and task-switching abilities.
Monitoring Apps
- Health Tracking: Monitoring apps track heart rate and breathing patterns, providing valuable health data.
- Mental Health Support: These apps can assist in managing stress and anxiety.
Psychotherapy and Educational Apps
- Mental Health Improvement: These apps offer psychotherapy and educational content to improve mood, sleep, and social support.
- Accessibility: Online interventions provide accessible and cost-effective mental health support.
Interested in diving deeper into this subject? Pioneer-technology.com offers more detailed articles and resources on cognitive enhancement and the impact of technology on our minds. Visit us to explore the latest insights and strategies.
 Brain activity during internet searching
Brain activity during internet searching
2. How Does Screen Time Affect Emotional and Social Intelligence?
Screen time negatively impacts emotional and social intelligence, particularly in young people. Spending excessive time with digital media reduces the opportunities for face-to-face interactions, which are essential for developing these crucial skills.
2.1 What Is the Impact of Reduced Face-to-Face Communication?
Reduced face-to-face communication can hinder the development of emotional and social skills. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends limiting screen time for children aged two years or younger, as this is a critical period for brain development.
- Impaired Emotion Recognition: Playing video games, particularly violent ones, can interfere with the ability to recognize emotions conveyed through facial expressions.
- Decreased Social Cues Recognition: Preteens restricted from screen-based media showed significantly better recognition of nonverbal emotional and social cues compared to those with regular screen time.
2.2 What Did the UCLA Study Reveal About Screen Time?
A study conducted at UCLA explored the impact of screen time on the ability to recognize nonverbal emotional and social cues. The study compared 51 schoolchildren who spent five days at an overnight nature camp where television, computers, and smartphones were forbidden with 54 school-based matched controls who continued their usual media practices (4 hours of screen time per day).
Key Findings
- Improved Recognition of Nonverbal Cues: After five days, the nature camp participants demonstrated significantly better recognition of nonverbal emotional and social cues compared to the control group.
- Enhanced Social Intelligence: Time away from screen-based media and digital communication tools improves both emotional and social intelligence.
- Implications: These findings suggest that reducing screen time can enhance the ability to understand and respond to social and emotional signals, which are critical for building and maintaining relationships.
2.3 How Does Social Media Use Relate to Social Isolation?
Social media use is paradoxically linked to social isolation. Despite the ability to connect with others online, excessive social media use can lead to a lack of genuine social connections and quality relationships.
The Primack Study
- Participants: 1787 young adults (ages 19 to 32 years).
- Findings: Using social media two or more hours each day doubled the odds for perceived social isolation compared with use less than 30 minutes each day.
- Explanation: Reduced offline social experiences and the tendency to make upward social comparisons based on highly curated social media feeds can produce unrealistic expectations of oneself.
Want to foster better emotional and social intelligence? Pioneer-technology.com provides resources and strategies for balancing technology use and promoting healthy social interactions. Explore our articles to learn more about the benefits of digital detox and mindful technology use.
 Children using computers
Children using computers
3. Can Technology Lead to Addiction and What Are the Consequences?
Yes, technology can lead to addiction, with consequences similar to substance-use disorders. Excessive and pathological internet use has been recognized as an internet addiction, sharing features with substance-use disorders or pathological gambling.
3.1 What Are the Common Features of Internet Addiction?
Internet addiction exhibits several common features that mirror those seen in substance-use disorders:
- Preoccupations: Constant thoughts about being online or planning the next online session.
- Mood Changes: Experiencing mood swings related to internet use, such as feeling euphoric while online and irritable when offline.
- Development of Tolerance: Needing to spend more time online to achieve the same level of satisfaction.
- Withdrawal: Experiencing negative symptoms, such as anxiety or depression, when unable to access the internet.
- Functional Impairment: Neglecting responsibilities, relationships, and other important aspects of life due to internet use.
3.2 What Is the Prevalence of Internet Addiction?
The global prevalence of internet addiction is estimated at 6%, but in some regions, such as the Middle East, the prevalence is as high as 11%. This highlights the significant impact of internet addiction on a global scale.
3.3 How Is Internet Addiction Linked to ADHD Symptoms?
Students with internet addiction are more likely to suffer from ADHD symptoms than from other psychiatric disorders. Several studies have found significant associations between internet addiction and symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
- You and Colleagues Study: Schoolchildren with internet addiction experienced significantly greater symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity than non–internet-addicted students.
- Panagiotidi and Overton Study: Adults aged 18 to 70 years with internet addiction reported greater ADHD symptoms, with predictors of addiction including younger age, playing massively multiplayer online role-playing games, and spending more time online.
3.4 What Are the Potential Causal Relationships?
The causal relationship between ADHD symptoms and internet addiction remains uncertain. There are two primary explanations:
- ADHD Symptoms Increase Risk: People with ADHD symptoms may have a greater risk of developing technology addiction.
- Technology Use Causes ADHD Symptoms: Extensive technology use from addictive behavior may cause ADHD symptoms.
Recognizing and addressing technology addiction is crucial for maintaining mental health. Pioneer-technology.com offers guidance on identifying addictive behaviors and strategies for healthy technology use. Visit our site for more information on digital wellness and responsible technology consumption.
4. How Can Digital Technology Impact Cognitive and Brain Development?
Digital technology can adversely impact cognitive and brain development, particularly in young children. Increased screen time has been associated with various negative outcomes.
4.1 What Are the Effects of Increased Screen Time on Young Children?
Children under age 2 spend over 1 hour each day in front of a screen, and by age 3, that number exceeds 3 hours. This increased screen time has several negative effects:
- Poorer Language Development: Increased screen time (and less reading time) has been associated with poorer language development and executive functioning, particularly in very young children.
- Behavioral Problems: In infants, increased screen time was one of several factors that predicted behavioral problems.
- Early Language Development Issues: For infants 6 to 12 months, increased screen time was linked to poorer early language development.
4.2 What Is the Role of Parental Interaction?
Digital media directed toward active learning can be educational for children of preschool age and older, but only when accompanied by parental interaction. Parental involvement is critical for ensuring that children benefit from digital media.
4.3 What Has Recent Research Revealed About Media Exposure and Brain Development?
Recent research has examined the effects of media exposure on brain development. A study of children aged 8 to 12 years found that more screen time and less reading time were associated with decreased brain connectivity between regions controlling word recognition and both language and cognitive control.
Key Findings
- Decreased Brain Connectivity: More screen time and less reading time were associated with decreased brain connectivity between regions controlling word recognition, language, and cognitive control.
- Impact on Reading Comprehension: Such connections are considered important for reading comprehension, suggesting a negative impact of screen time on the developing brain.
- Decreased White-Matter Integrity: Structurally, increased screen time relates to decreased integrity of white-matter pathways necessary for reading and language.
4.4 Why Is There Concern About Screen Use Among Young Children?
Given the growing prominence of screen use among even very young children at stages when brain plasticity is greatest, there is significant concern about the cognitive and brain development of the current generation of screen-exposed children. This concern requires greater understanding and attention.
For parents and educators, pioneer-technology.com offers practical advice and resources for promoting healthy cognitive and brain development in the digital age. Explore our articles to learn how to balance technology use with traditional learning methods and foster a positive learning environment for children.
5. How Does Screen Exposure Disrupt Sleep and Affect Cognition?
Screen exposure disrupts sleep, which can have a negative effect on cognition and behavior. The blue light emitted from screens interferes with circadian rhythms, leading to various sleep disturbances.
5.1 What Are the Sleep-Related Effects of Screen Use?
Recent studies indicate that screen exposure disrupts sleep, leading to several negative effects:
- Infants and Toddlers: Daily touch-screen use among infants and toddlers was shown to negatively impact sleep onset, sleep duration, and nighttime awakenings.
- Adolescents: More time using smartphones and touch screens was associated with greater sleep disturbances, and tablet time was associated with poor sleep quality and increased awakenings after sleep onset.
- Adults: Increased smartphone use was associated with shorter sleep duration and less efficient sleep.
5.2 How Does Poor Sleep Quality Affect the Brain?
Poor sleep quality is associated with brain changes, such as reduced functional connectivity and decreased gray-matter volume, as well as an increased risk for age-associated cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease.
5.3 What Is the Role of Blue Light?
Computer and phone light-emitting diode (LED) screens emit slow wave, blue light that interferes with circadian rhythms. Exposure to LED versus non-LED screens has been shown to produce changes in melatonin levels and sleep quality, and such exposure decreases cognitive performance.
5.4 What Can Be Done to Mitigate These Effects?
Recognizing the effects of screen time on sleep is crucial for mitigating various negative effects on cognition and brain function. Strategies to minimize screen-related sleep disruption include:
- Reducing Screen Time Before Bed: Avoid using screens for at least one to two hours before bedtime.
- Using Blue Light Filters: Enable blue light filters on devices or use blue light blocking glasses.
- Creating a Sleep-Friendly Environment: Ensure the bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool to promote better sleep.
Interested in improving your sleep and cognitive function? Pioneer-technology.com provides insights and tips on optimizing sleep habits in the digital age. Explore our articles to learn more about the connection between technology, sleep, and cognitive health.
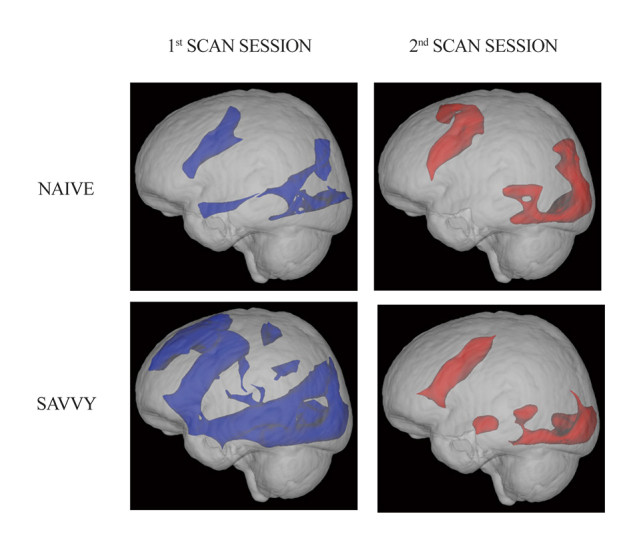
6. How Does Internet Training Affect Brain Function and Neural Activity?
Internet training can positively affect brain function and neural activity, particularly in older adults. Studies have shown that learning to search the internet can activate neural circuits and improve cognitive abilities.
6.1 What Did Early Studies on Internet Searching Reveal?
Early studies using functional MRI explored neural activity during simulated internet searching. These studies aimed to understand how internet searching might benefit brain health and delay cognitive decline.
Key Findings
- Neural Activation: Internet searching activates brain regions controlling decision-making, complex reasoning, and vision.
- Net-Savvy vs. Net-Naive: Net-savvy individuals (those with extensive internet experience) demonstrated significant activity in additional regions controlling decision-making, complex reasoning, and vision compared to net-naive individuals.
- Brain Neural Exercise: Searching online may be a form of brain neural exercise, leading to improved cognitive function.
6.2 What Were the Hypotheses for Internet Training and Brain Function?
Researchers hypothesized that net-naive volunteers would recruit a larger frontal lobe network after internet training and that net-savvy volunteers would show either no increase or a decrease in activation after training because of greater cognitive efficiency due to training.
6.3 How Was the Internet Training Conducted?
The internet training consisted of brief instructions on how to search online along with practice sessions (1 hour per day for a week). Participants were told that they would be quizzed on their knowledge of assigned search topics after the experiment to increase motivation.
6.4 What Were the Results of the Internet Training Study?
The results of the internet training study showed significant changes in brain activity patterns:
- Net-Naive Subjects: During their first session, net-naive subjects recruited a neural network that included the superior, middle, and inferior frontal gyri, as well as the lateral occipital cortex and occipital pole. During the second session (after internet training), additional regions in the middle and inferior frontal gyri were recruited only in the net-naive group.
- Net-Savvy Subjects: During their first scan session, the net-savvy subjects recruited a cortical network that, though overlapping with that of the net-naive subjects, showed more extensive regions of activation. After training, net-savvy participants showed a pattern of activation that was reduced.
6.5 What Do These Findings Suggest About Internet Searching?
These findings suggest that internet searching for relatively short periods of time can change brain-activity patterns in middle-aged and older adults. Additionally, the brain becomes more efficient and possibly habituates to the internet task over time.
Stay updated with the latest research on internet training and brain function by visiting pioneer-technology.com. Our articles provide valuable insights into how technology can be used to enhance cognitive abilities and promote brain health.
7. Can Cognitive Training Programs Improve Memory and Cognitive Function?
Yes, findings showing that mental stimulation and cognitive training improve memory in older adults have led to the development of several memory apps and computer games. These programs aim to enhance cognitive function through targeted exercises.
7.1 What Did the Miller and Associates Study on Brain-Training Exercises Show?
Miller and associates explored whether computerized brain-training exercises (Dakim Brain Fitness) improved cognitive performance in older adults without dementia (mean age of 82 years).
Study Design
- Participants: Older adults without dementia.
- Intervention: Computer program used 5 days a week for 20 to 25 minutes each day.
- Control Group: Wait-list control group.
- Duration: 6 months.
Key Findings
- Improved Delayed Memory: The intervention group improved significantly in delayed memory, and the control group did not.
- Benefits of Consistent Use: Participants who played the computer program for at least 40 sessions over 6 months improved in immediate memory, delayed memory, and language.
7.2 What Did the Meta-Analysis of Computerized Cognitive Training Reveal?
In a meta-analysis of computerized cognitive training, investigators found an overall moderate effect on cognition in mild cognitive impairment across 17 trials.
Key Findings
- Global Cognition: Small to moderate effects were reported for global cognition.
- Attention: Improvements in attention were observed.
- Working Memory: Working memory showed enhancement.
- Learning Abilities: Cognitive training positively influenced learning abilities.
7.3 What Are the Potential Benefits of Cognitive Training?
These findings point to the potential benefit of cognitive training using a computerized, self-paced program. Cognitive training can lead to improvements in:
- Memory Function: Both immediate and delayed memory can be enhanced through targeted exercises.
- Attention and Focus: Cognitive training can improve attention span and focus.
- Learning Abilities: Enhanced cognitive function can lead to improved learning abilities.
Explore the world of cognitive training and discover how these programs can benefit your brain health. Visit pioneer-technology.com to learn more about the latest apps, games, and strategies for enhancing cognitive function and improving your overall quality of life.
8. How Can Video Games Enhance Multitasking Skills?
Certain computer games can enhance multitasking, one of the cognitive domains that declines linearly across the lifespan. Research has shown that specific video games can improve the ability to perform multiple tasks simultaneously.
8.1 What Is Multitasking and Its Impact on Cognitive Performance?
Multitasking has been defined as performing two simultaneous tasks, which is only possible when the tasks are automatic, but it can also refer to rapid switching between tasks. Research has shown that such task switching increases error rates, but certain computer games may enhance multitasking abilities.
8.2 What Did the Anguera and Colleagues Study on NeuroRacer Show?
Anguera and colleagues trained volunteers (ages 60 to 85 years) over 4 weeks using a video game called NeuroRacer, in which players control a car on a winding road while responding to signs that randomly appear.
Study Design
- Participants: Older adults aged 60 to 85 years.
- Intervention: Training with the video game NeuroRacer for 4 weeks.
- Training Groups: Multitasking (both driving and sign reading), single-tasking mode (active controls; either sign reading or driving), and no training (no-contact controls).
Key Findings
- Significant Improvements in Performance Scores: Only the multitasking training group showed significant improvements in performance scores.
- Performance Exceeded Untrained Individuals in Their Twenties: The multitasking training group’s performance not only exceeded that of untrained individuals in their twenties but was maintained for 6 months without additional training.
- Improved Cognitive Skills: Multitasking training improved other cognitive skills, including working memory and divided and sustained attention.
8.3 What Are the Benefits of Multitasking Training?
The benefits of multitasking training include:
- Enhanced Multitasking Abilities: Improved ability to perform multiple tasks simultaneously.
- Improved Working Memory: Enhancement of working memory function.
- Better Attention Span: Improvement in divided and sustained attention.
Unlock your multitasking potential with the help of video games. Visit pioneer-technology.com to discover the latest games and training programs designed to enhance your cognitive skills. Learn how to improve your multitasking abilities and boost your overall cognitive performance.
9. How Can Working Memory Training Improve Fluid Intelligence?
Training in working memory may improve fluid intelligence, which refers to the capacity to reason and think flexibly. Research has shown that targeted training programs can enhance both working memory and fluid intelligence.
9.1 What Is Fluid Intelligence and Its Relationship to Working Memory?
Fluid intelligence refers to the capacity to reason and think flexibly and requires working memory, the ability to retain information over a brief period of time.
9.2 What Did the Jaeggi and Associates Study on Working-Memory Training Show?
Jaeggi and associates used a training program (n-back task) to investigate the effects of working-memory training on fluid intelligence.
Study Design
- Participants: Healthy subjects.
- Intervention: Working-memory training using the n-back task.
- Training Groups: Randomized according to number of training sessions (8, 12, 17, or 19 days), or a control group that received no training.
Key Findings
- Significant Improvements in Working Memory: All four training groups showed significant improvements in working memory.
- Improvements in Fluid Intelligence: The training groups also showed significant improvements on tests of fluid intelligence.
- Dose-Dependent Training Effect: The longer the training period, the greater the improvement in fluid intelligence.
9.3 What Are the Implications of These Findings?
These results indicated successful transfer of improved working memory to improved fluid intelligence measures with a dose-dependent training effect. The implications of these findings include:
- Enhanced Reasoning Abilities: Improved ability to reason and think flexibly.
- Cognitive Enhancement: Working-memory training can serve as an effective tool for cognitive enhancement.
Interested in boosting your fluid intelligence? Pioneer-technology.com offers resources and information on working-memory training programs. Explore our articles to learn how to enhance your cognitive abilities and improve your overall mental performance.
10. What Mental Health Interventions Are Available Through Technology?
Technological advances have brought about novel approaches for delivering mental health support and interventions in the form of apps for smartphones or tablets, as well as through telepsychiatry. Internet-based mental health interventions offer the advantages of accessibility, cost-effectiveness, and anonymity.
10.1 What Are the Benefits of Internet-Based Mental Health Interventions?
Internet-based mental health interventions offer several key benefits:
- Accessibility: They can reach individuals who may not have access to traditional mental health services.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Online interventions are often more affordable than face-to-face therapy.
- Anonymity: Some individuals may feel more comfortable seeking help anonymously online.
10.2 What Types of Online Mental Health Interventions Exist?
Investigators have studied the efficacy of various online mental health interventions:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia: Peter and colleagues found that an online, 4-week intervention using cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia reduced depression and insomnia ratings at levels comparable to traditional face-to-face interventions.
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy: Segal and associates evaluated the effectiveness of treating residual depressive symptoms with a web-based program that delivers mindfulness-based cognitive therapy. Use of this program in addition to usual depression care significantly improved depression and functional outcomes compared with usual depression care alone.
10.3 What Are Digital Mental Health Applications and Their Features?
Several digital mental health applications have been developed or are in development, such as:
- Self-Management Apps: These apps provide user feedback (e.g., medication reminders, stress management tips, heart rate, and breathing patterns).
- Skills Training Programs: These programs provide skills training using educational videos on anxiety management or the importance of social support.
- Data Collection Capabilities: Some applications have the capacity to collect data using smartphone sensors that record movement patterns, social interactions (e.g., number of texts and phone calls), and other behaviors throughout the day.
10.4 What Are the Limitations of These Apps?
Despite some promising early research, systematic studies demonstrating the efficacy of these emerging apps are limited. A recent review indicated that only 3% of downloadable apps had research to justify their effectiveness claims, and most of that research was performed by the program developers.
Take control of your mental health with the help of technology. Visit pioneer-technology.com to explore a range of mental health apps, resources, and support networks. Learn how to leverage technology to improve your mental well-being and access the help you need, anytime, anywhere. Contact us at Address: 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States. Phone: +1 (650) 723-2300.
FAQ: Technology and Intelligence
1. How does technology affect children’s cognitive development?
Technology can negatively affect children’s cognitive development if screen time is excessive, leading to poorer language development and decreased brain connectivity. Parental interaction is crucial to make digital media educational.
2. Can video games really improve cognitive skills?
Yes, certain video games can enhance cognitive skills such as multitasking, visual attention, and reaction time. Games like NeuroRacer have been shown to improve multitasking abilities in older adults.
3. Is social media use linked to social isolation?
Yes, paradoxically, social media use is linked to social isolation. Spending too much time on social media can reduce offline social experiences and lead to feelings of isolation.
4. What is the impact of blue light from screens on sleep?
Blue light emitted from screens can disrupt sleep by interfering with circadian rhythms, leading to reduced sleep quality and shorter sleep duration.
5. Can internet searching be beneficial for brain health?
Yes, internet searching can be a form of mental exercise that strengthens neural circuits. Studies have shown that older adults who learn to search online exhibit increased brain neural activity.
6. How can I balance technology use to benefit my intelligence?
Balancing technology use involves setting limits on screen time, engaging in face-to-face interactions, using technology for cognitive training, and ensuring good sleep hygiene.
7. Are there apps to improve mental health?
Yes, there are many digital mental health applications that offer self-management tools, skills training, and monitoring capabilities to improve mood and behavior.
8. Can working memory training improve fluid intelligence?
Yes, training in working memory can improve fluid intelligence, which is the capacity to reason and think flexibly. Programs like the n-back task have been shown to be effective.
9. What is technology addiction, and how can it be prevented?
Technology addiction is excessive and pathological internet use with symptoms similar to substance-use disorders. Prevention involves setting limits, seeking social support, and engaging in offline activities.
10. Where can I find reliable information on technology’s impact on intelligence?
Reliable information on technology’s impact on intelligence can be found at pioneer-technology.com, which offers detailed articles, research insights, and practical advice on cognitive enhancement and digital wellness.
By understanding both the positive and negative impacts of technology, we can make informed choices to maximize its benefits while minimizing its risks. Remember to visit pioneer-technology.com for more in-depth information and resources to help you navigate the digital age successfully.
