Cloud technology is revolutionizing how businesses operate and individuals interact with data. Are you ready to dive in and discover the power of cloud technology? This comprehensive guide, brought to you by pioneer-technology.com, breaks down everything you need to know, from its core principles to its transformative applications. Explore the digital frontier and unlock the potential of cloud computing, cloud services, and cloud solutions to stay ahead in the tech landscape.
Table of Contents
1. What Is Cloud Technology?
2. Types of Cloud Computing
3. Key Benefits and Challenges for Enterprises
4. Top 10 Cloud Computing Trends
5. FAQ
1. What Is Cloud Technology?
Cloud technology fundamentally means using hosted services over the internet, rather than relying on physical hardware or devices. Instead of storing files on a local hard drive, cloud technology allows you to save them on remote servers, accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. According to research from Stanford University’s Department of Computer Science, the adoption of cloud computing is expected to grow by 20% annually through 2027, driven by its ability to enhance collaboration and reduce operational costs.
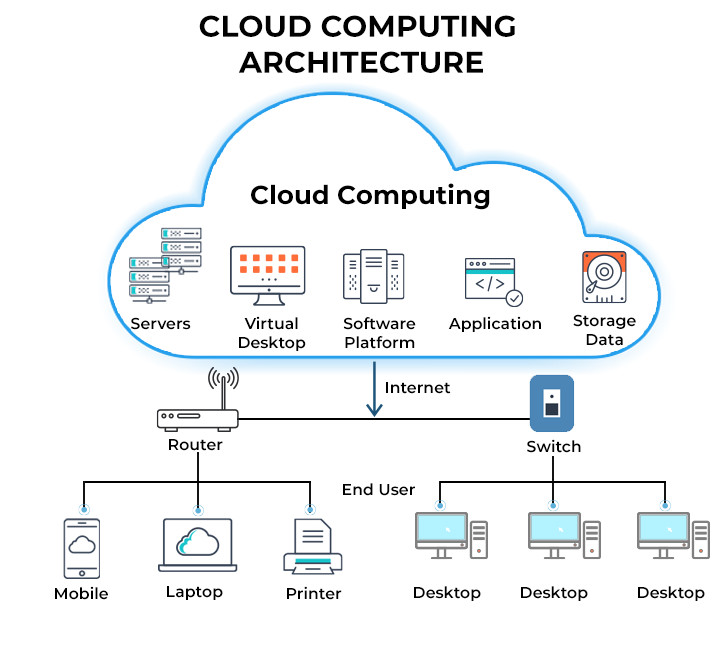 Cloud Computing Architecture
Cloud Computing Architecture
These services include everything from data storage and servers to databases, networking, and software. This means you can access and use these resources on-demand, without the need for direct management. This on-demand availability is a hallmark of cloud computing. These services are generally divided into three main categories: Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). Depending on the deployment model, cloud technology can also be classified as public, private, or hybrid.
Let’s break down the components further:
- Front-End Layer: This is the user interface that allows you to interact with the data stored in the cloud. It’s the software you use to access your files and applications.
- Back-End Layer: This layer comprises the hardware and software that form the core of the cloud infrastructure. It includes computers, servers, central servers, and databases responsible for securely storing your data.
- Middleware: To ensure smooth connectivity between devices linked via cloud computing, central servers use a software called middleware that acts as a bridge between the database and applications.
This architecture enables businesses to leverage scalable and flexible IT resources without the upfront costs and ongoing maintenance typically associated with traditional infrastructure.
2. Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing can be categorized based on the deployment model (public, private, hybrid) or the type of service it offers (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS). Each type offers distinct advantages and use cases, allowing organizations to tailor their cloud strategy to meet specific needs.
 Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing
2.1. What is a Private Cloud?
A private cloud offers computing services over a private IT network, exclusively for a single organization. Think of it as your own personal cloud, managed and maintained within your own infrastructure. According to a 2024 study by Gartner, organizations using private clouds reported a 20% improvement in data security compared to those relying solely on public cloud solutions.
Benefits of a Private Cloud:
- Enhanced Security: Internal firewalls and hosting ensure sensitive data remains protected from third-party access.
- Greater Control: Organizations have complete control over the infrastructure and data.
- Customization: Private clouds can be tailored to meet specific business requirements.
Drawbacks of a Private Cloud:
- Resource-Intensive: The organization is responsible for managing and maintaining the data centers.
- Higher Costs: Setting up and maintaining a private cloud can be expensive.
2.2. What is a Public Cloud?
A public cloud provides computing services over the internet by third-party providers, available to anyone who wants to use or purchase them. These services can be free or sold on-demand, where users pay only for the CPU cycles, storage, or bandwidth they consume. A recent report by Forrester indicates that public cloud adoption is accelerating, with a projected market size of $623.3 billion in 2023.
Benefits of a Public Cloud:
- Cost Savings: Businesses save on purchasing, managing, and maintaining on-premises infrastructure.
- Scalability: Offers scalable RAM and flexible bandwidth, making it easy to scale storage needs.
- Accessibility: Services are available to anyone with an internet connection.
Drawbacks of a Public Cloud:
- Security Concerns: Data is stored on third-party servers, raising potential security risks.
- Less Control: Organizations have less control over the infrastructure.
2.3. What is a Hybrid Cloud?
A hybrid cloud combines features of both public and private clouds, allowing workloads to shift between them as computing and cost requirements change. This model offers the flexibility to scale up to the public cloud during high demand while keeping sensitive data secure in a private cloud. According to a survey by Flexera, 87% of enterprises have adopted a hybrid cloud strategy as of 2023.
Benefits of a Hybrid Cloud:
- Flexibility: Allows businesses to scale their infrastructure up to the public cloud while keeping sensitive data in a private cloud.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Companies pay only for the resources they use temporarily.
- Enhanced Security: Offers the benefits of a public cloud without its security risks.
Drawbacks of a Hybrid Cloud:
- Complexity: Managing a hybrid cloud environment can be complex.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating public and private cloud infrastructure can be challenging.
2.4. What is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)?
IaaS is a cloud computing model where a service provider offers servers, storage, and networking over a virtual interface. The user doesn’t need to manage the cloud infrastructure but has control over the storage, operating systems, and deployed applications. According to research from the University of California, Berkeley, IaaS solutions can reduce IT infrastructure costs by up to 40% compared to traditional on-premises setups.
Benefits of IaaS:
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need for expensive hardware and maintenance.
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Control: Users have control over the operating systems and applications.
Drawbacks of IaaS:
- Security Concerns: Users are responsible for securing their applications and data.
- Technical Expertise: Requires technical expertise to manage and maintain the infrastructure.
2.5. What is Platform as a Service (PaaS)?
PaaS provides a development and deployment environment in the cloud, allowing users to develop and run applications without the complexity of building or maintaining the infrastructure. It offers resources to develop cloud-based applications, with users purchasing resources from a vendor on a pay-as-you-go basis and accessing them over a secure connection. A recent study by MarketsandMarkets projects the PaaS market to reach $71.62 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for agile application development.
Benefits of PaaS:
- Simplified Development: Simplifies the development process by providing a pre-configured environment.
- Scalability: Easily scale resources based on application needs.
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need for expensive hardware and software licenses.
Drawbacks of PaaS:
- Vendor Lock-In: Can lead to vendor lock-in, making it difficult to switch providers.
- Limited Control: Users have limited control over the underlying infrastructure.
2.6. What is Software as a Service (SaaS)?
SaaS allows users to access a vendor’s software on the cloud on a subscription basis. Users don’t need to install or download applications on their local devices; instead, the applications are located on a remote cloud network that can be directly accessed through the web or an API. The SaaS model sees the service provider manage all the hardware, middleware, application software, and security. According to a report by Statista, SaaS is the largest segment of the cloud market, with a projected revenue of $157 billion in 2020.
Benefits of SaaS:
- Accessibility: Access software from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Cost Savings: Reduces the need for expensive software licenses and maintenance.
- Automatic Updates: Software is automatically updated by the provider.
Drawbacks of SaaS:
- Limited Customization: Limited customization options compared to on-premises software.
- Security Concerns: Data is stored on third-party servers, raising potential security risks.
3. Key Benefits and Challenges for Enterprises
Cloud technology is rapidly growing due to the numerous benefits it offers. It saves businesses the time and resources required to set up full-fledged physical IT infrastructure.
Benefits of Cloud Technology:
- Reduced Costs: Cloud helps reduce the capital required to maintain IT systems. Businesses avoid the need to purchase expensive infrastructure, substantially reducing their expenditure by using resources provided by the cloud provider. Cloud providers work on the pay-as-you-go model, which means businesses only pay for the services they use.
- Scalability: Cloud allows organizations to grow their user base from a few to thousands in a short time. A business can scale their storage needs up or down depending on the need, allowing organizations to be flexible.
- Flexibility and Collaboration: Since data on the cloud can be accessed directly via the internet, employees can work from anywhere. Cloud gives you the freedom to set up your virtual office anywhere. It also allows teams to work on a project across locations by giving them access to the same files as third-party vendors.
- Business Continuity: Cloud safely stores and protects your data in the event of an outage or crisis, making it easier to resume work once systems are up and running again.
- Competitive Edge: Cloud takes care of various business aspects, such as maintaining the IT infrastructure, licensing software, or training personnel to manage your data, giving you an edge over your competitors since the time and resources you invest are minimal.
 Team Collaboration
Team Collaboration
Challenges of Cloud Technology:
- Security Concerns: Despite assurances from cloud service providers, there’s always a risk while storing your data on the cloud.
- Downtime: Outages are a common challenge. Cloud service providers may get overwhelmed, leading to technical outages that may temporarily interrupt your applications.
- Internet Connection Dependency: A user may not be able to access data on the cloud without a good internet connection and a compatible device. Using public Wi-Fi to access your files could pose a threat if the right security measures are not taken.
- Financial Commitment: Cloud providers use a pay-as-you-go pricing model, but businesses need to give a monthly or annual financial commitment for most subscription plans, which needs to be factored into their operating costs.
- Limited Access: A user may have minimal control since the cloud service provider owns and manages the infrastructure. The user would only be able to manage applications and not the backend infrastructure.
Navigating these challenges requires a strategic approach, including robust security measures, reliable internet connectivity, and careful budget planning.
4. Top 10 Cloud Computing Trends
The cloud computing market is mature and steadily growing. Valued at $321 billion in 2019, it is expected to reach $1025.9 billion in seven years. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of cloud computing, fueling new trends, focus areas, and opportunities.
4.1. Increased Spending on Public Clouds
The public cloud has the fewest barriers to entry and is the most accessible for small businesses, startups, and independent professionals. This segment is slated to grow by 18.4% in 2021, reaching a valuation of $304.9 billion.
4.2. Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies
Companies will invest in multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, along with cloud-agnostic platforms, to ensure greater IT resiliency, alleviating downtime worries.
4.3. Growing Popularity of Container Technology
Containers offer an independent virtual environment to develop and run applications, regardless of the parent hosting environment, allowing companies to set up tiny, segregated clouds within their infrastructure to improve their development capabilities.
4.4. Mainstream Adoption of Virtual Desktops
Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) lets you stream the desktop image remotely without coupling the desktop with the physical client device, seeing wider adoption even for non-technology use cases.
4.5. Cloud-Native and Edge-First Security Technologies
Security technologies will evolve to become cloud-native and edge-first, covering the entire IT landscape across clouds, data centers, SaaS, and edge devices.
4.6. Communication and Collaboration as Key Use Cases
Communication and collaboration will be important cloud use cases, including collaborative coding, document management, and business intelligence collaboration.
4.7. Serverless Computing Beyond the Tech Industry
Serverless architecture enables a type of enterprise IT design where code is modular and isolated, growing in adoption with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.7% globally.
4.8. Challenges in Keeping Cloud Budgets in Check
Organizations waste around 30% of their total cloud spends, making dedicated cloud cost optimization technologies essential.
4.9. Cloud Powering Widespread AI Adoption
Cloud computing and the availability of cloud-hosted AI libraries, modeling engines, and algorithms will be crucial to AI adoption.
4.10. Azure Catching Up to AWS
Microsoft Azure has grown at an accelerated pace, and the gap between it and Amazon Web Services (AWS) is shrinking.
By staying informed about these trends, businesses can make strategic decisions and leverage cloud technology to drive innovation and growth. For more in-depth analysis and the latest updates, visit pioneer-technology.com.
5. FAQ
5.1. What does cloud technology mean?
Cloud technology refers to using hosted services over the internet, such as data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software, instead of relying on physical hardware or devices.
5.2. What are the main types of cloud technology?
The main types of cloud technology include Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), as well as public, private, and hybrid cloud deployment models.
5.3. What are the benefits of using cloud technology?
Cloud technology offers benefits such as reduced costs, scalability, flexibility, enhanced collaboration, business continuity, and a competitive edge.
5.4. What are the challenges of adopting cloud technology?
Challenges include security concerns, downtime, dependency on internet connectivity, financial commitments, and limited access to the underlying infrastructure.
5.5. How does cloud technology improve collaboration?
Cloud technology enables teams to work on projects across locations by providing access to the same files and applications, facilitating seamless collaboration.
5.6. What is the difference between public and private clouds?
Public clouds are offered by third-party providers over the internet and are available to anyone, while private clouds are used exclusively by a single organization over a private IT network.
5.7. What is hybrid cloud and why is it beneficial?
Hybrid cloud combines features of both public and private clouds, allowing workloads to shift between them as computing and cost requirements change. It offers flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
5.8. How can businesses keep cloud budgets in check?
Businesses can keep cloud budgets in check by optimizing cloud costs, using dedicated cloud cost optimization technologies, and carefully planning their resource allocation.
5.9. What role does cloud technology play in AI adoption?
Cloud computing provides the infrastructure and resources needed for AI, including cloud-hosted AI libraries, modeling engines, and algorithms, making AI more accessible to businesses.
5.10. How can I stay updated on the latest cloud technology trends?
To stay updated on the latest cloud technology trends, you can follow industry news, attend webinars, and visit pioneer-technology.com for in-depth analysis and updates.
Ready to explore the boundless possibilities of cloud technology?
Visit pioneer-technology.com today to discover the latest articles, in-depth analyses, and cutting-edge trends in the world of pioneering technologies. Stay ahead of the curve and unlock the full potential of cloud technology with our expert insights.
For more information, contact us at:
Address: 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States
Phone: +1 (650) 723-2300
Website: pioneer-technology.com
