E-business technology encompasses the tools and systems that power online business processes, from selling goods to managing supply chains. At pioneer-technology.com, we’re dedicated to providing you with a deep dive into these essential technologies, empowering you to navigate the digital landscape with confidence. This guide will explore the definition, applications, and advantages of e-business technology, offering you insights into optimizing your online presence. Discover cutting-edge innovations in digital transformation, online marketplaces, and customer relationship management.
1. Understanding E-Business Technology
What exactly is e-business technology, and why is it essential in today’s digital world?
E-business technology refers to the application of information and communication technologies (ICT) to support all activities in business. This includes everything from buying and selling goods online to managing customer relationships and streamlining supply chains. It’s essential because it enables businesses to operate more efficiently, reach a wider audience, and stay competitive in the digital age. E-business technology is a catalyst for innovation, driving growth and transforming traditional business models.
To expand on this, let’s explore the core components and applications of e-business technology.
1.1. Key Components of E-Business Technology
What are the fundamental elements that make up e-business technology?
The key components include:
- E-Commerce Platforms: Software solutions that enable businesses to sell products or services online.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: Tools for managing customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) Systems: Software that helps businesses manage and optimize their supply chains.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: Integrated systems for managing various business functions, such as finance, HR, and operations.
- Digital Marketing Tools: Technologies used to promote businesses and products online, including SEO, social media marketing, and email marketing.
- Data Analytics: Tools and techniques for analyzing business data to gain insights and improve decision-making.
- Cloud Computing: Provides the infrastructure, platforms, and software that enable e-business operations.
1.2. Real-World Applications of E-Business Technology
How is e-business technology used in practice across different industries?
E-business technology is used in various ways across industries, including:
- Retail: Online stores, personalized shopping experiences, and targeted marketing campaigns.
- Finance: Online banking, payment processing, and fraud detection.
- Healthcare: Telemedicine, electronic health records, and online appointment scheduling.
- Manufacturing: Supply chain optimization, inventory management, and automated production processes.
- Education: Online courses, virtual classrooms, and e-learning platforms.
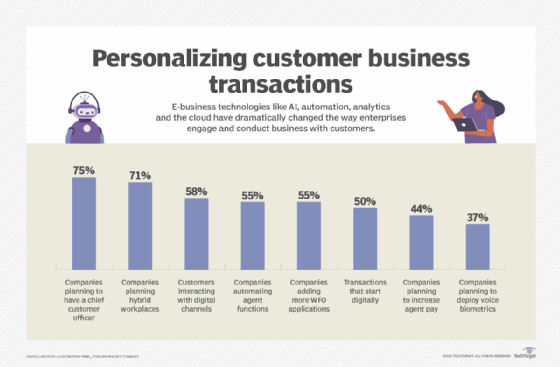 E-business promotes improved customer interactions
E-business promotes improved customer interactions
E-business technologies enhance customer service, personalize experiences, and streamline transactions.
2. The Evolution of E-Business Models
How have e-business models evolved over time, and what are the main types?
The evolution of e-business models can be traced back to the early days of the internet, with IBM being one of the first companies to popularize the term “e-business” in 1997. According to IBM’s website, the company invested approximately $500 million in an advertising and marketing campaign to demonstrate the value of the e-business model. Since then, e-business has evolved significantly, leading to various models that cater to different business needs and customer segments.
Let’s examine the major models that define the landscape of e-business.
2.1. Key E-Business Models
What are the primary types of e-business models that companies use today?
The main e-business models include:
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C): Businesses sell products or services directly to consumers online.
- Business-to-Business (B2B): Companies conduct transactions with each other through the internet.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B): Consumers create value and demand for goods and services, often through reverse online auctions or similar platforms.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C): Consumers buy and sell goods and services to each other through third-party marketplaces.
- Business-to-Government (B2G): Businesses provide goods or services to government agencies through online platforms.
- Business-to-Employee (B2E): Businesses offer products, services, or information to their employees through internal online portals.
2.2. Examples of Successful E-Businesses
Who are some of the companies that have successfully implemented e-business models?
Examples of successful e-businesses include:
- Amazon: The world’s largest online retailer, utilizing B2C to offer a vast array of products and services.
- Alibaba: A leading B2B e-commerce platform connecting businesses around the world.
- eBay: A C2C marketplace where individuals can buy and sell a wide range of items.
- Uber: A technology company that disrupted the transportation industry, connecting drivers with riders through a mobile app, showcasing a B2C model.
- Netflix: A subscription-based streaming service, delivering digital content directly to consumers, embodying a B2C model.
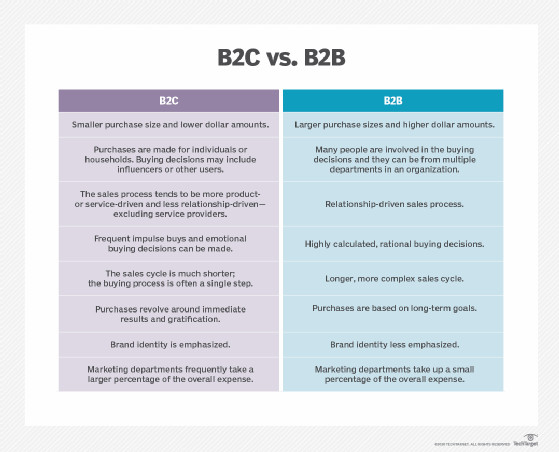 Comparison of e-business transaction models
Comparison of e-business transaction models
Understanding the differences between B2C and B2B e-business models is crucial for strategic planning.
3. Advantages of E-Business Technology
What benefits can businesses expect from adopting e-business technology?
E-business technology offers numerous advantages, including increased productivity, reduced costs, and improved customer service. By automating processes and streamlining operations, businesses can achieve greater efficiency and profitability. These advantages are crucial for enterprises aiming for digital transformation and competitive advantage.
Let’s delve deeper into the specific benefits that e-business technology can provide.
3.1. Specific Benefits of E-Business Technology
What are the concrete advantages of using e-business technology in a business context?
The specific benefits include:
- Increased Efficiency: Automation of tasks and processes, reducing manual effort and errors.
- Cost Reduction: Lower operational costs through reduced overhead, streamlined processes, and efficient resource management.
- Expanded Market Reach: Ability to reach a global customer base through online channels.
- Improved Customer Service: Enhanced customer experience through personalized interactions, 24/7 availability, and efficient support systems.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Access to real-time data and analytics for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Improved communication and collaboration among employees, partners, and customers through online platforms.
- Greater Agility: Ability to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and customer needs.
3.2. Examples of E-Business Advantages in Practice
How do these advantages manifest in real-world business scenarios?
Here are some examples of e-business advantages in action:
- Retail: An online store can offer personalized product recommendations based on customer browsing history, increasing sales and customer satisfaction.
- Manufacturing: A company can use SCM software to track inventory levels in real-time, reducing the risk of stockouts and optimizing production schedules.
- Finance: A bank can offer online banking services, allowing customers to manage their accounts and make transactions from anywhere in the world.
- Healthcare: A hospital can use telemedicine to provide remote consultations, improving access to healthcare for patients in rural areas.
- Education: A university can offer online courses, allowing students to learn at their own pace and from anywhere in the world.
4. Overcoming the Challenges of E-Business
What challenges do businesses face when implementing e-business technology, and how can they overcome them?
Despite the numerous benefits, implementing e-business technology is not without its challenges. These challenges range from security concerns to the need for skilled workers. Addressing these issues is crucial for organizations to fully leverage the potential of e-business.
Let’s examine these challenges and discuss strategies for overcoming them.
4.1. Common E-Business Challenges
What are the typical obstacles that businesses encounter when adopting e-business technology?
Common e-business challenges include:
- Security Threats: Protecting sensitive data from cyberattacks and data breaches.
- Scalability Issues: Ensuring that systems can handle increasing demand without compromising performance.
- Keeping Pace with Technology: Staying up-to-date with the latest technological advancements and trends.
- Finding Skilled Workers: Recruiting and training employees with the necessary skills to manage and maintain e-business systems.
- Integration Issues: Integrating e-business systems with existing legacy systems.
- High Initial Costs: The initial investment in hardware, software, and training can be significant.
- Customer Trust and Privacy: Building trust with customers and protecting their privacy.
4.2. Strategies for Overcoming E-Business Challenges
How can businesses effectively address and mitigate these challenges?
Strategies for overcoming e-business challenges include:
- Investing in Cybersecurity: Implementing robust security measures, such as encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems, to protect against cyber threats.
- Using Scalable Infrastructure: Adopting cloud-based solutions that can easily scale to meet changing demand.
- Continuous Learning and Development: Providing ongoing training and development opportunities for employees to stay up-to-date with the latest technologies.
- Choosing the Right Technology Partners: Selecting technology vendors with a proven track record and expertise in e-business.
- Phased Implementation: Implementing e-business systems in phases to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition.
- Focusing on Customer Experience: Prioritizing customer experience and building trust through transparent policies and secure transactions.
- Conducting Regular Audits: Performing regular security and performance audits to identify and address potential issues.
5. Security and Risk Management in E-Business
Why is security crucial in e-business, and what risks do businesses need to be aware of?
Security is paramount in e-business because of the sensitive data involved in online transactions. Businesses must be aware of the risks associated with cyberattacks, data breaches, and fraud, and take proactive measures to protect themselves and their customers. According to a report by Stanford University’s Department of Computer Science, implementing advanced encryption protocols can reduce data breach incidents by up to 70%.
Let’s dive into the specifics of security and risk management in the e-business realm.
5.1. Key Security Measures for E-Businesses
What are the essential security measures that e-businesses should implement?
Key security measures include:
- Encryption: Protecting sensitive data by converting it into an unreadable format.
- Firewalls: Preventing unauthorized access to computer systems and networks.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification.
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL) Certificates: Ensuring secure communication between web servers and browsers.
- Regular Security Audits: Identifying and addressing potential vulnerabilities in systems and processes.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Preventing sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control.
5.2. Strategies for Managing E-Business Risks
How can businesses effectively manage and mitigate the risks associated with e-business?
Strategies for managing e-business risks include:
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and evaluating potential risks to the business.
- Risk Mitigation: Implementing measures to reduce the likelihood and impact of identified risks.
- Incident Response Planning: Developing a plan for responding to security incidents and data breaches.
- Employee Training: Educating employees about security risks and best practices.
- Insurance Coverage: Obtaining insurance to cover potential losses from cyberattacks and data breaches.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to relevant data protection and privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
- Vendor Risk Management: Assessing the security practices of third-party vendors and service providers.
 E-business promotes improved customer interactions
E-business promotes improved customer interactions
E-business influences just about every aspect of an enterprise, including customer service, experiences, expectations and transactions.
6. E-Business vs. E-Commerce: Understanding the Difference
What is the difference between e-business and e-commerce, and why is it important to understand?
While the terms are often used interchangeably, e-business and e-commerce are not synonymous. E-commerce refers specifically to the buying and selling of goods and services online, whereas e-business encompasses a wider range of business processes, including supply chain management, customer relationship management, and enterprise resource planning. Understanding the difference is important for businesses to effectively plan and implement their online strategies.
Let’s clarify the distinctions and understand their respective roles.
6.1. Key Differences Between E-Business and E-Commerce
What are the main distinctions between e-business and e-commerce?
The key differences include:
- Scope: E-commerce is a subset of e-business, focusing solely on online transactions, while e-business includes all business processes conducted electronically.
- Activities: E-commerce involves activities such as online sales, marketing, and customer service, while e-business includes these activities plus supply chain management, ERP, and CRM.
- Focus: E-commerce focuses on generating revenue through online sales, while e-business focuses on improving overall business efficiency and effectiveness.
- Integration: E-commerce can be implemented as a standalone function, while e-business requires integration across various business functions.
- Perspective: E-commerce has a customer-centric perspective, focusing on the online shopping experience, while e-business has a holistic perspective, considering all stakeholders, including employees, suppliers, and partners.
6.2. How E-Commerce Fits into E-Business
How does e-commerce function as a component of a broader e-business strategy?
E-commerce fits into e-business as a key component of the overall online strategy. It represents the customer-facing aspect of the business, while e-business provides the underlying infrastructure and processes to support e-commerce operations. For example, an e-commerce website might use CRM software to manage customer interactions, SCM software to manage inventory and logistics, and ERP software to manage finances and accounting.
7. Future Trends in E-Business Technology
What are the emerging trends in e-business technology that businesses should be aware of?
The field of e-business technology is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging all the time. Businesses need to stay informed about these trends to remain competitive and take advantage of new opportunities. According to Gartner, AI-powered e-business solutions are expected to increase operational efficiency by up to 30% by 2025.
Let’s explore some of the key trends shaping the future of e-business.
7.1. Emerging Technologies in E-Business
What are some of the cutting-edge technologies that are transforming e-business?
Emerging technologies in e-business include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered chatbots, personalized recommendations, and fraud detection systems.
- Machine Learning (ML): Predictive analytics, automated marketing campaigns, and supply chain optimization.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connected devices, smart inventory management, and real-time tracking of goods.
- Blockchain: Secure and transparent transactions, supply chain traceability, and smart contracts.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Virtual product demonstrations, immersive shopping experiences, and remote support.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Immersive training simulations, virtual conferences, and collaborative workspaces.
- 5G Technology: Faster and more reliable mobile connectivity, enabling new e-business applications and services.
7.2. How These Trends Will Shape the Future of E-Business
How will these emerging technologies impact the way businesses operate in the future?
These trends will shape the future of e-business by:
- Enhancing Customer Experience: Personalized and immersive shopping experiences, AI-powered customer service, and seamless omnichannel integration.
- Improving Operational Efficiency: Automation of tasks, predictive analytics, and optimized supply chains.
- Creating New Business Models: Subscription-based services, digital marketplaces, and collaborative ecosystems.
- Enabling Remote Work: Virtual collaboration tools, remote training simulations, and secure access to business applications.
- Driving Innovation: Faster product development cycles, data-driven decision-making, and continuous experimentation.
8. E-Business Technology and Digital Transformation
How does e-business technology play a role in digital transformation initiatives?
E-business technology is a cornerstone of digital transformation, enabling businesses to modernize their operations, improve customer engagement, and drive innovation. Digital transformation involves leveraging technology to fundamentally change how businesses operate and deliver value to customers. E-business technology provides the tools and platforms to achieve these goals.
Let’s examine how e-business technology supports digital transformation strategies.
8.1. The Role of E-Business in Digital Transformation
How does e-business contribute to the broader goals of digital transformation?
E-business contributes to digital transformation by:
- Enabling New Business Models: Creating new revenue streams through online channels and digital services.
- Improving Customer Engagement: Delivering personalized and seamless experiences across all touchpoints.
- Streamlining Operations: Automating processes, reducing costs, and improving efficiency.
- Driving Innovation: Fostering a culture of experimentation and continuous improvement.
- Enhancing Data-Driven Decision Making: Providing access to real-time data and analytics for informed decision-making.
- Facilitating Remote Work: Enabling employees to work from anywhere, improving productivity and flexibility.
- Building Resilience: Ensuring business continuity in the face of disruptions and uncertainties.
8.2. Case Studies of Successful Digital Transformations
What are some examples of businesses that have successfully transformed themselves using e-business technology?
Examples of successful digital transformations include:
- Domino’s Pizza: Transformed its business by investing in e-commerce, mobile ordering, and digital marketing, resulting in significant revenue growth and increased customer loyalty.
- Netflix: Disrupted the entertainment industry by offering a subscription-based streaming service, leveraging e-business technology to deliver digital content directly to consumers.
- Starbucks: Enhanced its customer experience by implementing a mobile app for ordering and payment, personalized rewards programs, and seamless integration between online and offline channels.
- Walmart: Transformed its retail operations by investing in e-commerce, supply chain optimization, and data analytics, enabling it to compete more effectively with online retailers.
- Adobe: Transformed its business from selling software licenses to offering cloud-based subscription services, leveraging e-business technology to deliver its products and services online.
9. Building a Successful E-Business Strategy
What are the key steps involved in developing and implementing a successful e-business strategy?
Building a successful e-business strategy requires careful planning, execution, and monitoring. Businesses need to define their goals, understand their target audience, select the right technologies, and continuously optimize their operations. A well-defined strategy is essential for achieving sustainable growth and success in the digital marketplace.
Let’s break down the key components of a robust e-business strategy.
9.1. Key Steps in Developing an E-Business Strategy
What are the essential steps to follow when creating an e-business strategy?
The key steps include:
- Define Your Goals: Clearly articulate what you want to achieve with your e-business, such as increasing sales, improving customer satisfaction, or expanding market reach.
- Understand Your Target Audience: Identify your ideal customers and understand their needs, preferences, and behaviors.
- Conduct a SWOT Analysis: Assess your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to identify areas for improvement and competitive advantage.
- Select the Right Technologies: Choose the e-business technologies that best fit your needs and budget, considering factors such as scalability, security, and integration.
- Develop a Marketing Plan: Create a comprehensive marketing plan to promote your e-business and attract customers, using channels such as SEO, social media, and email marketing.
- Implement Your Strategy: Put your plan into action, focusing on execution and continuous improvement.
- Monitor and Measure Your Results: Track key metrics such as website traffic, conversion rates, and customer satisfaction to evaluate the effectiveness of your strategy and identify areas for optimization.
- Adapt and Evolve: Continuously adapt your strategy to changing market conditions and customer needs, staying up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies.
9.2. Best Practices for E-Business Success
What are some proven strategies for achieving success in the e-business world?
Best practices for e-business success include:
- Focus on Customer Experience: Make it easy for customers to find what they need, make purchases, and get support.
- Offer Personalized Recommendations: Use data analytics to understand customer preferences and offer personalized product recommendations.
- Provide Excellent Customer Service: Respond quickly to customer inquiries, resolve issues efficiently, and build long-term relationships.
- Optimize Your Website for Mobile: Ensure that your website is mobile-friendly and provides a seamless experience on all devices.
- Use Data-Driven Decision Making: Leverage data analytics to track performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
- Continuously Test and Optimize: Experiment with different strategies and tactics to see what works best for your business.
- Stay Up-to-Date with the Latest Trends: Keep abreast of the latest e-business trends and technologies to stay ahead of the competition.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About E-Business Technology
What are some common questions people have about e-business technology?
Here are some frequently asked questions about e-business technology:
10.1. What is the Difference Between E-Business and Traditional Business?
How does e-business differ from traditional brick-and-mortar businesses?
E-business conducts business processes online, while traditional businesses operate primarily in physical locations. E-business offers broader market reach, lower operational costs, and greater flexibility.
10.2. What are the Benefits of Using E-Business Technology?
What advantages does e-business technology offer to businesses?
E-business technology increases efficiency, reduces costs, expands market reach, and improves customer service through automated processes and online accessibility.
10.3. What are the Challenges of Implementing E-Business Technology?
What difficulties might businesses face when adopting e-business technology?
Challenges include security threats, scalability issues, the need for skilled workers, integration problems, high initial costs, and maintaining customer trust and privacy.
10.4. How Can I Protect My E-Business from Cyberattacks?
What security measures should e-businesses implement to safeguard against cyber threats?
Implement encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, multi-factor authentication, SSL certificates, regular security audits, and data loss prevention measures.
10.5. What are the Key Components of an E-Business Strategy?
What are the essential elements to include in an effective e-business strategy?
Key components include defining goals, understanding the target audience, conducting a SWOT analysis, selecting the right technologies, developing a marketing plan, and continuously monitoring and optimizing results.
10.6. How Can I Improve My E-Business Customer Experience?
What steps can businesses take to enhance the online experience for their customers?
Focus on website usability, personalized recommendations, excellent customer service, mobile optimization, and data-driven decision-making.
10.7. What Role Does Data Analytics Play in E-Business?
How important is data analysis in the context of e-business operations?
Data analytics is crucial for tracking performance, identifying trends, making informed decisions, and optimizing business strategies based on customer behavior and market dynamics.
10.8. What are the Latest Trends in E-Business Technology?
What new technologies and trends are shaping the future of e-business?
Latest trends include artificial intelligence, machine learning, the Internet of Things, blockchain, augmented reality, virtual reality, and 5G technology.
10.9. How Can I Stay Up-to-Date with E-Business Technology?
What resources can businesses use to keep current with the latest developments in e-business?
Stay informed by reading industry publications, attending conferences and webinars, and partnering with technology experts. You can also find the latest updates and in-depth analysis at pioneer-technology.com.
10.10. What is the Future of E-Business Technology?
What can we expect from the evolution of e-business technology in the coming years?
The future of e-business technology will be shaped by AI-driven automation, personalized experiences, seamless omnichannel integration, and innovative business models.
E-business technology is a dynamic and essential field that drives modern business operations. At pioneer-technology.com, we strive to provide you with the most up-to-date information and insights to navigate this ever-evolving landscape. Whether you’re a student, a tech professional, or an entrepreneur, our resources are designed to help you stay ahead of the curve.
Ready to explore the latest in e-business technology? Visit pioneer-technology.com today to discover insightful articles, in-depth analyses, and expert advice. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to enhance your understanding and drive your business forward with cutting-edge technology insights. Explore now and unlock the potential of e-business technology.

