Information technology is the backbone of modern business, encompassing the use of computers, networks, and software to manage and distribute data. At pioneer-technology.com, we break down this complex field to help you understand its core components and transformative power. Whether you’re exploring career paths, seeking to enhance your business, or just curious about the digital world, understanding information technology is essential for everyone and helps to solve any problems. Dive in to discover how IT shapes our world with data management, data security, and IT infrastructure.
1. Unveiling the Essence: What Exactly Is Information Technology?
Information Technology (IT) is the application of computers, storage, networking, and other physical devices, infrastructure, and processes to create, process, store, secure, and exchange all forms of electronic data. IT is typically used in business operations, distinguishing it from technology used for personal or entertainment purposes.
Expanding on the Definition:
- Scope of IT: IT encompasses both computer technology and telecommunications, making it a broad and vital field.
- Historical Context: The term “information technology” was coined in 1958 by Harvard Business Review to differentiate between specialized machines and general-purpose computing machines.
- Evolution of IT: Since the mid-20th century, IT has evolved with increasing computing capability and decreasing costs and energy consumption, a trend that continues with emerging technologies.
2. Decoding the IT Landscape: What Does Information Technology Encompass?
The IT department ensures that an organization’s systems, networks, applications, data, and information connect and function correctly. These functions fall into three major areas.
Key Responsibilities of an IT Department:
- Deployment and Maintenance: Deploying and maintaining business applications, services, and infrastructure, including servers, networks, and storage.
- Performance Optimization: Monitoring, optimizing, and troubleshooting the performance of applications, services, and infrastructure.
- Security and Governance: Overseeing the security and governance of applications, services, and infrastructure.
Roles Within an IT Team:
- Administration: Handling the day-to-day deployment, operation, and monitoring of IT environments.
- Support: Providing help desk support, gathering information, and directing troubleshooting efforts.
- Applications: Developing and maintaining applications and interfaces to deliver critical business capabilities.
- Compliance: Ensuring adherence to government and industry regulations and securing business data.
3. Why Does Information Technology Matter? Understanding Its Significance
Data processing plays a significant role in core business practices, making IT vital for organizations of all sizes. Few businesses can remain competitive without the ability to collect data and turn it into useful information.
Key Benefits of Information Technology:
- Facilitates Communication and Collaboration: IT enables seamless communication across different locations and time zones through tools like video conferencing and instant messaging.
- Advances Pervasive Computing: Computing has penetrated every part of business and personal lives, with devices like phones, tablets, and even kitchen appliances becoming essential.
- Enhances Efficiency and Productivity: IT systems streamline processes, automate tasks, and provide real-time data access, improving overall efficiency.
- Enables Access to Information: IT provides access to vast amounts of information in databases and online libraries, empowering informed decision-making.
- Supports Innovation and Creativity: IT fosters innovation by providing platforms for creative expression and problem-solving.
- Supports Critical Business Operations: IT is essential for managing operations, finances, marketing, and customer service.
- Helps with Education and Research: IT provides access to educational resources, facilitates distance learning, and supports research endeavors.
- Provides Cost Savings: IT reduces costs associated with paper-based processes, manual labor, and physical infrastructure.
- Provides Connectivity to the Internet: IT devices connect to the internet, interconnecting billions of devices worldwide.
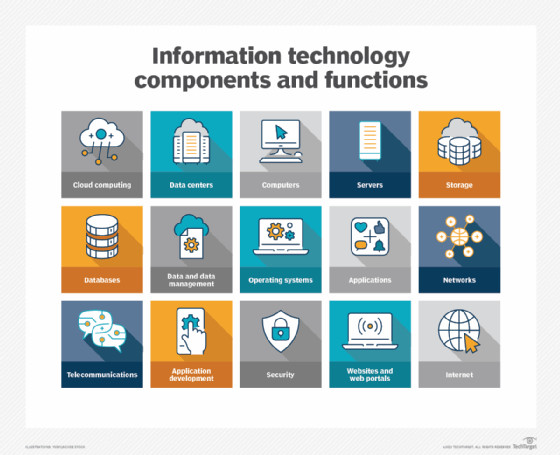 Components of IT include data, hardware, software and networking
Components of IT include data, hardware, software and networking
4. Diving into IT: What Are Some Examples of Information Technology in Action?
IT is involved in day-to-day business in many ways. Here are six common examples of IT and IT teams at work.
Examples of IT in Business Operations:
- Server Management:
- Selecting and procuring replacement servers.
- Configuring and deploying new servers.
- Backing up applications and data on existing servers.
- Transferring data and applications to new servers.
- Validating the proper functioning of new servers.
- Repurposing or decommissioning old servers.
- Security Monitoring:
- Using tools to monitor and log activity in applications, networks, and systems.
- Receiving alerts of potential threats or noncompliant behavior.
- Investigating and determining the root cause of alerts.
- Taking prompt action to address and remediate threats.
- Software Development:
- Developing new mobile applications for customer access to account information and transactions.
- Creating and refining applications according to planned roadmaps.
- Deploying back-end components of applications to the organization’s infrastructure.
- Business Improvement:
- Architecting high-availability clusters to provide greater performance and resilience for critical applications.
- Enhancing data storage protection and recovery.
- User Support:
- Creating new documentation for major application upgrades.
- Deploying upgrades for limited beta testing.
- Developing and delivering comprehensive user training.
- Digital Workplace Organization:
- Incorporating a digital filing and inventory management system.
- Scanning and storing documents electronically with relevant keywords.
- Tracking office supplies in a digital inventory database.
5. Software vs. Hardware: What Are the Main Differences?
Both software and hardware are integral and interdependent components of computer systems.
Software:
- Definition: A set of instructions that enables the hardware to perform specific tasks.
- Categories: System software (e.g., operating systems, BIOSes) and application software (e.g., databases, email servers).
- Examples: Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Exchange, SAP S/4HANA.
Hardware:
- Definition: The physical components of a computer.
- Examples: Monitors, servers, central processing units, keyboards, mice.
- Storage: Technology that holds information as data, including RAM, hard disk drives, and solid-state drives.
- Telecom Equipment: Network interface cards, cabling, wireless communications, and switching devices that connect hardware elements.
6. Abstracting Hardware and Software: How Does Abstraction Simplify Resource Management?
Abstraction simplifies resource provisioning, management, and scalability. By hiding the complexities of hardware, abstraction streamlines resource allocation and ensures optimal resource utilization.
Key Aspects of Abstraction:
- Virtualization and Cloud Computing: Physical resources are abstracted and pooled in different configurations to meet application requirements.
- Volatility: Virtualized resources can expand and contract as needed.
- Subscription-Based Resources: Resources like storage and composable architectures can be spun up as needed and released when processing is complete.
7. Information Technology vs. Computer Science: What’s the Difference?
While there’s an overlap between IT and computer science, the two disciplines are distinct and require different courses of study to prepare for careers.
Information Technology (IT):
- Focus: Application of technology to deal with business issues.
- Orientation: Developed technologies like hardware systems, OSes, and application software.
- Proficiency: Identifying hardware and software components to enhance business processes.
- Career Examples: Database administrator, cybersecurity specialist, network administrator.
- Preparation: Basic courses in hardware and software systems, business analysis, project management.
Computer Science:
- Focus: Logic and design of the underpinnings of the components that IT experts use.
- Requirements: Strong mathematics background.
- Work: Developing algorithms and logic and writing low-level code.
- Career Examples: Software developer, computer systems analyst, computer programmer.
- Preparation: Foundation in computer concepts and advanced mathematics, AI, ML, neural networks.
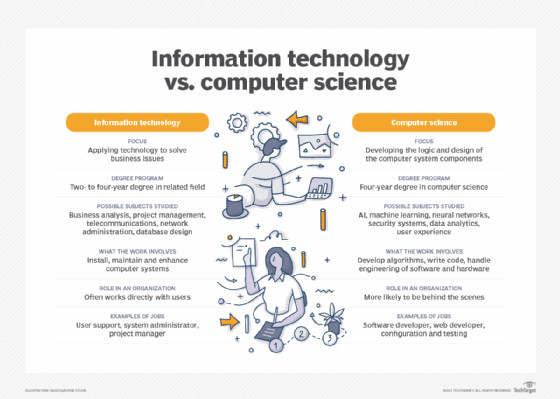 IT differs from computer science in that it's the application of technology
IT differs from computer science in that it's the application of technology
8. Charting Your Path: What Are Some Careers in Information Technology?
The information technology profession is extremely diverse. IT workers can specialize in fields, including software development, application management, hardware components, server, storage or network administration, and network architecture.
Common IT Job Titles:
- Chief Information Officer (CIO): Responsible for IT and computer systems that support the goals of the business.
- Chief Technology Officer (CTO): Sets the technology goals and policies within an organization.
- IT Director: Responsible for the functioning of the business’s technology tools and processes.
- System Administrator: Configures, manages, supports, and troubleshoots a multiuser computing environment.
- Application Manager: Focuses on the provisioning and management of high-demand business applications.
- Developer or Software Engineer: Writes, updates, and tests code for computer programs to meet business objectives.
- Chief IT Architect or IT Architect: Examines and changes IT functions to best support the business.
- Information Security Analyst: Protects organizations from threats and data breaches.
- Cloud Engineer: Manages and designs cloud-based systems for organizations.
9. Essential Skills: What IT Skills and Certifications Should You Pursue?
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 15% growth in employment within the computer and information technology sector between now and 2032. Developing technical skills is crucial for a successful IT career.
In-Demand IT Skills:
- Cybersecurity
- Cloud Computing
- Edge Computing and IoT
- IT Automation
- Software Development
- Big Data Management and Data Analytics
- DevOps
- AI
- ML
- Mobile Application Development
Highly Regarded IT Certifications:
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect — Professional
- CompTIA A+
- Certified Ethical Hacker
- Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control
- Certified Information Security Manager
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional
- Cisco Certified Network Associate
- Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect
- Microsoft role-based certifications
- Project Management Professional
- VMware Certified Professional
10. The Future of IT: Emerging Trends and Innovations
Keeping up with the latest trends and innovations in IT is crucial for staying competitive and relevant. Here are some of the key areas to watch:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- Impact: AI and ML are transforming industries by enabling automation, improving decision-making, and enhancing customer experiences.
- Applications: AI-powered chatbots for customer service, ML algorithms for data analysis, and predictive analytics for business forecasting.
- Trends: Increased adoption of AI in cybersecurity, healthcare, and finance; development of more sophisticated ML models for complex problem-solving.
- According to research from Stanford University’s Department of Computer Science: AI and ML will be integral components of most business applications, enabling increased efficiency and innovation.
Cloud Computing
- Impact: Cloud computing provides scalable and cost-effective solutions for data storage, processing, and application deployment.
- Applications: Cloud-based infrastructure for businesses, software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications, and platform-as-a-service (PaaS) environments for developers.
- Trends: Hybrid cloud solutions, multi-cloud strategies, and serverless computing are gaining traction; enhanced security features and compliance certifications for cloud services.
- According to Gartner: Worldwide end-user spending on public cloud services is forecast to reach nearly $600 billion in 2023.
Cybersecurity
- Impact: Cybersecurity is more critical than ever as businesses face increasing threats from cyberattacks and data breaches.
- Applications: Threat detection and prevention systems, data encryption, and security awareness training for employees.
- Trends: Increased focus on zero-trust security models, AI-powered threat detection, and proactive security measures to protect against evolving cyber threats.
- According to Cybersecurity Ventures: Global spending on cybersecurity is projected to reach $1.75 trillion cumulatively from 2017 to 2025.
Internet of Things (IoT)
- Impact: IoT connects devices and systems, enabling new levels of automation, data collection, and remote monitoring.
- Applications: Smart homes, wearable devices, industrial IoT (IIoT) for manufacturing, and connected vehicles.
- Trends: Integration of IoT with AI and cloud computing; enhanced security measures for IoT devices; expansion of 5G networks to support IoT connectivity.
- According to Statista: The number of connected IoT devices worldwide is forecast to reach 75 billion by 2025.
Big Data and Analytics
- Impact: Big data and analytics provide insights that drive better decision-making, improve business performance, and create new opportunities.
- Applications: Data mining, predictive analytics, and business intelligence tools for analyzing large datasets.
- Trends: Real-time data analytics, edge computing for data processing, and integration of AI and ML in analytics platforms.
- According to the International Data Corporation (IDC): Worldwide revenues for big data and business analytics are forecast to reach $274.3 billion in 2023.
Edge Computing
- Impact: Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance for applications that require real-time responses.
- Applications: Autonomous vehicles, remote healthcare monitoring, and industrial automation.
- Trends: Increased deployment of edge computing infrastructure, integration of edge computing with 5G networks, and development of edge-native applications.
- According to MarketsandMarkets: The global edge computing market is projected to reach $67.2 billion by 2027.
Blockchain Technology
- Impact: Blockchain technology provides secure and transparent solutions for data management, supply chain tracking, and digital identity verification.
- Applications: Cryptocurrency, supply chain management, healthcare data management, and digital voting systems.
- Trends: Increased adoption of blockchain in enterprise applications, development of blockchain-as-a-service (BaaS) platforms, and integration of blockchain with IoT.
- According to Gartner: Blockchain technology will generate $3.1 trillion in business value by 2030.
Quantum Computing
- Impact: Quantum computing has the potential to solve complex problems that are beyond the capabilities of classical computers.
- Applications: Drug discovery, materials science, financial modeling, and cryptography.
- Trends: Development of more stable and scalable quantum computers, increased investment in quantum computing research, and exploration of quantum algorithms for specific applications.
- According to McKinsey: Quantum computing could create value ranging from $50 billion to $100 billion by 2030.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
- Impact: AR and VR technologies enhance user experiences and create new opportunities for training, collaboration, and entertainment.
- Applications: Training simulations, remote collaboration tools, and immersive gaming experiences.
- Trends: Increased adoption of AR in retail, healthcare, and education; development of more affordable and user-friendly VR headsets; integration of AR and VR with 5G networks.
- According to PwC: AR and VR technologies are projected to add $1.5 trillion to the global economy by 2030.
5G Technology
- Impact: 5G technology provides faster and more reliable wireless connectivity, enabling new applications and services.
- Applications: Enhanced mobile broadband, massive machine-type communications (mMTC) for IoT, and ultra-reliable low latency communications (URLLC) for critical applications.
- Trends: Increased deployment of 5G networks, integration of 5G with edge computing, and development of 5G-enabled devices and applications.
- According to Ericsson: There will be 4.4 billion 5G subscriptions worldwide by the end of 2027.
By staying informed about these emerging trends and innovations, businesses and individuals can better prepare for the future and leverage the power of IT to drive success.
FAQ: Your Top Questions About Information Technology Answered
-
What is the primary goal of information technology?
The primary goal is to manage and use information to meet the goals of an organization or individual, enhancing efficiency and productivity. -
How does information technology benefit businesses?
IT improves communication, streamlines operations, provides access to critical information, and supports innovation, helping businesses stay competitive. -
What are the main components of an IT system?
The main components include hardware, software, networks, data, and the people who manage and use the system. -
What is the role of an IT department in a company?
An IT department manages the company’s technology infrastructure, ensures data security, provides technical support, and aligns IT strategy with business goals. -
What is the difference between IT and computer engineering?
IT focuses on using technology to solve practical problems, while computer engineering involves designing and building computer systems and hardware. -
What skills are essential for an IT professional?
Essential skills include technical proficiency, problem-solving abilities, communication skills, and the ability to adapt to new technologies. -
How is information technology used in healthcare?
IT is used for electronic health records, telemedicine, medical imaging, data analysis, and improving patient care and operational efficiency. -
What are the ethical considerations in information technology?
Ethical considerations include data privacy, security, intellectual property rights, and responsible use of AI and automation. -
How can I start a career in information technology?
Start with education or certifications in IT-related fields, gain practical experience through internships, and stay updated with the latest technology trends. -
What are the emerging trends in information technology?
Emerging trends include AI, cloud computing, cybersecurity, IoT, big data analytics, edge computing, blockchain, quantum computing, AR/VR, and 5G technology.
Unlock the full potential of technology with pioneer-technology.com, your gateway to understanding and mastering the ever-evolving world of IT.
Are you ready to dive deeper into the world of technology and discover how it can transform your business or career? Visit pioneer-technology.com today to explore our in-depth articles, cutting-edge analysis, and expert insights on the latest technology trends in the USA. Stay ahead of the curve and unlock new opportunities with our comprehensive resources.

