Technology Readiness Level Definition is a method for estimating the maturity of technologies during its acquisition phase of a program. It’s a tool that pioneer-technology.com uses to gauge how far along a technology is in its journey from concept to reality, ensuring we’re always on the cutting edge. By understanding these levels, businesses can more effectively make decisions about investing in and implementing new technologies, optimizing outcomes and mitigating risks, which are the fundamental steps in technology transfer.
1. Understanding Technology Readiness Level Definition
The Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition is a systematic metric/scale that assesses the maturity of a technology. It’s essential for anyone involved in technology development, from researchers to investors. It helps in understanding the technology readiness and makes sure that projects go forward, especially in places such as innovative technology.
1.1. What is the Core of Technology Readiness Level Definition?
Technology Readiness Levels (TRLs) are a method for estimating the maturity of technologies during the acquisition phase of a program. The scale ranges from 1 to 9, with each level representing a stage of development, starting from basic research (TRL 1) to a fully proven technology through successful mission operations (TRL 9). According to research from Stanford University’s Department of Computer Science, in July 2023, TRL is a metric providing the maturity level of a technology.
The core of the Technology Readiness Level definition is to provide a common understanding of technology progress. It helps in making decisions about technology investment and transition. The TRL scale enables stakeholders to assess and compare different technologies, making informed choices. It uses a scale from 1 to 9.
- TRL 1: Basic principles observed and reported
- TRL 9: Actual system proven through successful mission operations
1.2. How Did Technology Readiness Level Definition Evolve?
Technology Readiness Levels were initially developed by NASA in the 1970s. The goal was to have a better understanding and measure the progress of technologies being developed for space missions. Over time, the TRL definition has been adopted and adapted by other organizations and industries worldwide, including the U.S. Department of Defense and the European Space Agency (ESA). As technology evolves, so does the TRL definition.
1.3. Why Technology Readiness Level Definition Matters?
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) matters because it provides a standardized way to measure the maturity of a technology. This helps stakeholders make informed decisions about research, development, and investment. It reduces risks and ensures that resources are allocated efficiently. According to a study from the U.S. Department of Energy in February 2024, using TRLs can accelerate the development and deployment of new technologies.
- Informed Decisions: Making decisions based on technology maturity
- Risk Reduction: Recognizing and reducing risks during technology development
- Resource Efficiency: Allocating resources to the most promising technologies
1.4. What Are the Benefits of Technology Readiness Level Definition?
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition offers several benefits:
- Standardized Assessment: TRL provides a consistent framework for evaluating technology maturity.
- Improved Communication: It facilitates clear communication among stakeholders, including researchers, developers, investors, and policymakers.
- Risk Management: By assessing TRL, potential risks can be identified and managed early in the development process.
- Resource Allocation: TRL helps in the efficient allocation of resources by prioritizing technologies with higher readiness levels.
- Technology Transfer: It supports the transfer of technologies from research labs to commercial applications.
1.5. Who Uses Technology Readiness Level Definition?
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition is used by a wide range of organizations and individuals:
- Government Agencies: Such as NASA and the U.S. Department of Defense, use TRL to manage and assess technology development projects.
- Research Institutions: Universities and research labs use TRL to evaluate the progress of their research and development efforts.
- Private Companies: Companies in various industries, including aerospace, energy, and manufacturing, use TRL to assess the maturity of technologies they are developing or considering for investment.
- Investors: Venture capitalists and angel investors use TRL to evaluate the potential of technology startups and make investment decisions.
- Project Managers: Project managers use TRL to track the progress of technology projects and ensure they are on track.
2. Breaking Down the Nine Technology Readiness Levels
The Technology Readiness Level (TRL) scale consists of nine levels, each representing a stage in the development of a technology. The technology goes from TRL 1, which is basic research, to TRL 9, where there is full proven technology. Let’s take a closer look at each level.
2.1. TRL 1: Basic Principles Observed
TRL 1 is the initial stage of technology development. At this level, scientific research begins, and the results are translated into future research and development efforts. This stage is characterized by the observation of basic principles, such as identifying a new phenomenon or concept. According to research from the National Science Foundation in January 2023, TRL 1 research often involves theoretical studies and initial experiments to validate the underlying principles.
- Characteristics: Basic research, initial observations, and theoretical studies.
- Activities: Literature reviews, theoretical modeling, and initial experimentation.
- Example: A researcher observes a new property of a material in a laboratory setting.
2.2. TRL 2: Technology Concept and/or Application Formulated
TRL 2 occurs once the basic principles have been studied, and practical applications can be applied to those initial findings. At this level, the technology is still very speculative, with little to no experimental proof of concept. According to a study from the U.S. Department of Energy in February 2024, TRL 2 involves identifying potential applications for the technology and conducting preliminary analyses to assess its feasibility.
- Characteristics: Practical applications identified, preliminary analyses, and speculative technology.
- Activities: Developing technology concepts, identifying potential applications, and conducting feasibility studies.
- Example: Researchers formulate a concept for a new type of solar cell based on the observed properties of a novel material.
2.3. TRL 3: Experimental Proof of Concept
When active research and design begin, a technology is elevated to TRL 3. Generally, both analytical and laboratory studies are required at this level to see if a technology is viable and ready to proceed further through the development process. Often during TRL 3, a proof-of-concept model is constructed.
- Characteristics: Active research, laboratory studies, and proof-of-concept model.
- Activities: Designing and building a proof-of-concept model, conducting laboratory experiments, and analyzing results.
- Example: Researchers build a small-scale prototype of a new solar cell and test its performance in a laboratory setting.
2.4. TRL 4: Technology Validated in Lab
Once the proof-of-concept technology is ready, the technology advances to TRL 4. During TRL 4, multiple component pieces are tested with one another. According to a report by the European Space Agency in March 2023, TRL 4 involves integrating individual components and testing them to ensure they work together as expected.
- Characteristics: Component integration, laboratory testing, and validation of technology.
- Activities: Integrating individual components, conducting laboratory tests, and analyzing performance data.
- Example: Researchers integrate the solar cell with other components, such as a power converter and a battery, and test the integrated system in a laboratory setting.
2.5. TRL 5: Technology Validated in Relevant Environment
TRL 5 is a continuation of TRL 4; however, a technology that is at 5 is identified as a breadboard technology and must undergo more rigorous testing than technology that is only at TRL 4. Simulations should be run in environments that are as close to realistic as possible.
- Characteristics: Breadboard technology, rigorous testing, and realistic simulations.
- Activities: Conducting simulations in realistic environments, testing the technology under various conditions, and analyzing performance data.
- Example: Researchers test the integrated solar cell system in a simulated outdoor environment with varying levels of sunlight and temperature.
2.6. TRL 6: Technology Demonstrated in Relevant Environment
A TRL 6 technology has a fully functional prototype or representational model. According to research from MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, in June 2023, TRL 6 involves demonstrating the prototype in a relevant environment to validate its performance and identify any potential issues.
- Characteristics: Fully functional prototype, demonstration in relevant environment, and performance validation.
- Activities: Building and testing a fully functional prototype, demonstrating the technology in a relevant environment, and collecting performance data.
- Example: Researchers deploy the solar cell system in a real-world outdoor environment and monitor its performance over an extended period.
2.7. TRL 7: System Prototype Demonstrated in an Operational Environment
TRL 7 technology requires that the working model or prototype be demonstrated in a space environment. This level represents a major step towards the practical application of the technology. This often involves testing the prototype in a real-world operational environment to validate its performance and reliability.
- Characteristics: System prototype, demonstration in operational environment, and performance validation.
- Activities: Integrating the technology into a complete system, testing the system in an operational environment, and collecting performance data.
- Example: Researchers integrate the solar cell system into a microgrid and test its performance under real-world operating conditions.
2.8. TRL 8: System Complete and Qualified
TRL 8 technology has been tested and “flight qualified,” and it’s ready for implementation into an already existing technology or technology system. According to a study from the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory in April 2023, TRL 8 involves verifying that the technology meets all requirements and is ready for deployment.
- Characteristics: System complete, qualified for deployment, and verified performance.
- Activities: Conducting final testing and verification, preparing the technology for deployment, and documenting performance data.
- Example: The solar cell system has undergone extensive testing and verification and is ready for integration into a commercial microgrid.
2.9. TRL 9: Actual System Proven in Operational Environment
Once a technology has been “flight proven” during a successful mission, it can be called TRL 9. According to NASA’s Technology Readiness Level Guidebook in May 2023, TRL 9 represents the highest level of technology readiness, indicating that the technology has been successfully deployed and operated in its final form under real-world conditions.
- Characteristics: Actual system, proven performance, and operational deployment.
- Activities: Monitoring system performance, collecting operational data, and documenting lessons learned.
- Example: The solar cell system has been successfully operating in a commercial microgrid for an extended period, providing reliable and cost-effective power.
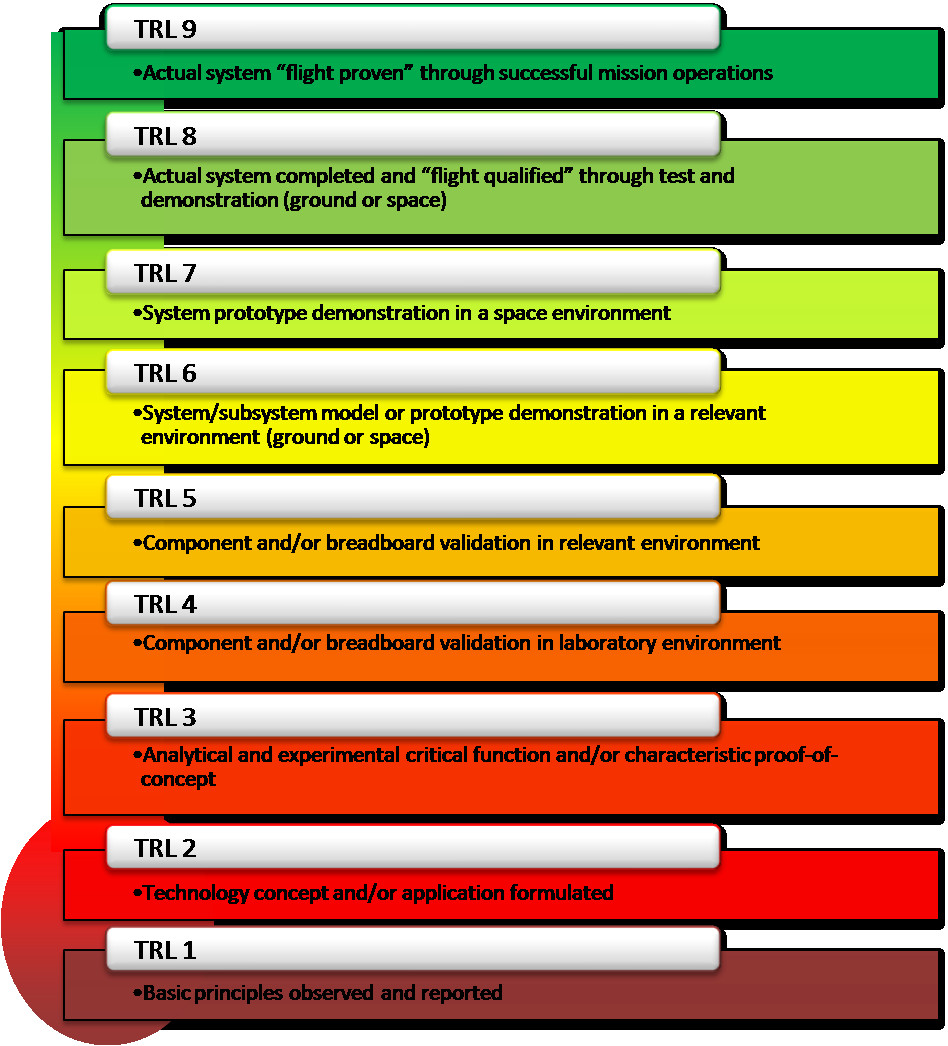 Technology Readiness Levels
Technology Readiness Levels
3. Practical Applications of Technology Readiness Level Definition
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition is not just a theoretical framework; it has numerous practical applications across various industries and sectors. Understanding these applications can help organizations leverage TRL to improve technology development and decision-making.
3.1. How is Technology Readiness Level Definition Used in Aerospace?
In the aerospace industry, Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition is used to assess the maturity of technologies for space missions and aircraft development. NASA, for example, uses TRL to manage the development of new technologies for its exploration programs. According to NASA’s Technology Readiness Level Guidebook in May 2023, TRL helps ensure that technologies are ready for deployment in space environments, reducing the risk of mission failures.
- Space Missions: Assessing the readiness of technologies for deployment in space.
- Aircraft Development: Managing the development of new technologies for aircraft.
- Risk Reduction: Ensuring technologies are ready to minimize mission failure risks.
3.2. What Role Does Technology Readiness Level Definition Play in Defense?
The defense sector relies on Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition to evaluate the maturity of technologies for military applications. The U.S. Department of Defense uses TRL to manage the development and acquisition of new weapons systems and defense technologies. A study from the U.S. Department of Defense in July 2023 indicates that TRL helps in making informed decisions about technology investments and ensuring that new systems are ready for deployment.
- Weapons Systems: Evaluating the maturity of technologies for military applications.
- Acquisition Management: Managing the development and acquisition of new defense technologies.
- Informed Decisions: Making decisions about technology investments.
3.3. How is Technology Readiness Level Definition Applied in Energy?
In the energy industry, Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition is used to assess the maturity of new energy technologies, such as solar power, wind energy, and energy storage systems. The U.S. Department of Energy uses TRL to manage the development of these technologies and promote their adoption. According to research from the U.S. Department of Energy in August 2023, TRL helps in identifying and addressing the challenges associated with deploying new energy technologies.
- Solar Power: Assessing the maturity of solar energy technologies.
- Wind Energy: Evaluating wind energy systems.
- Energy Storage: Managing the development of energy storage technologies.
3.4. What is the Impact of Technology Readiness Level Definition on Manufacturing?
The manufacturing sector uses Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition to evaluate the maturity of new manufacturing processes and technologies, such as additive manufacturing and robotics. The goal is to identify and implement technologies that can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. A report by the National Institute of Standards and Technology in September 2023 suggests that TRL helps in making informed decisions about technology investments and ensuring that new processes are ready for implementation.
- Additive Manufacturing: Evaluating the maturity of additive manufacturing technologies.
- Robotics: Assessing the readiness of robotics for manufacturing applications.
- Process Improvement: Identifying and implementing technologies to improve efficiency.
3.5. How is Technology Readiness Level Definition Utilized in Healthcare?
In the healthcare industry, Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition is used to assess the maturity of new medical devices and healthcare technologies. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) uses TRL to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of new medical products before they are approved for use. Research from the National Institutes of Health in October 2023 indicates that TRL helps in ensuring that new medical technologies are safe and effective for patients.
- Medical Devices: Evaluating the maturity of new medical devices.
- Healthcare Technologies: Assessing the readiness of healthcare technologies.
- Safety and Effectiveness: Ensuring new medical technologies are safe and effective.
4. Technology Readiness Level Definition: Challenges and Considerations
While Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition is a valuable tool, it is not without its challenges and limitations. Understanding these challenges and considering them when applying TRL can help ensure its effective use.
4.1. What Are the Limitations of Technology Readiness Level Definition?
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition has some limitations:
- Subjectivity: The assessment of TRL can be subjective and depend on the individual or organization conducting the assessment.
- Oversimplification: TRL provides a simplified view of technology maturity and may not capture the full complexity of technology development.
- Context Dependence: The relevance of TRL can depend on the specific technology and its application.
- Linearity Assumption: TRL assumes a linear progression from basic research to operational deployment, which may not always be the case.
4.2. How Can Subjectivity Be Minimized in Technology Readiness Level Definition Assessment?
To minimize subjectivity in Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition assessment:
- Use Clear Criteria: Establish clear and objective criteria for each TRL level.
- Involve Multiple Experts: Involve multiple experts in the assessment process to obtain diverse perspectives.
- Document Evidence: Document all evidence and data used to support the TRL assessment.
- Conduct Independent Reviews: Conduct independent reviews of TRL assessments to ensure accuracy and consistency.
4.3. What Is the Role of Context in Technology Readiness Level Definition Assessment?
Context plays a crucial role in Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition assessment. The TRL of a technology can depend on the specific application and environment in which it will be used. According to a report by the Government Accountability Office in June 2023, it is important to consider the context when assessing TRL to ensure that the technology is truly ready for its intended use.
- Application Specificity: The TRL of a technology should be assessed in the context of its intended application.
- Environmental Factors: Consider the environmental factors that may impact the technology’s performance.
- System Integration: Assess the technology’s readiness for integration with other systems.
4.4. How Does Technology Readiness Level Definition Relate to Technology Transfer?
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition is closely related to technology transfer, which is the process of moving technologies from research labs to commercial applications. TRL provides a framework for assessing the maturity of technologies and identifying the steps needed to transfer them to the market. According to the Association of University Technology Managers in July 2023, TRL helps in bridging the gap between research and commercialization.
- Maturity Assessment: TRL provides a way to assess the maturity of technologies for transfer.
- Roadmap Development: It helps in developing a roadmap for technology transfer.
- Stakeholder Communication: TRL facilitates communication among stakeholders involved in technology transfer.
4.5. What Are the Best Practices for Using Technology Readiness Level Definition?
To effectively use Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition, it is important to follow best practices:
- Understand the TRL Scale: Have a clear understanding of the TRL scale and the criteria for each level.
- Use Objective Criteria: Use objective criteria and data to support TRL assessments.
- Consider Context: Consider the specific application and environment when assessing TRL.
- Involve Experts: Involve experts from various disciplines in the TRL assessment process.
- Document Everything: Document all evidence and data used to support TRL assessments.
- Regularly Review: Regularly review and update TRL assessments as the technology evolves.
5. Case Studies: Technology Readiness Level Definition in Action
Examining real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into how Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition is applied in practice and the benefits it can offer.
5.1. NASA’s Use of Technology Readiness Level Definition for Space Exploration
NASA uses Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition extensively for its space exploration programs. For example, NASA used TRL to assess the readiness of the Orion spacecraft’s heat shield technology. The heat shield had to withstand extreme temperatures during re-entry into the Earth’s atmosphere. According to NASA’s Technology Readiness Level Guidebook in May 2023, the heat shield technology was rigorously tested and assessed at each TRL level to ensure its reliability and performance.
- Technology: Orion spacecraft’s heat shield.
- Application: Protecting the spacecraft during re-entry.
- Outcome: Successful deployment of the heat shield, ensuring the safety of the astronauts.
5.2. Department of Defense’s Application of Technology Readiness Level Definition to New Weapons Systems
The Department of Defense (DoD) uses Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition to manage the development of new weapons systems. For example, the DoD used TRL to assess the readiness of a new laser weapon system. The laser weapon system had to meet stringent performance requirements and operate in harsh environments. A study from the U.S. Department of Defense in July 2023 indicates that the TRL assessment helped in identifying and addressing technical challenges early in the development process.
- Technology: New laser weapon system.
- Application: Military defense and offense.
- Outcome: Successful development and deployment of the laser weapon system.
5.3. How Technology Readiness Level Definition Aided the Development of Renewable Energy Technologies
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition has played a crucial role in the development of renewable energy technologies. For example, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) used TRL to assess the readiness of a new solar power technology. The solar power technology had to be cost-effective and efficient to compete with traditional energy sources. According to research from the U.S. Department of Energy in August 2023, the TRL assessment helped in identifying and addressing the technical and economic challenges associated with deploying the technology.
- Technology: New solar power technology.
- Application: Renewable energy generation.
- Outcome: Successful development and deployment of the solar power technology.
5.4. Medical Device Innovation and Technology Readiness Level Definition
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition has been instrumental in driving innovation in the medical device industry. For example, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) used TRL to assess the readiness of a new medical device for treating heart disease. The medical device had to be safe and effective to be approved for use in patients. Research from the National Institutes of Health in October 2023 indicates that the TRL assessment helped in ensuring that the device met all safety and performance requirements.
- Technology: New medical device for treating heart disease.
- Application: Healthcare and medical treatment.
- Outcome: Successful approval and use of the medical device in patients.
5.5. Manufacturing Advancements Through Technology Readiness Level Definition
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition has facilitated advancements in the manufacturing sector. For example, a manufacturing company used TRL to assess the readiness of a new additive manufacturing technology. The additive manufacturing technology had to improve efficiency and reduce costs. A report by the National Institute of Standards and Technology in September 2023 suggests that the TRL assessment helped in identifying and implementing the technology, leading to significant improvements in manufacturing processes.
- Technology: New additive manufacturing technology.
- Application: Improving manufacturing processes.
- Outcome: Enhanced efficiency and reduced costs in manufacturing.
6. Future Trends in Technology Readiness Level Definition
As technology continues to evolve, so will the application and interpretation of Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition. Several future trends are expected to shape the use of TRL in the coming years.
6.1. How Will Artificial Intelligence Impact Technology Readiness Level Definition?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to have a significant impact on Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition. AI can be used to automate the TRL assessment process, making it more efficient and objective. AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of data to identify patterns and trends that may not be apparent to human assessors. According to a study from Stanford University’s AI Lab in November 2023, AI can improve the accuracy and consistency of TRL assessments.
- Automation: AI can automate the TRL assessment process.
- Data Analysis: AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of data.
- Accuracy Improvement: AI can improve the accuracy of TRL assessments.
6.2. What Role Will Big Data Play in Technology Readiness Level Definition?
Big data will play a crucial role in Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition by providing more comprehensive and objective data for assessing technology maturity. Big data analytics can be used to analyze data from various sources, such as research papers, patents, and market reports, to assess the TRL of a technology. According to research from MIT’s Center for Digital Business in December 2023, big data can provide a more complete picture of technology maturity.
- Comprehensive Data: Big data provides more comprehensive data for TRL assessment.
- Objective Assessment: Big data analytics can provide a more objective assessment of technology maturity.
- Trend Identification: Big data can help in identifying trends and patterns in technology development.
6.3. How Will Technology Readiness Level Definition Adapt to Emerging Technologies?
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition will need to adapt to emerging technologies such as nanotechnology, biotechnology, and quantum computing. These technologies have unique characteristics and challenges that may not be adequately addressed by the current TRL framework. According to a report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine in January 2024, the TRL framework will need to be updated to reflect the specific challenges and opportunities associated with these technologies.
- Nanotechnology: Adapting TRL to address the unique challenges of nanotechnology.
- Biotechnology: Modifying TRL to reflect the complexities of biotechnology development.
- Quantum Computing: Updating TRL to account for the rapid advancements in quantum computing.
6.4. What Are the Implications of Technology Readiness Level Definition for Sustainable Development?
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition has important implications for sustainable development. By assessing the maturity of sustainable technologies, such as renewable energy and energy efficiency technologies, TRL can help in promoting their adoption and deployment. According to the United Nations Environment Programme in February 2024, TRL can play a crucial role in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Renewable Energy: Promoting the adoption of renewable energy technologies.
- Energy Efficiency: Assessing the maturity of energy efficiency technologies.
- Sustainable Development Goals: Contributing to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals.
6.5. How Can Technology Readiness Level Definition Be Integrated with Other Assessment Frameworks?
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition can be integrated with other assessment frameworks, such as the Manufacturing Readiness Level (MRL) and the System Readiness Level (SRL), to provide a more comprehensive assessment of technology maturity. Integrating these frameworks can help in identifying and addressing the challenges associated with transitioning technologies from research to commercialization. According to the Aerospace Industries Association in March 2024, integrating TRL with other frameworks can improve the effectiveness of technology development efforts.
- Manufacturing Readiness Level (MRL): Integrating TRL with MRL to assess manufacturing readiness.
- System Readiness Level (SRL): Combining TRL with SRL to evaluate system-level readiness.
- Comprehensive Assessment: Providing a more comprehensive assessment of technology maturity.
7. Optimizing Your Technology Development with Technology Readiness Level Definition at pioneer-technology.com
At pioneer-technology.com, we understand the importance of staying ahead in the fast-paced world of technology. That’s why we offer in-depth analysis and insights into emerging technologies, helping you navigate the complexities of technology development and make informed decisions.
7.1. Pioneer-technology.com’s Role in Understanding Technology Readiness Level Definition
Pioneer-technology.com is your go-to resource for understanding Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition. We provide clear, concise explanations of the TRL scale and its applications across various industries. Our articles, case studies, and expert analysis help you grasp the nuances of TRL and its impact on technology development.
- Clear Explanations: We offer clear explanations of the TRL scale.
- Case Studies: Our case studies illustrate how TRL is applied in practice.
- Expert Analysis: We provide expert analysis of the impact of TRL on technology development.
7.2. Expert Insights on Utilizing Technology Readiness Level Definition Effectively
Our team of technology experts at pioneer-technology.com offers valuable insights on how to utilize Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition effectively. We provide guidance on conducting TRL assessments, minimizing subjectivity, and integrating TRL with other assessment frameworks. Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge and tools you need to optimize your technology development efforts.
- TRL Assessment Guidance: We provide guidance on conducting TRL assessments.
- Subjectivity Minimization: Our insights help in minimizing subjectivity in TRL assessments.
- Integration Strategies: We offer strategies for integrating TRL with other frameworks.
7.3. Real-World Examples and Technology Readiness Level Definition Success Stories Featured on Pioneer-technology.com
Pioneer-technology.com features real-world examples and success stories that demonstrate the power of Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition. From NASA’s use of TRL for space exploration to the Department of Defense’s application of TRL to new weapons systems, our case studies showcase the diverse applications and benefits of TRL. These examples provide valuable lessons and inspiration for your own technology development endeavors.
- NASA Case Studies: Examples of NASA’s use of TRL for space exploration.
- DoD Case Studies: Applications of TRL to new weapons systems by the Department of Defense.
- Diverse Applications: Showcasing the diverse applications and benefits of TRL.
7.4. How Pioneer-technology.com Keeps You Updated on the Latest in Technology Readiness Level Definition
At pioneer-technology.com, we are committed to keeping you updated on the latest developments in Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition. We regularly publish articles, reports, and analysis on emerging trends, best practices, and innovative applications of TRL. Our goal is to provide you with the most current and relevant information to help you stay ahead in the world of technology.
- Regular Updates: We regularly publish articles and reports on TRL.
- Emerging Trends: We cover emerging trends in TRL application.
- Best Practices: We provide insights on best practices for using TRL.
7.5. Unlock the Full Potential of Your Technology with Pioneer-technology.com’s Technology Readiness Level Definition Resources
Unlock the full potential of your technology with pioneer-technology.com’s comprehensive Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition resources. Whether you are a researcher, developer, investor, or policymaker, our resources can help you understand, assess, and optimize your technology development efforts. Visit pioneer-technology.com today to explore our resources and take your technology to the next level.
- Comprehensive Resources: We offer comprehensive resources on TRL.
- Targeted Support: Our resources support researchers, developers, and investors.
- Technology Optimization: We help you optimize your technology development efforts.
Want to explore the innovative edge of technology? At pioneer-technology.com, we break down the complexities, offering you clear insights and expert analysis on the latest tech trends. From AI to renewable energy, we’ve got you covered. Facing challenges in keeping up with rapid technological advancements? Ready to discover how new technologies can transform your business or research? Visit pioneer-technology.com today and dive into a world of pioneering technologies. Explore our articles, case studies, and resources, and contact us for personalized guidance to help you stay ahead. Don’t get left behind—innovate with us now. Our address is 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States, and you can reach us at +1 (650) 723-2300.
8. Frequently Asked Questions About Technology Readiness Level Definition
Here are some frequently asked questions about Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition:
8.1. What is the Difference Between Technology Readiness Level Definition and Manufacturing Readiness Level (MRL)?
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition assesses the maturity of a technology, while Manufacturing Readiness Level (MRL) assesses the maturity of manufacturing processes. TRL focuses on the technology itself, while MRL focuses on the ability to manufacture the technology at scale.
8.2. How Long Does It Take to Advance a Technology from One Technology Readiness Level Definition to the Next?
The time it takes to advance a technology from one Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition to the next can vary widely depending on the technology, the resources available, and the complexity of the development process. Some technologies may advance quickly, while others may take years to progress.
8.3. Can a Technology Skip Technology Readiness Level Definition?
In some cases, a technology may skip Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition, especially if it is based on existing technologies or if there is a strong understanding of the underlying principles. However, it is generally recommended to follow the TRL scale to ensure that all aspects of the technology are properly assessed.
8.4. What Resources Are Available to Help Assess Technology Readiness Level Definition?
There are many resources available to help assess Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition, including:
- NASA’s Technology Readiness Level Guidebook
- U.S. Department of Defense’s Technology Readiness Assessment Guidance
- European Space Agency’s Technology Readiness Level Handbook
- Industry-specific TRL guidelines and standards
8.5. How Is Technology Readiness Level Definition Used in Government Contracts?
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition is often used in government contracts to assess the maturity of technologies being proposed for development or acquisition. Government agencies may require contractors to provide TRL assessments as part of their proposals.
8.6. Is Technology Readiness Level Definition Only for Technology Projects?
While Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition is primarily used for technology projects, it can also be applied to other types of projects, such as software development or process improvement.
8.7. What Happens After Reaching Technology Readiness Level Definition 9?
After reaching Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition 9, the technology is considered fully proven and ready for widespread deployment. At this point, the focus shifts to scaling up production, reducing costs, and improving performance.
8.8. How Can Technology Readiness Level Definition Help Secure Funding?
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition can help secure funding by providing a clear and objective assessment of the technology’s maturity. Investors and funding agencies often use TRL to evaluate the potential of a technology and assess the risk associated with investing in it.
8.9. What Is the Importance of Technology Readiness Level Definition in Research and Development?
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition is essential in research and development because it provides a framework for tracking progress, identifying challenges, and making informed decisions. It helps in ensuring that research and development efforts are aligned with the goals of the organization.
8.10. How Often Should Technology Readiness Level Definition Be Assessed?
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) definition should be assessed regularly throughout the technology development process, especially at key milestones. The frequency of assessment can depend on the complexity of the technology and the pace of development.
