BYOD technology, or Bring Your Own Device, empowers employees to utilize their personal devices for work, enhancing flexibility and potentially boosting productivity; pioneer-technology.com provides in-depth analyses and insights to navigate this evolving landscape. To leverage BYOD successfully, you must understand its intricacies, encompassing benefits, risks, security protocols, and implementation strategies, ensuring a secure and productive work environment. Master BYOD with our expert guide on mobile device management, data security, and employee empowerment!
1. What Exactly Is BYOD Technology?
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) technology refers to a business policy that allows employees to use their personal devices—smartphones, tablets, laptops—for work-related tasks. In essence, BYOD is about leveraging personal technology for professional productivity.
1.1 Why Is BYOD Becoming Increasingly Popular?
Several factors contribute to the rising popularity of BYOD:
- Cost Savings: Companies can reduce hardware costs by allowing employees to use their own devices.
- Employee Satisfaction: Employees often prefer using their own familiar devices.
- Increased Productivity: Familiarity with personal devices can lead to greater efficiency.
- Flexibility: BYOD supports remote work and flexible working arrangements.
According to a study by Grand View Research, the global BYOD market is expected to reach $367.07 billion by 2025, reflecting its growing adoption across various industries.
1.2 What Are the Key Components of a BYOD Policy?
A comprehensive BYOD policy should include the following:
- Acceptable Use Policy (AUP): Outlines what constitutes acceptable and unacceptable use of devices for work.
- Security Protocols: Specifies the security measures employees must adhere to, such as password requirements, encryption, and antivirus software.
- Device Management: Defines how devices will be managed, including software updates, remote wiping capabilities, and monitoring.
- Privacy Guidelines: Addresses employee privacy concerns regarding data access and monitoring.
- Support and Reimbursement: Specifies the level of IT support provided and any reimbursements for data usage.
1.3 How Does BYOD Differ From Other Device Management Models?
BYOD differs from other device management models like COBO (Company-Owned, Business-Only), CYOD (Choose Your Own Device), and COPE (Company-Owned, Personally-Enabled). Here’s a quick comparison:
| Model | Description | Ownership | Flexibility | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BYOD | Employees use their personal devices for work. | Employee | High | Low |
| COBO | Company provides devices strictly for business use. | Company | Low | High |
| CYOD | Employees choose from a pre-approved list of devices provided by the company. | Company | Medium | Medium |
| COPE | Company provides devices for both business and personal use, with some restrictions. | Company | Medium | Medium |
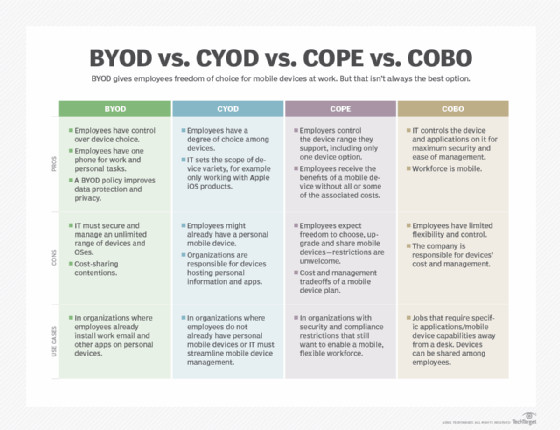 Comparison between BYOD, CYOD, COPE, and COBO policies
Comparison between BYOD, CYOD, COPE, and COBO policies
2. What Are the Benefits of Implementing BYOD?
Implementing BYOD can offer significant advantages to both organizations and employees. Let’s examine some of the primary benefits:
2.1 Cost Efficiency
One of the most compelling benefits of BYOD is cost reduction. Organizations save on device procurement, maintenance, and upgrades. Employees bear these costs, leading to substantial savings for the company.
2.2 Increased Employee Satisfaction and Productivity
Employees are generally more comfortable and efficient when using their own devices. This familiarity can lead to increased productivity and job satisfaction. According to a Cisco study, 69% of employees believe that BYOD improves their work efficiency.
2.3 Access to Latest Technology
Employees often upgrade their personal devices more frequently than companies upgrade their hardware. This ensures that the workforce has access to the latest technology without the company incurring additional expenses.
2.4 Enhanced Flexibility and Mobility
BYOD enables employees to work from anywhere, at any time, promoting a more flexible work environment. This can be particularly beneficial for remote workers and employees who travel frequently.
2.5 Reduced Training Time
Employees are already familiar with their own devices, reducing the need for extensive training. This can save time and resources, allowing employees to quickly integrate their devices into their work routines.
2.6 Competitive Advantage
Offering a BYOD option can make a company more attractive to potential employees, especially in tech-savvy industries. It signals a forward-thinking approach and a willingness to embrace modern technology.
3. What Are the Potential Risks and Challenges of BYOD?
While BYOD offers numerous advantages, it also presents several risks and challenges that organizations must address:
3.1 Security Risks
Security is a primary concern with BYOD. Personal devices may not have the same level of security as company-owned devices, making them vulnerable to malware, data breaches, and other cyber threats.
3.2 Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Issues
Ensuring that sensitive company data is protected on personal devices can be challenging. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategies are crucial to prevent unauthorized access and data leakage.
3.3 Compliance and Legal Issues
BYOD policies must comply with various regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and other data protection laws. Failure to comply can result in significant fines and legal repercussions.
3.4 Privacy Concerns
Employees may have privacy concerns about allowing their employers to access and manage their personal devices. Clear policies and transparent communication are essential to address these concerns.
3.5 Support and Compatibility Issues
Supporting a wide range of devices and operating systems can strain IT resources. Compatibility issues with company software and applications may also arise.
3.6 Loss or Theft of Devices
The loss or theft of personal devices can lead to data breaches and other security incidents. Organizations must have protocols in place to remotely wipe data and secure compromised devices.
4. How Can Organizations Mitigate BYOD Risks?
To successfully implement BYOD, organizations must take proactive measures to mitigate potential risks. Here are some key strategies:
4.1 Develop a Comprehensive BYOD Policy
A well-defined BYOD policy is the foundation of a secure and effective BYOD program. The policy should clearly outline acceptable use, security requirements, privacy guidelines, and support procedures.
4.2 Implement Mobile Device Management (MDM) Software
Mobile Device Management (MDM) software allows IT administrators to manage and secure mobile devices used within the organization. MDM features include:
- Remote Device Configuration: Configure devices with necessary settings and security policies.
- Application Management: Deploy and manage applications on devices.
- Security Enforcement: Enforce security policies, such as password requirements and encryption.
- Remote Wipe: Remotely wipe data from lost or stolen devices.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Monitor device usage and generate reports for compliance purposes.
4.3 Use Mobile Application Management (MAM) Tools
Mobile Application Management (MAM) focuses on managing and securing applications on personal devices. MAM tools enable IT administrators to:
- Control Access to Corporate Apps: Restrict access to sensitive applications based on security policies.
- Manage App Data: Control how corporate data is stored and accessed within applications.
- Enforce Security Policies Within Apps: Implement security measures such as encryption and multi-factor authentication within applications.
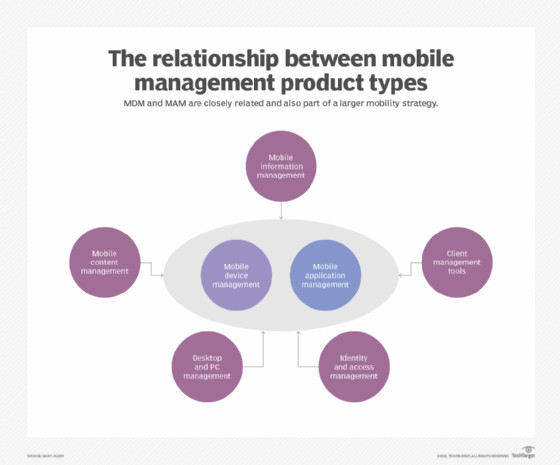 Diagram illustrating mobile management product types
Diagram illustrating mobile management product types
4.4 Enforce Strong Security Protocols
Implementing strong security protocols is crucial to protect against cyber threats. These protocols should include:
- Password Protection: Require strong passwords and enforce regular password changes.
- Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data on devices to prevent unauthorized access.
- Antivirus Software: Mandate the use of antivirus software to protect against malware.
- Firewall Protection: Implement firewall protection to block unauthorized network access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Use MFA to add an extra layer of security to user accounts.
4.5 Provide Security Awareness Training
Security awareness training is essential to educate employees about the risks associated with BYOD and how to mitigate them. Training should cover topics such as:
- Phishing Awareness: Teach employees how to recognize and avoid phishing attacks.
- Malware Prevention: Educate employees about the dangers of malware and how to prevent infections.
- Data Security Best Practices: Provide guidance on how to protect sensitive data on personal devices.
- Incident Reporting: Instruct employees on how to report security incidents and data breaches.
4.6 Implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Strategies
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategies are designed to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. DLP measures include:
- Data Classification: Classify data based on its sensitivity and implement appropriate security controls.
- Content Filtering: Monitor and filter data transmitted through email, web browsing, and other channels to prevent data leakage.
- Access Controls: Restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles and permissions.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access.
4.7 Regularly Update and Patch Devices
Keeping devices up to date with the latest security patches and software updates is crucial to protect against vulnerabilities. Organizations should:
- Automate Patch Management: Use MDM software to automate the process of deploying security patches and software updates.
- Remind Employees to Update Devices: Send regular reminders to employees to update their devices.
- Enforce Update Policies: Implement policies that require employees to install updates within a specified timeframe.
4.8 Monitor and Audit Device Usage
Regularly monitoring and auditing device usage can help identify potential security threats and compliance issues. Organizations should:
- Use MDM Software for Monitoring: Leverage MDM software to monitor device usage, track security incidents, and generate compliance reports.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Perform regular audits to ensure that employees are adhering to BYOD policies and security protocols.
- Analyze Audit Logs: Analyze audit logs to identify suspicious activity and potential security breaches.
5. What Are the Key Considerations When Creating a BYOD Policy?
Creating an effective BYOD policy requires careful consideration of various factors. Here are some key considerations:
5.1 Scope of the Policy
Define the scope of the policy, including which devices are covered, which employees are eligible, and which types of data and applications are subject to the policy.
5.2 Security Requirements
Specify the security requirements that employees must meet, such as password complexity, encryption, antivirus software, and firewall protection.
5.3 Acceptable Use Guidelines
Outline what constitutes acceptable and unacceptable use of devices for work purposes. This should include guidelines on personal use, data privacy, and compliance with company policies.
5.4 Privacy Considerations
Address employee privacy concerns by clearly defining what data will be accessed and monitored, and how it will be protected.
5.5 Support and Reimbursement
Specify the level of IT support provided to employees and any reimbursements for data usage or device maintenance.
5.6 Legal and Compliance Requirements
Ensure that the policy complies with all applicable laws and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and other data protection laws.
5.7 Enforcement and Consequences
Clearly outline the consequences of violating the BYOD policy, such as suspension of access, disciplinary action, or legal penalties.
5.8 Review and Update Procedures
Establish procedures for regularly reviewing and updating the BYOD policy to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
6. What Role Does Mobile Device Management (MDM) Play in BYOD?
Mobile Device Management (MDM) plays a critical role in BYOD by providing organizations with the tools they need to manage and secure mobile devices used within the company.
6.1 Key Features of MDM for BYOD
- Device Enrollment: MDM allows IT administrators to enroll devices into the management system, providing them with the ability to configure and monitor the devices.
- Configuration Management: MDM enables IT administrators to configure devices with necessary settings, such as Wi-Fi passwords, email accounts, and VPN connections.
- Application Management: MDM allows IT administrators to deploy and manage applications on devices, ensuring that employees have access to the tools they need to do their jobs.
- Security Enforcement: MDM enforces security policies, such as password requirements, encryption, and remote wipe capabilities, to protect against cyber threats.
- Monitoring and Reporting: MDM provides IT administrators with the ability to monitor device usage, track security incidents, and generate compliance reports.
6.2 Benefits of Using MDM in a BYOD Environment
- Enhanced Security: MDM enhances security by enforcing security policies and providing remote wipe capabilities.
- Improved Compliance: MDM helps organizations comply with data protection laws and regulations by providing monitoring and reporting capabilities.
- Simplified Management: MDM simplifies the management of mobile devices by providing a centralized platform for configuration, application deployment, and security enforcement.
- Reduced Support Costs: MDM reduces support costs by providing self-service tools for employees and automating many management tasks.
6.3 Selecting the Right MDM Solution
When selecting an MDM solution for BYOD, consider the following factors:
- Features: Choose an MDM solution that offers the features you need to manage and secure mobile devices, such as device enrollment, configuration management, application management, security enforcement, and monitoring and reporting.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the MDM solution is compatible with the devices and operating systems used within your organization.
- Scalability: Select an MDM solution that can scale to meet the needs of your organization as it grows.
- Ease of Use: Choose an MDM solution that is easy to use and administer, with a user-friendly interface and comprehensive documentation.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the MDM solution, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance expenses.
7. What Are Some Real-World Examples of Successful BYOD Implementations?
Many organizations have successfully implemented BYOD programs, demonstrating the benefits and potential of this approach. Here are a few real-world examples:
7.1 IBM
IBM implemented a BYOD program that allows employees to use their personal devices for work, resulting in significant cost savings and increased productivity. The company uses MDM software to manage and secure devices, and provides employees with clear guidelines on acceptable use and security protocols.
7.2 Cisco
Cisco implemented a BYOD program that enables employees to work from anywhere, at any time, using their personal devices. The company uses MDM software to enforce security policies and protect sensitive data, and provides employees with security awareness training to mitigate risks.
7.3 VMware
VMware implemented a BYOD program that allows employees to choose from a range of devices and applications, providing them with the flexibility they need to do their jobs effectively. The company uses MDM software to manage and secure devices, and provides employees with clear guidelines on acceptable use and security protocols.
7.4 Intel
Intel’s BYOD program focuses on enhancing employee productivity by allowing them to use their preferred devices. The company emphasizes strong security measures, including multi-factor authentication and data encryption, to protect sensitive corporate information.
7.5 SAP
SAP’s BYOD initiative aims to create a more flexible and collaborative work environment. Employees are encouraged to use their own devices, while SAP provides the necessary security infrastructure to safeguard company data.
These examples demonstrate that with careful planning and execution, BYOD can be a successful strategy for organizations of all sizes.
8. How Can Employees Protect Their Personal Data in a BYOD Environment?
In a BYOD environment, employees play a crucial role in protecting their personal data. Here are some steps employees can take to safeguard their information:
8.1 Use Strong Passwords
Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts and devices. Avoid using easily guessable passwords, such as birthdays or pet names.
8.2 Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Enable MFA for all accounts that support it. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of authentication, such as a code sent to your phone.
8.3 Keep Devices Up to Date
Keep devices up to date with the latest security patches and software updates. These updates often include fixes for security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers.
8.4 Install Antivirus Software
Install antivirus software on devices and keep it up to date. Antivirus software can help protect against malware and other cyber threats.
8.5 Be Careful What You Click
Be cautious about clicking on links or opening attachments in emails or messages from unknown senders. These could be phishing attacks designed to steal your personal information.
8.6 Use a VPN When on Public Wi-Fi
Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks. A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, protecting it from eavesdropping.
8.7 Back Up Your Data Regularly
Back up your data regularly to protect against data loss in the event of device failure or theft. Use cloud-based backup services or external hard drives to store your backups.
8.8 Be Aware of Your Surroundings
Be aware of your surroundings when using devices in public places. Avoid displaying sensitive information on your screen where others can see it.
8.9 Follow Company Policies
Follow company BYOD policies and guidelines. These policies are designed to protect both company data and your personal information.
8.10 Report Security Incidents
Report any security incidents or suspicious activity to your IT department immediately. This will help them take steps to mitigate the threat and prevent further damage.
9. What Are the Latest Trends in BYOD Technology?
BYOD technology is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging to address the changing needs of organizations and employees. Here are some of the latest trends:
9.1 Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust Security is a security model that assumes that no user or device is trustworthy, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the organization’s network. Zero Trust requires all users and devices to be authenticated and authorized before they are granted access to resources.
9.2 Cloud-Based MDM
Cloud-Based MDM solutions are becoming increasingly popular, as they offer greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional on-premises MDM solutions.
9.3 Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are being used to enhance security in BYOD environments by detecting and responding to threats in real time. AI-powered security solutions can analyze device behavior, identify anomalies, and automatically take action to mitigate risks.
9.4 Containerization
Containerization involves creating a secure container on personal devices to separate corporate data and applications from personal data and applications. This helps to protect sensitive information and prevent data leakage.
9.5 Biometric Authentication
Biometric Authentication, such as fingerprint scanning and facial recognition, is being used to enhance security in BYOD environments. Biometric authentication provides a more secure and convenient alternative to traditional passwords.
9.6 Enhanced Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Enhanced Data Loss Prevention (DLP) technologies are being used to protect sensitive data on personal devices. These technologies can monitor data usage, detect potential data breaches, and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
9.7 Integration with Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Integration with Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems is becoming increasingly important in BYOD environments. IAM systems provide a centralized platform for managing user identities and access privileges, ensuring that only authorized users have access to corporate resources.
10. What Are Some Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About BYOD Technology?
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about BYOD technology:
10.1 Is BYOD secure?
BYOD can be secure if organizations implement appropriate security measures, such as MDM software, strong security protocols, and security awareness training.
10.2 What are the benefits of BYOD?
The benefits of BYOD include cost savings, increased employee satisfaction, access to the latest technology, and enhanced flexibility and mobility.
10.3 What are the risks of BYOD?
The risks of BYOD include security breaches, data loss, compliance issues, and privacy concerns.
10.4 How can organizations mitigate BYOD risks?
Organizations can mitigate BYOD risks by developing a comprehensive BYOD policy, implementing MDM software, enforcing strong security protocols, and providing security awareness training.
10.5 What is Mobile Device Management (MDM)?
Mobile Device Management (MDM) is software that allows IT administrators to manage and secure mobile devices used within the organization.
10.6 What is Mobile Application Management (MAM)?
Mobile Application Management (MAM) focuses on managing and securing applications on personal devices.
10.7 How can employees protect their personal data in a BYOD environment?
Employees can protect their personal data by using strong passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, keeping devices up to date, and following company policies.
10.8 What are the latest trends in BYOD technology?
The latest trends in BYOD technology include Zero Trust Security, Cloud-Based MDM, AI and ML, Containerization, and Biometric Authentication.
10.9 Is BYOD suitable for all organizations?
BYOD may not be suitable for all organizations, particularly those with strict security or compliance requirements.
10.10 How often should a BYOD policy be reviewed and updated?
A BYOD policy should be reviewed and updated regularly, at least annually, to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
Understanding BYOD is essential for organizations striving to balance flexibility with security. Stay ahead of the curve by visiting pioneer-technology.com for the latest insights, trends, and best practices in BYOD and other pioneering technologies. Address: 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States. Phone: +1 (650) 723-2300. Website: pioneer-technology.com.
Are you ready to embrace the future of technology? Dive deeper into the world of BYOD and discover how it can transform your workplace by exploring related articles and resources at pioneer-technology.com today!

