Augmented reality (AR) technology integrates digital information with our real-world environment, offering immersive and interactive experiences. Pioneer-technology.com helps you navigate this exciting field by providing clear explanations, real-world applications, and insights into the future of AR. Discover how AR enhances perception, transforms industries, and opens new possibilities by diving into mixed reality applications and spatial computing innovations.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Augmented Reality (AR) Technology
- How Does Augmented Reality (AR) Work?
- What Are the Key Components of AR Systems?
- AR vs. VR: What Are the Key Differences?
- What are the Types of Augmented Reality?
- What Are the Practical Applications of AR Technology?
- What Are Some Real-World Examples of Augmented Reality?
- Who Are the Major Players in the AR Technology Market?
- What Are the Challenges and Limitations of AR Technology?
- What is the Future of AR Technology?
- FAQ about Augmented Reality (AR)
1. Understanding Augmented Reality (AR) Technology
Augmented Reality (AR) technology enhances our perception of the real world by overlaying computer-generated images, sounds, and other sensory information onto it. AR blends digital and physical worlds, creating interactive and immersive experiences. Instead of creating a completely virtual environment like Virtual Reality (VR), AR supplements the existing environment with digital elements.
What is the Definition of Augmented Reality (AR)?
AR is defined as an interactive experience that combines a real-world environment with computer-generated perceptual information. It enhances the user’s current perception of reality by adding layers of digital content. Unlike VR, which creates an entirely artificial environment, AR allows users to interact with virtual elements in their real surroundings. This integration can be achieved through various devices, including smartphones, tablets, AR glasses, and head-mounted displays.
What Are the Key Features of Augmented Reality?
- Real-World Integration: AR blends digital content with the real world, allowing users to interact with virtual elements in their physical surroundings.
- Interactivity: AR systems often allow users to interact with the overlaid digital content in real-time, enhancing the user experience.
- Sensory Enhancement: AR can enhance various senses, including sight, sound, and even touch, through the use of haptic feedback.
- Accessibility: AR is increasingly accessible through devices like smartphones and tablets, making it available to a broad audience.
What Are the Benefits of Augmented Reality?
- Enhanced User Experience: AR provides more engaging and informative experiences by overlaying digital content onto the real world.
- Improved Decision Making: AR can assist in decision-making processes by providing additional information and visualizations in real-time.
- Increased Efficiency: AR applications can streamline tasks in various industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and education.
- Innovative Marketing: AR offers new and creative ways for businesses to engage with customers and promote their products and services.
2. How Does Augmented Reality (AR) Work?
AR technology works by using a combination of hardware and software components to overlay digital content onto the real world. This process involves capturing the real-world environment, processing the data, and rendering the augmented view to the user.
What Are the Basic Steps Involved in AR Technology?
- Environment Capture: The AR system uses cameras and sensors to capture the real-world environment.
- Data Processing: The captured data is processed to identify and track objects, recognize surfaces, and understand the spatial relationships within the environment.
- Digital Content Overlay: Computer-generated images, sounds, or other sensory information are overlaid onto the real-world view.
- Rendering and Display: The augmented view is rendered and displayed to the user through a device like a smartphone, tablet, or AR glasses.
What Are the Core Technologies Behind AR Systems?
- Computer Vision: Enables the AR system to “see” and understand the real-world environment through image and video analysis.
- Sensor Technology: Provides data about the user’s location, orientation, and movement, which is crucial for accurate augmentation.
- Display Technology: Renders the augmented view to the user, using devices like smartphones, tablets, AR glasses, and head-mounted displays.
- Software Algorithms: Process the data captured by the sensors and cameras to create a seamless integration of digital and physical elements.
How Does AR Software Work?
AR software uses algorithms to recognize and track real-world objects and surfaces. There are two main approaches:
- Marker-Based AR: Relies on specific markers (e.g., QR codes) to trigger the overlay of digital content. The software recognizes the marker and displays the associated augmented information.
- Markerless AR: Uses advanced computer vision algorithms to identify and track objects and surfaces in the real world without the need for specific markers. This approach is more flexible and allows for more seamless integration of digital and physical elements.
3. What Are the Key Components of AR Systems?
AR systems consist of several key components that work together to create augmented experiences. These components include hardware, software, and input/output devices.
What Hardware is Required for AR?
- Processors: Handle the computational tasks required for processing sensor data and rendering augmented content.
- Sensors: Capture data about the user’s environment, including cameras, accelerometers, gyroscopes, and GPS.
- Displays: Present the augmented view to the user, using devices like smartphone screens, tablets, AR glasses, and head-mounted displays.
What Software is Essential for AR?
- AR Development Platforms: Provide tools and frameworks for creating AR applications, such as ARKit (Apple), ARCore (Google), and Vuforia.
- Computer Vision Libraries: Enable the AR system to analyze and understand images and videos from the real world.
- Rendering Engines: Generate the digital content that is overlaid onto the real-world view, such as Unity and Unreal Engine.
What Input/Output Devices Are Used in AR?
- Cameras: Capture the real-world environment and provide visual data for the AR system.
- Microphones: Capture audio data for sound augmentation and voice interaction.
- Touchscreens: Allow users to interact with the augmented content through touch gestures.
- AR Glasses and Headsets: Display the augmented view and provide a hands-free AR experience.
 Components of an Augmented Reality System
Components of an Augmented Reality System
How Do These Components Work Together?
These components work together seamlessly to deliver AR experiences. The sensors capture data about the environment, which is processed by the processor and analyzed by the computer vision libraries. The rendering engine generates the digital content, which is then displayed to the user through the display device. Input devices allow users to interact with the augmented content, providing a feedback loop that enhances the overall AR experience.
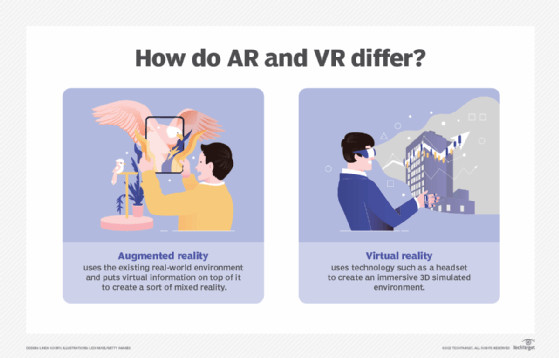
4. AR vs. VR: What Are the Key Differences?
AR and VR are both immersive technologies that enhance user experiences, but they differ significantly in their approach and application.
What is Virtual Reality (VR)?
VR creates a completely artificial environment that immerses the user in a simulated world. Users typically wear a headset that blocks out the real world and replaces it with a virtual one.
How Does AR Differ From VR?
| Feature | Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their surroundings. | Creates a completely virtual environment that immerses the user in a simulated world. |
| User Experience | Integrates virtual elements into the real world, allowing users to interact with digital content in their physical surroundings. | Completely immerses the user in a virtual world, blocking out the real world and providing a fully simulated experience. |
| Devices | Typically uses devices like smartphones, tablets, AR glasses, and head-mounted displays to overlay digital content onto the real world. | Requires a VR headset that blocks out the real world and displays a virtual environment. |
| Applications | Useful for tasks like navigation, retail, education, and training, where users need to interact with digital content in their real-world environment. | Commonly used for gaming, entertainment, training simulations, and virtual tours, where users benefit from a fully immersive and simulated experience. |
| Interaction | Allows users to interact with virtual elements in their real-world environment, enhancing their perception and providing additional information. | Enables users to interact with the virtual environment through controllers, gestures, and voice commands, providing a sense of presence and immersion. |
| Accessibility | Increasingly accessible through devices like smartphones and tablets, making it available to a broad audience. | Requires specialized VR headsets and equipment, which can be more expensive and less accessible. |
| Focus | Augments reality by adding digital elements, enhancing the user’s perception of their surroundings. | Replaces reality with a virtual environment, providing a fully immersive and simulated experience. |
What is Mixed Reality (MR)?
Mixed Reality (MR) is often considered a hybrid of AR and VR. It combines elements of both technologies to create experiences where real-world and virtual objects can interact. In MR, virtual objects are not just overlaid onto the real world but can also respond to and interact with it, creating a more seamless and immersive experience. Devices like the Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest 3 utilize passthrough technology to blend the real and virtual worlds, allowing users to interact with digital elements in a natural and intuitive way.
5. What are the Types of Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality (AR) comes in various forms, each employing different methods to integrate digital content with the real world. Understanding these types can help in recognizing their specific applications and benefits.
Marker-Based AR
Marker-based AR, also known as recognition-based AR, uses specific visual markers, such as QR codes or unique images, to trigger the overlay of digital content. When the AR application detects the marker through the device’s camera, it overlays the associated digital information onto the marker.
- How it works: The AR software recognizes a specific marker and displays the pre-defined augmented content.
- Advantages: Simple to implement and relatively accurate.
- Disadvantages: Requires the presence of a marker, which can limit the user experience.
- Use Cases: Interactive print media, educational tools, and product packaging.
Markerless AR
Markerless AR, also known as location-based or position-based AR, does not require specific markers. Instead, it uses the device’s sensors (GPS, accelerometer, gyroscope) to determine the user’s location and orientation, and then overlays digital content onto the real world.
- How it works: The AR software uses sensor data to recognize objects and surfaces in the real world and overlay digital content accordingly.
- Advantages: More flexible and seamless, as it does not require markers.
- Disadvantages: Can be less accurate and more computationally intensive.
- Use Cases: Navigation apps, mobile games, and retail applications.
Projection-Based AR
Projection-based AR projects digital images onto physical surfaces. The user interacts with these projected images, creating an augmented experience.
- How it works: A projector displays digital images onto real-world surfaces, and sensors track the user’s interactions with these images.
- Advantages: Allows for interactive and engaging experiences without the need for a display device.
- Disadvantages: Requires controlled lighting conditions and specialized equipment.
- Use Cases: Interactive advertising, entertainment, and industrial applications.
Overlay AR
Overlay AR replaces the entire view of an object with an augmented view. This type of AR is commonly used in medical and industrial applications.
- How it works: The AR system replaces the real-world view of an object with a digital representation, providing additional information and insights.
- Advantages: Provides detailed information and insights that are not visible in the real world.
- Disadvantages: Can be disorienting and require specialized equipment.
- Use Cases: Medical imaging, industrial maintenance, and training simulations.
6. What Are the Practical Applications of AR Technology?
AR technology has a wide range of practical applications across various industries, transforming how we interact with the world around us.
Retail and E-commerce
AR enhances the shopping experience by allowing customers to visualize products in their own environment before making a purchase.
- Virtual Try-On: Customers can use AR apps to virtually try on clothing, accessories, and makeup, ensuring a better fit and reducing returns.
- Home Visualization: AR apps allow customers to visualize furniture and decor in their homes, helping them make informed purchasing decisions.
- Interactive Catalogs: AR-enabled catalogs bring products to life with interactive 3D models and animations.
Healthcare
AR is revolutionizing healthcare by providing medical professionals with real-time information and enhancing training and patient care.
- Surgical Assistance: AR overlays patient data onto the surgeon’s view, providing real-time guidance and improving surgical precision.
- Medical Training: AR simulations provide realistic and interactive training environments for medical students and professionals.
- Patient Education: AR apps help patients understand their conditions and treatment options through visual aids and interactive models.
Education
AR enhances learning by making educational content more engaging and interactive.
- Interactive Textbooks: AR-enabled textbooks bring lessons to life with 3D models, animations, and interactive exercises.
- Virtual Field Trips: AR apps allow students to explore historical sites, museums, and natural environments from the classroom.
- Hands-On Learning: AR simulations provide hands-on learning experiences that enhance understanding and retention.
Manufacturing and Industrial
AR improves efficiency and safety in manufacturing and industrial environments by providing workers with real-time information and guidance.
- Assembly and Maintenance: AR apps provide step-by-step instructions and visual aids for assembly, maintenance, and repair tasks.
- Remote Assistance: AR enables remote experts to provide guidance and support to on-site workers through live video and augmented annotations.
- Quality Control: AR systems can overlay inspection data onto the product, allowing workers to quickly identify and address quality issues.
Gaming and Entertainment
AR enhances gaming and entertainment experiences by blending virtual elements with the real world.
- AR Games: Mobile AR games like Pokémon Go bring virtual creatures into the real world, creating immersive and engaging experiences.
- Interactive Storytelling: AR apps bring stories to life with interactive characters and environments that blend with the user’s surroundings.
- Live Events: AR enhances live events with augmented visuals, interactive content, and personalized experiences.
7. What Are Some Real-World Examples of Augmented Reality?
AR technology is already being used in many innovative and impactful ways across various industries.
Pokémon Go
Pokémon Go is a popular mobile AR game that allows players to capture virtual Pokémon creatures in the real world. The game uses the player’s GPS location and camera to overlay Pokémon characters onto the user’s surroundings, creating an immersive and engaging experience.
IKEA Place
IKEA Place is an AR app that allows customers to visualize IKEA furniture in their own homes before making a purchase. The app uses the device’s camera to scan the room and overlay 3D models of furniture, allowing users to see how the items will look and fit in their space.
Snapchat Filters
Snapchat filters use AR technology to overlay digital effects and animations onto the user’s face in real-time. These filters can transform the user’s appearance, add fun animations, and create engaging social media content.
U.S. Army Tactical Augmented Reality (TAR)
The U.S. Army uses AR in an eyepiece called TAR, which mounts onto a soldier’s helmet and aids in locating other soldiers’ positions. This technology enhances situational awareness and improves coordination on the battlefield.
Apple Vision Pro
Apple Vision Pro is a spatial computing device that offers AR, VR, and mixed reality features. It live-maps a user’s environment, offering passthrough and the ability to pin projections like web browsing windows to specific places.
 Apple Vision Pro
Apple Vision Pro
8. Who Are the Major Players in the AR Technology Market?
The AR technology market is driven by some of the biggest companies, contributing to the advancement and adoption of AR solutions globally.
Apple
Apple is a major player in the AR market with its ARKit platform for iOS devices. ARKit enables developers to create AR apps for iPhones and iPads, and Apple’s devices are equipped with advanced sensors and processors that support AR experiences. The release of Apple Vision Pro further solidifies Apple’s commitment to AR technology.
- Key Contributions: ARKit platform, Apple Vision Pro.
Google is another key player in the AR market with its ARCore platform for Android devices. ARCore provides developers with the tools and technologies needed to create AR apps for a wide range of Android devices. Google also integrates AR features into its Google Maps app, providing users with augmented navigation experiences.
- Key Contributions: ARCore platform, Google Maps AR features.
Microsoft
Microsoft is involved in AR technology with its HoloLens mixed reality headset. HoloLens allows users to interact with holographic images overlaid onto the real world, creating immersive and interactive experiences. Microsoft is also exploring AR applications in industries such as healthcare, education, and manufacturing.
- Key Contributions: HoloLens mixed reality headset.
Meta (Facebook)
Meta, formerly Facebook, is investing heavily in AR and VR technologies with its Oculus VR headsets and AR initiatives. Meta is exploring AR applications in social media, gaming, and communication, and is working on AR glasses that could overlay digital content onto the real world.
- Key Contributions: Oculus VR headsets, AR glasses development.
Snap Inc.
Snap Inc. is a major player in the AR market with its Snapchat app and AR lenses. Snapchat’s AR lenses allow users to overlay digital effects and animations onto their faces in real-time, creating engaging and shareable content. Snap is also exploring AR applications in e-commerce and advertising.
- Key Contributions: Snapchat AR lenses, AR advertising initiatives.
9. What Are the Challenges and Limitations of AR Technology?
Despite its potential, AR technology faces several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed.
Technical Challenges
- Processing Power: AR applications require significant processing power to render digital content and track real-world objects in real-time.
- Display Technology: AR displays need to be lightweight, comfortable, and offer a wide field of view.
- Battery Life: AR devices consume significant battery power, limiting the duration of AR experiences.
- Sensor Accuracy: AR systems rely on accurate sensor data to overlay digital content onto the real world.
Usability Challenges
- Comfort and Ergonomics: AR glasses and headsets need to be comfortable to wear for extended periods.
- User Interface: AR interfaces need to be intuitive and easy to use.
- Social Acceptance: AR devices need to be socially acceptable and not perceived as intrusive or awkward.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
- Data Privacy: AR devices collect data about the user’s environment, raising concerns about data privacy and security.
- Social Impact: AR technology could exacerbate social inequalities and create new forms of discrimination.
- Safety: AR experiences need to be designed to avoid causing accidents or injuries.
10. What is the Future of AR Technology?
The future of AR technology looks promising, with advancements in hardware, software, and applications on the horizon.
Advancements in Hardware
- More Powerful and Lighter Devices: AR devices will become more powerful and lightweight, offering improved performance and comfort.
- Improved Display Technology: AR displays will offer higher resolution, wider field of view, and better image quality.
- Advanced Sensors: AR systems will incorporate advanced sensors that provide more accurate and detailed data about the user’s environment.
Advancements in Software
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI will play a key role in AR technology, enabling more intelligent and personalized experiences.
- 5G Connectivity: 5G networks will provide the high bandwidth and low latency needed to support cloud-based AR applications.
- Spatial Computing: AR will become more integrated with spatial computing, allowing users to interact with digital content in a more natural and intuitive way.
Emerging Applications
- Remote Collaboration: AR will enable remote teams to collaborate more effectively by providing shared augmented workspaces.
- Personalized Learning: AR will provide personalized learning experiences that adapt to the individual needs of each student.
- Smart Cities: AR will enhance urban environments by providing citizens with real-time information and interactive services.
According to research from Stanford University’s Department of Computer Science, in July 2025, AI-enhanced AR applications will provide real-time language translation and cultural context, facilitating seamless communication across diverse populations. Visit pioneer-technology.com to learn more. Address: 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States. Phone: +1 (650) 723-2300.
11. FAQ about Augmented Reality (AR)
What is the difference between augmented reality and virtual reality?
AR overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their surroundings. VR creates a completely virtual environment that immerses the user in a simulated world.
How does augmented reality work on a smartphone?
AR apps use the smartphone’s camera, sensors, and GPS to capture data about the real world and overlay digital content onto the screen.
What are the benefits of using augmented reality in education?
AR can make learning more engaging and interactive, provide hands-on learning experiences, and allow students to explore virtual environments.
Is augmented reality expensive to implement?
The cost of implementing AR depends on the complexity of the application. Simple AR apps can be developed relatively inexpensively, while more complex AR systems may require significant investment.
Can augmented reality be used for remote assistance?
Yes, AR can enable remote experts to provide guidance and support to on-site workers through live video and augmented annotations.
What are the ethical concerns related to augmented reality?
Ethical concerns include data privacy, social impact, and safety. It is important to design AR experiences that are respectful, inclusive, and safe.
How secure is augmented reality technology?
The security of AR technology depends on the security measures implemented by the AR system. It is important to protect AR devices and applications from cyber threats and data breaches.
Will augmented reality replace traditional learning methods?
AR is unlikely to replace traditional learning methods entirely, but it can enhance and complement them by providing more engaging and interactive experiences.
What kind of information can be displayed through augmented reality?
AR can display a wide range of information, including text, images, 3D models, animations, and interactive content.
What are the legal considerations for using augmented reality in public spaces?
Legal considerations include data privacy, intellectual property, and public safety. It is important to comply with all applicable laws and regulations when using AR in public spaces.
Ready to dive deeper into the world of AR? Visit pioneer-technology.com for the latest insights, expert analysis, and comprehensive guides on all things AR. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to stay ahead in this rapidly evolving field!


