Infra technology, also known as infrastructure technology, encompasses digital and non-digital solutions that drive significant improvements in economic, social, and environmental outcomes across the infrastructure lifecycle, and at pioneer-technology.com, we aim to demystify these advancements. By exploring cutting-edge infra solutions, digital platforms, and smart infrastructure, we empower you to understand and leverage the transformative power of InfraTech, smart technology, and innovative materials for sustainable progress.
1. Understanding Infra Technology
InfraTech, short for infrastructure technology, refers to digital and non-digital technologies that, when applied throughout the infrastructure lifecycle, significantly improve economic, social, or environmental outcomes. It’s about leveraging innovation to make infrastructure more efficient, sustainable, and resilient.
According to research from Stanford University’s Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, InfraTech solutions are projected to reduce infrastructure costs by up to 30% by 2030, demonstrating the significant economic benefits of adopting these technologies.
1.1. What is the Origin of the Term “InfraTech?”
The Global Infrastructure Hub (GI Hub) first used the term “InfraTech” during the Saudi Arabian G20 presidency to emphasize technology’s pivotal role in helping countries respond to crises, bridge infrastructure investment gaps, enhance resilience, and stimulate economic growth.
1.2. What is the Scope of InfraTech Solutions?
InfraTech solutions range from complex digital platforms that combine multiple technologies to support improved decision-making to simple, innovative materials that support decarbonization. What unites all InfraTech solutions is their ability to deliver improved outcomes.
1.3. Who Benefits from InfraTech?
InfraTech solutions benefit a wide range of stakeholders. For example, smart water meters at home increase access to clean water for customers. Remote monitoring of hazardous locations keeps employees safe for operators.
1.4. What Outcomes Can Be Achieved Through InfraTech?
InfraTech enables several critical outcomes, including:
- Improving the efficiency of infrastructure investment and reducing cost overruns.
- Enabling infrastructure to decarbonize and transition to net-zero.
- Creating social value through infrastructure.
- Improving the whole-life resilience of assets and systems.
Consider the application of AI and machine learning in predictive maintenance for transportation infrastructure. A study by McKinsey & Company found that these technologies can reduce maintenance costs by up to 20% and extend asset life by up to 10%. This is a concrete example of how InfraTech delivers tangible economic and operational benefits.
 InfraTech Adoption
InfraTech Adoption
1.5. What Are Examples of InfraTech in Action?
InfraTech solutions are diverse and can be applied across various infrastructure sectors. Here are a few examples:
- Smart Grids: These grids use sensors, data analytics, and automation to optimize energy distribution, reduce waste, and improve reliability. For instance, Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E) in California has implemented smart grid technologies to enhance grid resilience and integrate renewable energy sources, reducing outage times by 30%.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM is a digital representation of physical and functional characteristics of a facility. It facilitates collaboration among stakeholders, improves project planning, and reduces construction errors. According to a report by Dodge Data & Analytics, BIM adoption has led to an average of 25% reduction in project costs and 20% reduction in project timelines.
- Smart Transportation Systems: These systems use technologies like GPS, sensors, and data analytics to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve safety. The city of Los Angeles has implemented a smart traffic management system that has reduced traffic congestion by 15% and travel times by 12%.
1.6. Why is InfraTech Important?
InfraTech is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for building sustainable and resilient infrastructure. The world faces significant challenges, including climate change, population growth, and resource scarcity. InfraTech provides the tools and solutions needed to address these challenges and create a better future.
2. The Growing Importance of InfraTech
Technology in infrastructure was already a key industry trend pre-COVID, but now it has taken on a more profound purpose: to ensure the continued operation of critical infrastructure in the event of future crises, particularly the climate crisis and the current economic pressures faced by advanced, developing, and emerging economies. InfraTech is now critical for delivering sustainable and resilient infrastructure, not just a “nice to have.”
2.1. How Does InfraTech Attract and Mobilize Private Capital?
InfraTech often reduces overall project risk by providing data and analytics for better, more informed decisions across the value chain. As risks and costs are reduced or better quantified, infrastructure investment becomes more attractive to private capital, helping reduce the burden on government budgets.
2.2. How Does InfraTech Enable Doing More with Less?
InfraTech not only attracts private capital to assets but also enables cost-effective upgrades of existing infrastructure, extends asset life, and defers costly asset maintenance and renewals.
2.3. How Does InfraTech Enhance Climate Change Resilience?
By using data and analytics to automate, monitor, and optimize operations, resilience is built into the provision of infrastructure services, allowing them to operate without disruption, even during extreme weather events.
The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) estimates that the U.S. needs to invest $5.9 trillion in infrastructure by 2029 to bring it to a state of good repair. InfraTech can help bridge this funding gap by making infrastructure projects more attractive to private investors and by optimizing the use of existing infrastructure assets.
3. Key Components of Infra Technology
InfraTech encompasses a wide range of technologies that can be applied across various infrastructure sectors. Here are some of the key components:
3.1. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices, such as sensors and smart meters, collect data from physical assets and environments. This data can be used to monitor performance, detect anomalies, and optimize operations.
3.2. Big Data and Analytics
Big data analytics tools process and analyze large volumes of data collected from IoT devices and other sources. This helps identify patterns, trends, and insights that can inform decision-making.
3.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML algorithms can automate tasks, predict outcomes, and optimize processes. They can be used for predictive maintenance, traffic management, and energy optimization.
3.4. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing provides the infrastructure and platforms needed to store, process, and analyze data. It also enables remote access to data and applications.
3.5. Digital Twins
Digital twins are virtual representations of physical assets. They can be used to simulate performance, test scenarios, and optimize designs.
3.6. Blockchain
Blockchain technology can be used to improve transparency, security, and efficiency in infrastructure projects. It can be used for supply chain management, contract management, and payment processing.
3.7. Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation technologies can perform tasks that are dangerous, repetitive, or time-consuming. They can be used for construction, inspection, and maintenance.
The adoption of these technologies is not uniform across all infrastructure sectors. According to a survey by KPMG, the energy and utilities sector is the most advanced in terms of InfraTech adoption, followed by transportation and then water and wastewater. This highlights the need for targeted efforts to promote InfraTech adoption in sectors that are lagging behind.
4. Applications of Infra Technology Across Industries
InfraTech is transforming various industries, enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and resilience. Let’s explore some key applications.
4.1. Transportation
InfraTech optimizes traffic flow, reduces congestion, and enhances safety through smart traffic management systems, autonomous vehicles, and connected infrastructure.
- Smart Traffic Management: Real-time data from sensors and cameras adjusts traffic signals to optimize flow and reduce congestion.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars and trucks promise safer and more efficient transportation, reducing accidents and fuel consumption.
- Connected Infrastructure: Communication between vehicles and infrastructure (e.g., traffic lights, road sensors) enhances safety and enables coordinated traffic management.
4.2. Energy
Smart grids, renewable energy integration, and energy storage solutions optimize energy distribution, reduce waste, and enhance grid reliability.
- Smart Grids: Advanced sensors and control systems optimize energy distribution, reduce outages, and integrate renewable energy sources.
- Renewable Energy Integration: InfraTech facilitates the integration of solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources into the grid, promoting clean energy adoption.
- Energy Storage Solutions: Battery storage and other energy storage technologies enhance grid stability and enable the use of renewable energy even when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing.
4.3. Water and Wastewater
Smart water meters, leak detection systems, and advanced treatment technologies improve water management, reduce waste, and ensure water quality.
- Smart Water Meters: Real-time monitoring of water consumption helps detect leaks, reduce waste, and optimize water distribution.
- Leak Detection Systems: Advanced sensors and analytics identify leaks in water pipelines, reducing water loss and improving efficiency.
- Advanced Treatment Technologies: Innovative filtration and disinfection technologies ensure clean and safe drinking water.
4.4. Construction
Building Information Modeling (BIM), 3D printing, and drone technology enhance project planning, reduce construction errors, and improve safety.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): Digital representation of physical and functional characteristics of a facility facilitates collaboration, improves project planning, and reduces errors.
- 3D Printing: Additive manufacturing techniques enable the creation of complex building components on-site, reducing waste and construction time.
- Drone Technology: Aerial surveys and inspections provide real-time data on construction progress, improving safety and efficiency.
4.5. Urban Development
Smart city platforms, IoT-enabled infrastructure, and data analytics enhance urban planning, improve public services, and promote sustainable development.
- Smart City Platforms: Integrated data platforms collect and analyze data from various urban systems (e.g., transportation, energy, waste management) to optimize city operations.
- IoT-Enabled Infrastructure: Smart streetlights, waste management systems, and public transportation enhance efficiency and improve quality of life for residents.
- Data Analytics: Data-driven insights inform urban planning decisions, improve public services, and promote sustainable development.
The city of Barcelona, Spain, is a prime example of a city leveraging InfraTech to improve the lives of its citizens. The city has implemented a smart city platform that integrates data from various urban systems, including transportation, energy, and waste management. This platform has enabled the city to optimize resource allocation, reduce traffic congestion, and improve public safety.
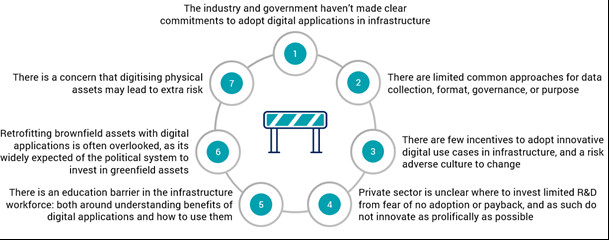
5. Overcoming Barriers to Infra Technology Adoption
Despite the numerous benefits of InfraTech, several barriers hinder its widespread adoption. Addressing these challenges is crucial for unlocking the full potential of InfraTech.
5.1. Lack of Awareness and Understanding
Many stakeholders lack awareness of the benefits and potential applications of InfraTech. Education and outreach programs can help bridge this knowledge gap.
5.2. High Upfront Costs
The initial investment in InfraTech can be significant, particularly for smaller organizations. Government incentives, grants, and innovative financing models can help reduce the financial burden.
5.3. Data Security and Privacy Concerns
The collection and analysis of large volumes of data raise concerns about security and privacy. Robust data governance frameworks and cybersecurity measures are essential.
5.4. Integration Challenges
Integrating new technologies with existing infrastructure can be complex and challenging. Open standards and interoperability protocols can facilitate seamless integration.
5.5. Regulatory Hurdles
Outdated regulations and bureaucratic processes can hinder InfraTech adoption. Streamlining regulations and creating a supportive regulatory environment can accelerate innovation.
5.6. Skills Gap
A shortage of skilled professionals who can design, implement, and maintain InfraTech solutions is a major challenge. Investing in education and training programs can help close the skills gap.
The World Economic Forum estimates that closing the infrastructure gap by 2040 would require an additional $3.7 trillion in annual investment. Overcoming the barriers to InfraTech adoption is essential for attracting this investment and ensuring that infrastructure projects are sustainable, resilient, and efficient.
6. The Role of Governments in Promoting Infra Technology
Governments play a crucial role in promoting InfraTech adoption through policy, funding, and regulation.
6.1. Policy Support
Governments can create policies that incentivize InfraTech adoption, such as tax breaks, subsidies, and grants.
6.2. Funding and Investment
Public funding can support research and development, pilot projects, and large-scale deployments of InfraTech solutions.
6.3. Regulatory Frameworks
Governments can establish clear and consistent regulatory frameworks that promote innovation while ensuring safety, security, and privacy.
6.4. Standards and Interoperability
Developing open standards and interoperability protocols can facilitate the integration of different InfraTech solutions.
6.5. Public-Private Partnerships
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) can leverage the expertise and resources of both the public and private sectors to accelerate InfraTech adoption.
The European Union’s “Digital Europe Programme” is an example of a government-led initiative that is promoting InfraTech adoption. The program provides funding for projects that develop and deploy digital technologies in areas such as smart cities, smart grids, and smart transportation.
7. Case Studies of Successful Infra Technology Implementations
Real-world examples demonstrate the transformative impact of InfraTech across various sectors.
7.1. Smart Grid in Boulder, Colorado
Boulder, Colorado, implemented a smart grid that uses advanced sensors, data analytics, and automation to optimize energy distribution and reduce waste. The smart grid has reduced energy consumption by 12% and peak demand by 18%.
7.2. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for the Shanghai Tower
The Shanghai Tower, one of the world’s tallest buildings, used BIM to improve project planning, reduce construction errors, and enhance safety. BIM helped reduce construction costs by 10% and construction time by 6 months.
7.3. Smart Transportation System in Los Angeles
Los Angeles implemented a smart traffic management system that uses real-time data from sensors and cameras to adjust traffic signals and optimize traffic flow. The system has reduced traffic congestion by 15% and travel times by 12%.
7.4. Smart Water Management in Singapore
Singapore implemented a smart water management system that uses smart water meters, leak detection systems, and advanced treatment technologies to improve water management and reduce waste. The system has reduced water loss by 20% and water consumption by 7%.
7.5. Digital Twin for the Port of Rotterdam
The Port of Rotterdam created a digital twin of the port that uses real-time data from sensors and cameras to simulate port operations and optimize logistics. The digital twin has improved port efficiency by 20% and reduced turnaround times for ships by 10%.
These case studies illustrate the tangible benefits of InfraTech, including cost savings, improved efficiency, enhanced sustainability, and increased resilience.
8. The Future of Infra Technology
InfraTech is poised for continued growth and innovation, driven by technological advancements, evolving societal needs, and increasing recognition of its potential to address global challenges.
8.1. Integration with Emerging Technologies
InfraTech will increasingly integrate with emerging technologies such as 5G, edge computing, and quantum computing.
8.2. Focus on Sustainability and Resilience
InfraTech will play a critical role in building sustainable and resilient infrastructure that can withstand the impacts of climate change and other disruptions.
8.3. Data-Driven Decision Making
Data analytics and artificial intelligence will enable more informed and data-driven decision-making in infrastructure planning, design, and operation.
8.4. Increased Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics will streamline infrastructure construction, inspection, and maintenance, reducing costs and improving safety.
8.5. Smart and Connected Infrastructure
Infrastructure will become increasingly smart and connected, enabling real-time monitoring, optimization, and control.
According to a report by Deloitte, the global smart infrastructure market is expected to reach $400 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand for sustainable, resilient, and efficient infrastructure.
9. How to Get Started with Infra Technology
Adopting InfraTech doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Here are some practical steps to get started:
9.1. Identify Your Needs and Priorities
Assess your infrastructure challenges and identify the areas where InfraTech can have the greatest impact.
9.2. Research and Explore Solutions
Explore the various InfraTech solutions available and identify the ones that best meet your needs and priorities.
9.3. Develop a Strategy and Roadmap
Create a comprehensive InfraTech strategy and roadmap that outlines your goals, objectives, and implementation plan.
9.4. Start with Pilot Projects
Begin with small-scale pilot projects to test and validate InfraTech solutions before deploying them on a larger scale.
9.5. Collaborate and Partner
Collaborate with other organizations, technology providers, and research institutions to share knowledge, expertise, and resources.
9.6. Invest in Training and Education
Invest in training and education programs to develop the skills and expertise needed to implement and maintain InfraTech solutions.
By taking these steps, you can successfully adopt InfraTech and unlock its full potential to transform your infrastructure and create a better future.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Infra Technology
Here are some common questions about InfraTech:
10.1. What is InfraTech?
InfraTech refers to digital and non-digital technologies that, when applied throughout the infrastructure lifecycle, significantly improve economic, social, or environmental outcomes.
10.2. What are the benefits of InfraTech?
InfraTech offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, improved efficiency, enhanced sustainability, increased resilience, and better decision-making.
10.3. What are the key components of InfraTech?
Key components of InfraTech include the Internet of Things (IoT), big data and analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, digital twins, blockchain, and robotics.
10.4. What are some examples of InfraTech in action?
Examples of InfraTech in action include smart grids, Building Information Modeling (BIM), smart transportation systems, and smart water management systems.
10.5. What are the barriers to InfraTech adoption?
Barriers to InfraTech adoption include lack of awareness, high upfront costs, data security concerns, integration challenges, regulatory hurdles, and skills gaps.
10.6. What is the role of governments in promoting InfraTech?
Governments can promote InfraTech through policy support, funding and investment, regulatory frameworks, standards and interoperability, and public-private partnerships.
10.7. How can I get started with InfraTech?
To get started with InfraTech, identify your needs, research solutions, develop a strategy, start with pilot projects, collaborate with partners, and invest in training.
10.8. What is the future of InfraTech?
The future of InfraTech involves integration with emerging technologies, a focus on sustainability and resilience, data-driven decision-making, increased automation, and smart and connected infrastructure.
10.9. How does InfraTech contribute to sustainability?
InfraTech promotes sustainability by optimizing resource consumption, reducing waste, integrating renewable energy sources, and enhancing the resilience of infrastructure to climate change.
10.10. Where can I learn more about InfraTech?
You can learn more about InfraTech by visiting pioneer-technology.com for updated information, in-depth analysis, and easy-to-understand explanations of pioneering technologies, and exploring resources from industry organizations, research institutions, and technology providers.
For more detailed information and real-world case studies, visit the Stanford Center for Sustainable Development and Global Competitiveness at 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States, or contact them at +1 (650) 723-2300.
Ready to explore the world of InfraTech and stay ahead of the curve? Visit pioneer-technology.com today to discover the latest articles, in-depth analysis, and cutting-edge insights into the technologies transforming our world. Stay informed, stay inspired, and unlock the potential of InfraTech with us!

