Information technology (IT) devices are the core of how we create, process, store, secure, and exchange digital information, pivotal for business operations and beyond. This definition comes to you from the experts at pioneer-technology.com. Understanding these devices, from computers and networks to software and security systems, is crucial in today’s tech-driven world. Dive in to explore the capabilities, applications, and future trends of IT devices, and discover how they are revolutionizing industries on pioneer-technology.com.
1. What Exactly Is an Information Technology Device?
An information technology (IT) device is any physical or virtual component that facilitates the creation, processing, storage, securing, and exchange of data. These devices are essential for managing information within business operations. According to a July 2025 study by Stanford University’s Department of Computer Science, the efficiency of data processing directly correlates with a company’s ability to innovate and compete, emphasizing the critical role IT devices play in modern business environments.
1.1 What Does an IT Device Encompass?
IT devices encompass a broad spectrum of technologies and systems used to handle data for specific purposes.
- Computers: The cornerstone of IT, handling a wide range of tasks from data processing to running complex applications.
- Servers: Powerful computers that manage network resources, providing services like data storage and application hosting.
- Networking Equipment: Includes routers, switches, and firewalls, which ensure seamless communication and data transfer.
- Storage Devices: Devices such as hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), and cloud storage solutions that store data securely and efficiently.
- Software: Applications and operating systems that instruct hardware to perform specific tasks.
1.2 What Are the Key Functions of IT Devices?
IT devices perform several critical functions that are essential for modern business operations:
- Data Creation: Input devices like keyboards, mice, and scanners allow users to enter data into the system.
- Data Processing: Central Processing Units (CPUs) and Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) process data, performing calculations and executing instructions.
- Data Storage: Storage devices like hard drives and SSDs store data for later retrieval.
- Data Security: Firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption tools protect data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Data Exchange: Networking equipment enables the transfer of data between devices and networks.
 Components of IT showing networking, storage and software
Components of IT showing networking, storage and software
2. What Are the Different Types of Information Technology Devices?
IT devices come in various forms, each serving specific purposes within an organization’s IT infrastructure. Understanding these types is crucial for effectively managing and optimizing IT resources.
2.1 Computing Devices
Computing devices are the core of any IT infrastructure, responsible for processing data and executing instructions.
- Desktops: Traditional computers designed for general-purpose use, suitable for office tasks, software development, and more.
- Laptops: Portable computers that offer similar capabilities to desktops, providing flexibility for users on the go.
- Servers: High-performance computers that manage network resources and provide services like data storage, application hosting, and web hosting.
- Mobile Devices: Smartphones and tablets that offer computing capabilities in a compact form factor, used for communication, productivity, and accessing information.
2.2 Networking Devices
Networking devices facilitate communication and data transfer between different components of an IT infrastructure.
- Routers: Devices that forward data packets between networks, enabling internet connectivity and internal network communication.
- Switches: Devices that connect multiple devices within a network, allowing them to communicate efficiently.
- Firewalls: Security devices that monitor network traffic and block unauthorized access, protecting the network from cyber threats.
- Wireless Access Points: Devices that provide wireless connectivity to networks, allowing users to connect their devices without physical cables.
2.3 Storage Devices
Storage devices are essential for storing data, whether it’s for short-term access or long-term archiving.
- Hard Disk Drives (HDDs): Traditional storage devices that use magnetic platters to store data, offering high capacity at a relatively low cost.
- Solid State Drives (SSDs): Storage devices that use flash memory to store data, providing faster access times and greater durability compared to HDDs.
- Network Attached Storage (NAS): Storage devices that connect directly to a network, allowing multiple users to access and share files.
- Cloud Storage: Off-site storage solutions that store data on remote servers, providing scalability, accessibility, and data redundancy.
2.4 Input/Output Devices
Input/output devices enable users to interact with IT systems, entering data and receiving information.
- Keyboards: Input devices used to enter text and commands into a computer.
- Mice: Input devices used to navigate and interact with graphical user interfaces.
- Monitors: Output devices that display visual information, allowing users to see the results of their actions.
- Printers: Output devices that produce hard copies of documents and images.
- Scanners: Input devices that convert physical documents and images into digital formats.
2.5 Security Devices
Security devices protect IT systems and data from unauthorized access, cyber threats, and data breaches.
- Firewalls: Security devices that monitor network traffic and block unauthorized access, protecting the network from cyber threats.
- Antivirus Software: Software that detects and removes malicious software, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Systems that monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and alert administrators to potential security breaches.
- Encryption Devices: Devices that encrypt data to protect it from unauthorized access, ensuring confidentiality and data integrity.
Understanding the different types of IT devices and their specific functions is crucial for designing, implementing, and maintaining an effective IT infrastructure. This knowledge enables organizations to optimize their IT resources, enhance security, and support their business objectives.
3. What Are the Key Components of an Information Technology Device?
Understanding the key components of IT devices is essential for effective management, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and performance of the device.
3.1 Hardware Components
Hardware components are the physical parts of an IT device that you can see and touch.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The “brain” of the computer, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. According to Intel, the latest CPUs can perform trillions of calculations per second, significantly enhancing processing power.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): Volatile memory used to store data and instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly. More RAM allows the computer to handle more tasks simultaneously without slowing down.
- Storage Devices: Devices such as Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid State Drives (SSDs) that store data persistently. SSDs offer faster access times and greater durability compared to HDDs.
- Motherboard: The main circuit board that connects all the components of the computer, allowing them to communicate with each other.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): A specialized processor that handles graphics rendering, essential for gaming, video editing, and other visually intensive tasks. NVIDIA reports that their GPUs can significantly accelerate AI and machine learning workloads.
- Networking Components: Includes Network Interface Cards (NICs), routers, and switches that enable the device to connect to a network and communicate with other devices.
3.2 Software Components
Software components are the programs and instructions that tell the hardware what to do.
- Operating System (OS): The foundation of the software environment, managing hardware resources and providing services for applications. Examples include Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Applications: Software programs designed to perform specific tasks, such as word processing, web browsing, and data analysis.
- Drivers: Software that allows the operating system to communicate with hardware devices, such as printers, scanners, and network adapters.
- Firmware: Software embedded in hardware devices that provides basic instructions for the device to operate.
3.3 Connectivity Components
Connectivity components enable IT devices to communicate with each other and with external networks.
- Network Interface Card (NIC): A hardware component that allows a device to connect to a network.
- Wireless Adapter: A hardware component that enables wireless connectivity via Wi-Fi.
- Bluetooth Adapter: A hardware component that enables short-range wireless communication with other Bluetooth-enabled devices.
- Ports: Physical interfaces that allow devices to connect to external peripherals, such as USB ports, HDMI ports, and Ethernet ports.
3.4 Power Components
Power components provide the necessary electricity for the IT device to operate.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): Converts AC power from the wall outlet into DC power that the computer can use.
- Battery: Provides backup power in case of a power outage, allowing the device to continue operating for a limited time.
- Power Cables: Cables that connect the power supply to the motherboard and other components.
Understanding these key components of IT devices is crucial for IT professionals and anyone involved in managing or maintaining IT infrastructure. It enables them to diagnose problems effectively, upgrade components as needed, and ensure the overall reliability and performance of the IT systems.
4. Why Are Information Technology Devices Important?
IT devices are indispensable in today’s world, playing a pivotal role in business, education, healthcare, and everyday life. Their importance stems from their ability to enhance efficiency, productivity, communication, and access to information.
4.1 Enhancing Business Operations
IT devices have revolutionized business operations, enabling companies to streamline processes, improve decision-making, and enhance customer service.
- Automation: IT devices automate repetitive tasks, reducing the need for manual labor and minimizing errors. According to a McKinsey report, automation can increase productivity by up to 30% in many industries.
- Data Analysis: IT devices enable businesses to collect, process, and analyze vast amounts of data, providing valuable insights for decision-making. Data analytics tools help companies identify trends, optimize strategies, and improve performance.
- Communication: IT devices facilitate seamless communication and collaboration among employees, customers, and partners. Email, instant messaging, video conferencing, and collaboration platforms enable efficient communication regardless of location.
- Customer Service: IT devices enhance customer service through online portals, chatbots, and CRM systems. These tools enable businesses to respond quickly to customer inquiries, resolve issues efficiently, and personalize customer experiences.
4.2 Facilitating Education
IT devices have transformed education, providing students with access to vast amounts of information, interactive learning tools, and online resources.
- Online Learning: IT devices enable online learning, allowing students to access educational materials and participate in courses remotely. Online learning platforms provide flexibility and convenience, making education accessible to a wider audience.
- Research: IT devices provide students and researchers with access to online libraries, databases, and academic journals, facilitating research and knowledge discovery.
- Interactive Learning: IT devices support interactive learning through educational software, simulations, and virtual reality experiences. These tools engage students and enhance their understanding of complex concepts.
4.3 Improving Healthcare
IT devices have significantly improved healthcare, enabling doctors and healthcare professionals to diagnose diseases more accurately, treat patients more effectively, and manage healthcare operations more efficiently.
- Medical Imaging: IT devices such as MRI machines, CT scanners, and X-ray machines provide detailed images of the human body, enabling doctors to diagnose diseases and injuries more accurately.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): IT devices enable the storage and management of electronic health records, allowing healthcare professionals to access patient information quickly and securely.
- Telemedicine: IT devices facilitate telemedicine, allowing doctors to provide remote consultations, monitor patients’ conditions, and prescribe medications online.
- Medical Research: IT devices support medical research by enabling scientists to analyze large datasets, conduct simulations, and develop new treatments for diseases.
4.4 Enhancing Everyday Life
IT devices have become integral to everyday life, providing people with access to information, entertainment, communication, and convenience.
- Communication: IT devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets enable people to communicate with friends, family, and colleagues via email, instant messaging, and social media.
- Entertainment: IT devices provide access to a wide range of entertainment options, including streaming movies, music, and games.
- Information: IT devices provide access to vast amounts of information via the internet, allowing people to stay informed about current events, learn new skills, and explore their interests.
- Convenience: IT devices enhance convenience through online shopping, mobile banking, and smart home automation. These tools enable people to manage their finances, shop for goods, and control their homes remotely.
In summary, IT devices are crucial for enhancing efficiency, productivity, communication, and access to information in various aspects of life. Their ability to automate tasks, analyze data, facilitate communication, and provide access to information makes them indispensable in today’s interconnected world.
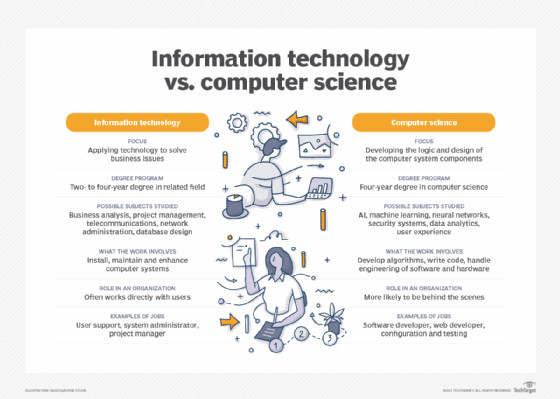 A comparison between IT and computer science
A comparison between IT and computer science
5. What Are the Benefits of Using Information Technology Devices?
The integration of IT devices into various sectors offers numerous benefits, significantly improving efficiency, productivity, and overall performance. Understanding these advantages can help organizations and individuals make informed decisions about leveraging IT solutions.
5.1 Increased Efficiency
IT devices automate tasks and streamline processes, leading to significant gains in efficiency.
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks: IT devices can automate repetitive tasks, such as data entry, report generation, and customer service inquiries. According to a report by Deloitte, robotic process automation (RPA) can reduce operational costs by up to 60%.
- Faster Processing Speeds: IT devices, such as high-performance computers and servers, can process data much faster than humans. This enables organizations to handle large volumes of data quickly and efficiently.
- Improved Data Management: IT devices facilitate efficient data management through databases, data warehouses, and cloud storage solutions. These tools enable organizations to store, organize, and retrieve data easily.
5.2 Enhanced Productivity
IT devices empower employees with tools that enhance their productivity and enable them to accomplish more in less time.
- Access to Information: IT devices provide employees with access to vast amounts of information via the internet, online libraries, and corporate knowledge bases. This enables them to make informed decisions and solve problems quickly.
- Collaboration Tools: IT devices support collaboration through email, instant messaging, video conferencing, and collaboration platforms. These tools enable employees to communicate and collaborate effectively, regardless of their location.
- Mobile Devices: IT devices, such as laptops, tablets, and smartphones, enable employees to work remotely and stay connected while on the go. This flexibility enhances productivity and allows employees to balance work and personal life.
5.3 Better Communication
IT devices facilitate seamless communication and collaboration among employees, customers, and partners.
- Email: IT devices enable efficient communication via email, allowing employees to exchange messages, documents, and files quickly and easily.
- Instant Messaging: IT devices support instant messaging, allowing employees to communicate in real-time and resolve issues quickly.
- Video Conferencing: IT devices enable video conferencing, allowing employees to conduct virtual meetings, collaborate on projects, and communicate with remote team members.
- Social Media: IT devices provide access to social media platforms, allowing businesses to connect with customers, promote their products and services, and gather feedback.
5.4 Cost Reduction
IT devices can help organizations reduce costs by automating tasks, improving efficiency, and minimizing errors.
- Reduced Labor Costs: IT devices automate tasks that were previously performed by human workers, reducing the need for manual labor and lowering labor costs.
- Paperless Operations: IT devices enable paperless operations by digitizing documents, forms, and processes. This reduces the need for paper, printing supplies, and storage space.
- Energy Efficiency: IT devices, such as energy-efficient computers and servers, can help organizations reduce their energy consumption and lower their utility bills.
- Remote Work: IT devices enable remote work, allowing organizations to reduce their office space and lower their real estate costs.
5.5 Improved Decision-Making
IT devices provide access to real-time data and analytical tools that support informed decision-making.
- Data Analytics: IT devices enable organizations to collect, process, and analyze vast amounts of data, providing valuable insights for decision-making.
- Business Intelligence (BI): IT devices support BI through dashboards, reports, and data visualization tools. These tools enable decision-makers to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
- Real-Time Data: IT devices provide access to real-time data, allowing decision-makers to respond quickly to changing market conditions and customer needs.
5.6 Enhanced Security
IT devices offer advanced security features that protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Firewalls: IT devices, such as firewalls, monitor network traffic and block unauthorized access, protecting the network from cyber threats.
- Antivirus Software: IT devices support antivirus software, which detects and removes malicious software, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans.
- Encryption: IT devices enable data encryption, which protects sensitive data from unauthorized access by scrambling it into an unreadable format.
- Access Controls: IT devices provide access controls, such as passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication, to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data.
By leveraging the benefits of IT devices, organizations can enhance efficiency, productivity, communication, reduce costs, improve decision-making, and enhance security. These advantages make IT devices an essential component of modern business operations.
6. What Are the Applications of Information Technology Devices?
Information technology (IT) devices are used across a wide range of industries and applications, transforming the way businesses operate and individuals live. Their versatility and capabilities make them indispensable in today’s digital world.
6.1 Business and Finance
IT devices are essential for managing finances, processing transactions, and making data-driven decisions in the business and finance sectors.
- Financial Management: IT devices are used for managing financial transactions, tracking expenses, and generating financial reports. Accounting software, such as QuickBooks and Xero, automates accounting tasks and provides real-time financial data.
- Banking: IT devices are used for online banking, mobile banking, and ATM transactions. Banks use IT systems to process transactions, manage customer accounts, and detect fraud.
- Trading: IT devices are used for online trading, allowing investors to buy and sell stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments. Trading platforms provide real-time market data, charting tools, and order execution capabilities.
- E-commerce: IT devices are used for e-commerce, enabling businesses to sell products and services online. E-commerce platforms, such as Shopify and Magento, provide tools for managing inventory, processing orders, and accepting payments.
6.2 Healthcare
IT devices are revolutionizing healthcare by improving patient care, streamlining administrative processes, and enabling medical research.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): IT devices are used for storing and managing electronic health records, allowing healthcare providers to access patient information quickly and securely. EHR systems improve patient care by providing a comprehensive view of a patient’s medical history.
- Telemedicine: IT devices are used for telemedicine, allowing doctors to provide remote consultations, monitor patients’ conditions, and prescribe medications online. Telemedicine improves access to healthcare for patients in remote areas or with limited mobility.
- Medical Imaging: IT devices are used for medical imaging, such as MRI, CT scans, and X-rays. Medical imaging systems provide detailed images of the human body, enabling doctors to diagnose diseases and injuries more accurately.
- Medical Research: IT devices are used for medical research, enabling scientists to analyze large datasets, conduct simulations, and develop new treatments for diseases.
6.3 Education
IT devices are transforming education by providing students with access to online resources, interactive learning tools, and remote learning opportunities.
- Online Learning: IT devices are used for online learning, allowing students to access educational materials and participate in courses remotely. Online learning platforms provide flexibility and convenience, making education accessible to a wider audience.
- Virtual Classrooms: IT devices are used for virtual classrooms, allowing teachers to conduct live lessons, interact with students, and provide feedback in real-time.
- Educational Software: IT devices are used for educational software, providing students with interactive learning tools, simulations, and games that enhance their understanding of complex concepts.
- Research: IT devices provide students and researchers with access to online libraries, databases, and academic journals, facilitating research and knowledge discovery.
6.4 Manufacturing
IT devices are used for automating manufacturing processes, improving quality control, and optimizing supply chain management.
- Automation: IT devices are used for automating manufacturing processes, such as assembly, welding, and painting. Automated systems improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and minimize errors.
- Robotics: IT devices are used for controlling robots in manufacturing, enabling them to perform tasks that are too dangerous or difficult for humans.
- Quality Control: IT devices are used for quality control, enabling manufacturers to inspect products for defects, measure dimensions, and test performance.
- Supply Chain Management: IT devices are used for supply chain management, enabling manufacturers to track inventory, manage orders, and coordinate logistics.
6.5 Retail
IT devices are used for managing inventory, processing transactions, and enhancing customer experiences in the retail sector.
- Point of Sale (POS) Systems: IT devices are used for point of sale (POS) systems, allowing retailers to process transactions, manage inventory, and track sales data.
- E-commerce: IT devices are used for e-commerce, enabling retailers to sell products and services online. E-commerce platforms provide tools for managing inventory, processing orders, and accepting payments.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): IT devices are used for customer relationship management (CRM), enabling retailers to track customer interactions, personalize marketing messages, and improve customer service.
- Inventory Management: IT devices are used for inventory management, enabling retailers to track stock levels, manage orders, and optimize supply chain management.
These are just a few examples of the many applications of IT devices across various industries and sectors. Their versatility and capabilities make them an essential tool for businesses, organizations, and individuals in today’s digital world.
7. What Are the Future Trends in Information Technology Devices?
The field of information technology is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging regularly. Staying informed about these trends is crucial for businesses and individuals to remain competitive and take advantage of new opportunities.
7.1 Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming IT devices by enabling them to learn, adapt, and make decisions without human intervention.
- AI-Powered Assistants: AI-powered assistants, such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, are becoming increasingly common in IT devices. These assistants can perform tasks, answer questions, and provide personalized recommendations based on user behavior.
- Predictive Analytics: AI and ML are used for predictive analytics, enabling IT devices to forecast future trends, identify potential problems, and optimize performance.
- Automation: AI and ML are used for automating tasks, such as data entry, report generation, and customer service inquiries. Automated systems improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and minimize errors.
- Cybersecurity: AI and ML are used for cybersecurity, enabling IT devices to detect and prevent cyber threats, such as malware, phishing attacks, and data breaches.
7.2 Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is connecting everyday objects to the internet, creating a vast network of interconnected devices that can communicate, share data, and automate tasks.
- Smart Homes: IoT devices are used for smart homes, enabling homeowners to control lighting, temperature, security, and appliances remotely.
- Wearable Devices: IoT devices are used for wearable technology, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, which can monitor health metrics, track activity levels, and provide personalized recommendations.
- Smart Cities: IoT devices are used for smart cities, enabling city planners to monitor traffic patterns, optimize energy consumption, and improve public safety.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): IoT devices are used for industrial IoT (IIoT), enabling manufacturers to monitor equipment performance, optimize production processes, and improve quality control.
7.3 Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is transforming IT devices by providing access to on-demand computing resources, such as servers, storage, and software, over the internet.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Cloud computing enables software as a service (SaaS), allowing users to access software applications over the internet without having to install or maintain them on their own devices.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Cloud computing enables platform as a service (PaaS), providing developers with tools and resources for building, testing, and deploying applications in the cloud.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Cloud computing enables infrastructure as a service (IaaS), providing organizations with access to virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, over the internet.
- Hybrid Cloud: Cloud computing enables hybrid cloud deployments, allowing organizations to combine on-premises infrastructure with cloud resources to create a flexible and scalable IT environment.
7.4 Edge Computing
Edge computing is bringing computing resources closer to the edge of the network, reducing latency, improving performance, and enabling new applications.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing is used for autonomous vehicles, enabling them to process sensor data, make decisions, and control vehicle functions in real-time.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Edge computing is used for augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications, enabling them to deliver immersive experiences with low latency and high performance.
- Remote Monitoring: Edge computing is used for remote monitoring, enabling businesses to monitor equipment, track assets, and analyze data in real-time.
- Smart Retail: Edge computing is used for smart retail, enabling retailers to personalize customer experiences, optimize inventory management, and improve store operations.
7.5 Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important as IT devices become more interconnected and vulnerable to cyber threats.
- AI-Powered Security: AI and ML are used for cybersecurity, enabling IT devices to detect and prevent cyber threats, such as malware, phishing attacks, and data breaches.
- Blockchain Security: Blockchain technology is used for cybersecurity, enabling IT devices to secure data, verify transactions, and prevent fraud.
- Endpoint Security: Endpoint security is used for protecting IT devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets, from cyber threats.
- Cloud Security: Cloud security is used for protecting data and applications in the cloud from cyber threats.
These are just a few examples of the many future trends in information technology devices. As technology continues to evolve, it is important for businesses and individuals to stay informed and adapt to new trends in order to remain competitive and take advantage of new opportunities.
8. What Are Some Examples of Information Technology Devices?
Information technology devices are ubiquitous in today’s world, powering various aspects of our lives and businesses. Here are some common examples:
8.1 Computers
Computers are the cornerstone of IT, handling a wide range of tasks from data processing to running complex applications.
- Desktops: Traditional computers designed for general-purpose use, suitable for office tasks, software development, and more.
- Laptops: Portable computers that offer similar capabilities to desktops, providing flexibility for users on the go.
- Tablets: Mobile computing devices that offer a balance of portability and functionality, used for entertainment, productivity, and accessing information.
- Smartphones: Mobile phones with advanced computing capabilities, used for communication, accessing information, and running applications.
8.2 Servers
Servers are high-performance computers that manage network resources and provide services like data storage, application hosting, and web hosting.
- Web Servers: Servers that host websites and web applications, delivering content to users over the internet.
- Database Servers: Servers that store and manage databases, providing access to data for applications and users.
- File Servers: Servers that store and manage files, allowing users to share and access files over a network.
- Email Servers: Servers that manage email communications, sending, receiving, and storing email messages.
8.3 Networking Equipment
Networking equipment facilitates communication and data transfer between different components of an IT infrastructure.
- Routers: Devices that forward data packets between networks, enabling internet connectivity and internal network communication.
- Switches: Devices that connect multiple devices within a network, allowing them to communicate efficiently.
- Firewalls: Security devices that monitor network traffic and block unauthorized access, protecting the network from cyber threats.
- Wireless Access Points: Devices that provide wireless connectivity to networks, allowing users to connect their devices without physical cables.
8.4 Storage Devices
Storage devices are essential for storing data, whether it’s for short-term access or long-term archiving.
- Hard Disk Drives (HDDs): Traditional storage devices that use magnetic platters to store data, offering high capacity at a relatively low cost.
- Solid State Drives (SSDs): Storage devices that use flash memory to store data, providing faster access times and greater durability compared to HDDs.
- USB Drives: Portable storage devices that connect to computers via USB ports, used for transferring and backing up files.
- Cloud Storage: Off-site storage solutions that store data on remote servers, providing scalability, accessibility, and data redundancy.
8.5 Peripherals
Peripherals are devices that connect to computers and other IT devices, extending their functionality and providing additional input and output capabilities.
- Printers: Devices that produce hard copies of documents and images.
- Scanners: Devices that convert physical documents and images into digital formats.
- Keyboards: Input devices used to enter text and commands into a computer.
- Mice: Input devices used to navigate and interact with graphical user interfaces.
- Monitors: Output devices that display visual information, allowing users to see the results of their actions.
These are just a few examples of the many types of information technology devices that are used in homes, businesses, and organizations around the world. Their versatility and capabilities make them an essential tool for communication, productivity, and accessing information in today’s digital world.
9. How to Choose the Right Information Technology Devices?
Selecting the right IT devices is crucial for optimizing performance, enhancing productivity, and ensuring compatibility with existing systems. Consider these factors:
9.1 Identify Your Needs
Start by identifying your specific needs and requirements.
- What tasks will the device be used for? Determine the primary tasks for which the device will be used, such as word processing, data analysis, graphic design, or gaming.
- What software will you be running? Identify the software applications that will be used on the device and ensure that it meets the minimum system requirements.
- What are your portability requirements? Determine whether you need a portable device, such as a laptop or tablet, or a stationary device, such as a desktop computer.
- What is your budget? Set a budget for the IT device and look for options that offer the best value for your money.
9.2 Evaluate Performance
Assess the performance capabilities of the IT device.
- Processor: Choose a processor that is powerful enough to handle your workload. Consider factors such as clock speed, number of cores, and cache size.
- RAM: Ensure that the device has enough RAM to run your applications smoothly. The amount of RAM needed will depend on the types of applications you will be running.
- Storage: Choose a storage device that offers enough capacity and speed for your needs. Consider factors such as storage type (HDD or SSD), capacity, and access time.
- Graphics Card: If you will be using the device for gaming or graphic design, choose a graphics card that is powerful enough to handle the workload.
9.3 Consider Compatibility
Ensure that the IT device is compatible with your existing systems and devices.
- Operating System: Choose an operating system that is compatible with your applications and hardware devices.
- Ports and Connectors: Ensure that the device has the necessary ports and connectors to connect to your peripherals, such as printers, scanners, and external storage devices.
- Network Compatibility: Ensure that the device is compatible with your network infrastructure, including routers, switches, and wireless access points.
9.4 Check Reviews and Ratings
Research and read reviews and ratings from other users.
- Online Reviews: Read online reviews from reputable sources, such as tech websites, magazines, and user forums.
- Customer Ratings: Check customer ratings on e-commerce websites, such as Amazon and Best Buy.
- Expert Opinions: Consult with IT experts and professionals for their recommendations and advice.
9.5 Test the Device
If possible, test the IT device before making a purchase.
- Hands-On Testing: Visit a local electronics store and test the device in person.
- Demo Units: Ask for a demo unit to try out the device at home or in the office.
- Return Policy: Check the retailer’s return policy to ensure that you can return the device if it does not meet your expectations.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the right information technology devices to meet your specific needs, optimize performance, and enhance productivity.
10. What Are Some Common Issues with Information Technology Devices?
IT devices, while powerful and essential, are prone to various issues. Understanding these common problems can help you troubleshoot and maintain your devices effectively.
10.1 Hardware Failures
Hardware failures are among the most common issues with IT devices.
- Hard Drive Failure: Hard drives can fail due to mechanical issues, electrical problems, or data corruption. Symptoms of hard drive failure include slow performance, frequent crashes, and data loss.
- RAM Failure: RAM can fail due to manufacturing defects, overheating, or electrical surges. Symptoms of RAM failure include frequent crashes, blue screen errors, and memory errors.
- Power Supply Failure: Power supplies can fail due to overheating, electrical surges, or component failure. Symptoms of power supply failure include the device not turning on, frequent crashes, and power fluctuations.
- Motherboard Failure: Motherboards can fail due to manufacturing defects, overheating, or electrical surges. Symptoms of motherboard failure include the device not turning on, frequent crashes, and component failures.
10.2 Software Issues
Software issues can also cause problems with IT devices.
- Operating System Errors: Operating systems can experience errors due to corrupted files, driver conflicts, or software bugs. Symptoms of operating system errors include frequent crashes, blue screen errors, and slow performance.
- Driver Problems: Driver problems can occur when drivers are outdated, corrupted, or incompatible with the hardware. Symptoms of driver problems include device malfunctions, blue screen errors, and slow performance.
- Malware Infections: Malware infections can cause a variety of problems, including data loss, system crashes, and slow performance. Malware includes viruses, worms, Trojans, spyware, and adware.
10.3 Networking Problems
Networking problems can prevent IT devices from connecting to the internet or other devices on the network.
- Connectivity Issues: Connectivity issues can occur due to problems with the network adapter, router, or internet service provider. Symptoms of connectivity issues include the device not connecting to the internet, slow internet speeds, and frequent disconnections.
- IP Address Conflicts: IP address conflicts can occur when two devices on the same network have the same IP address. Symptoms of IP address conflicts include the device not connecting to the internet, slow network performance, and intermittent connectivity.
- Firewall Problems: Firewall problems can prevent IT devices from accessing certain websites or services on the internet. Symptoms of firewall problems include the device not being able to access certain websites or services, error messages, and slow performance.
10.4 Performance Issues
Performance issues can cause IT devices to run slowly or become unresponsive.
- Slow Performance: Slow performance can be caused by a variety of factors, including low RAM, a slow processor, a fragmented hard drive, or malware infections.
- Overheating: Overheating can cause IT devices to run slowly, crash frequently, or shut down unexpectedly.
- Fragmentation: Fragmentation can cause hard drives to run slowly, as the operating system has to search multiple locations to find the files it needs.
10.5 Security Vulnerabilities
Security vulnerabilities can expose IT devices to cyber threats.
- Outdated Software: Outdated software can contain security vulnerabilities that can be exploited by hackers.
- Weak Passwords: Weak passwords can be easily guessed by hackers, allowing them to gain unauthorized access to IT devices.
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing attacks can trick users into revealing their passwords or other
