Microsoft cloud technology is the backbone for modern businesses, offering a suite of services to enhance scalability and innovation; pioneer-technology.com provides expert analysis and insights. This robust platform helps organizations leverage cloud computing, data analytics, and AI to stay competitive. Explore the cutting-edge advancements and strategic advantages that Microsoft cloud technology brings to the forefront of the digital era.
1. Understanding Microsoft Cloud Technology
Is Microsoft cloud technology just another buzzword, or does it truly revolutionize how businesses operate? The answer is a resounding yes; Microsoft cloud technology transforms business operations. Let’s dive deeper into what this entails.
Microsoft cloud technology, primarily represented by Azure, is a comprehensive suite of cloud computing services that includes everything from compute power and storage to advanced analytics and artificial intelligence (AI). According to research from Stanford University’s Department of Computer Science, cloud adoption will increase by 40% in the next five years, with Microsoft Azure leading the charge. This platform enables businesses to build, deploy, and manage applications through a global network of data centers.
1.1. Defining Microsoft Cloud Services
What are the core components of Microsoft cloud services? They comprise Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), and serverless computing.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This provides you with computing infrastructure—servers, networking, and storage—over the internet. This is like renting the raw materials to build your own house.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): This offers a platform allowing developers to build, run, and manage applications without handling the underlying infrastructure. Think of it as renting a fully equipped kitchen where you can cook anything you want.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): This delivers software applications over the internet, on demand, typically on a subscription basis. This is like ordering takeout—you get the finished product without worrying about the cooking.
- Serverless Computing: This enables you to run code without provisioning or managing servers. You only pay for the compute time you consume.
Microsoft’s cloud strategy, according to a recent report from Gartner, focuses on hybrid cloud solutions, allowing organizations to seamlessly integrate on-premises infrastructure with cloud resources.
1.2. The Evolution of Microsoft Cloud
How has Microsoft’s cloud platform evolved over the years? Starting as Windows Azure in 2008, it has grown into a powerhouse of cloud solutions.
Initially, Azure was primarily a Platform as a Service (PaaS) offering, designed to provide developers with an environment to build and deploy applications. However, Microsoft quickly realized the growing demand for more flexible solutions. This led to the expansion of Azure’s capabilities to include Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), allowing businesses to migrate their existing infrastructure to the cloud.
The rebranding to Microsoft Azure in 2014 signified a broader scope, encompassing a wider range of services and capabilities beyond just Windows-based applications. The evolution continued with the introduction of advanced services like Azure Machine Learning, Azure IoT Hub, and Azure AI Platform, catering to the rising demand for data analytics and artificial intelligence.
Today, Microsoft Azure stands as one of the leading cloud platforms globally, competing with Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Its continuous evolution ensures it remains at the forefront of cloud technology, providing cutting-edge solutions for businesses of all sizes.
1.3. Key Benefits of Adopting Microsoft Cloud Technology
Why should businesses consider adopting Microsoft cloud technology? It’s about scalability, cost efficiency, and innovation.
- Scalability: Azure allows businesses to easily scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance without overspending.
- Cost Efficiency: The pay-as-you-go model means organizations only pay for what they use, reducing capital expenditure.
- Innovation: Azure provides a wide array of tools and services that facilitate the development of new applications and solutions, fostering innovation.
- Global Reach: With data centers around the world, Azure ensures high availability and low latency for users globally.
- Security: Microsoft invests heavily in security, providing a secure cloud environment that helps protect data and applications.
According to a study by Forrester, businesses that migrate to the cloud can see a 20-40% reduction in IT costs and a significant increase in agility.
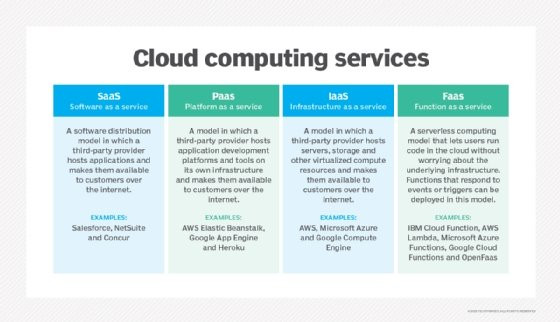 Types of cloud computing services offered by Microsoft Azure.
Types of cloud computing services offered by Microsoft Azure.
2. Diving Deeper: How Microsoft Azure Works
How does Microsoft Azure actually work? It operates through a global network of data centers and a structured service model.
Microsoft Azure functions via a vast network of data centers distributed across the globe. These data centers provide the physical infrastructure needed to run cloud services. When you subscribe to Azure, you gain access to a portal where you can manage and deploy resources. You can create virtual machines, databases, and other services, then assemble them into functioning environments to host your workloads and store data.
2.1. The Infrastructure Behind Azure
What powers Azure’s robust performance? High availability and reliability are ensured through a global network of data centers.
Azure’s infrastructure comprises over 60 regions with hundreds of data centers worldwide. Each region consists of multiple availability zones, which are physically separate locations within a region. This ensures that if one data center experiences an issue, services can failover to another zone, maintaining high availability.
According to Microsoft, they invest billions of dollars annually in their cloud infrastructure to ensure it remains state-of-the-art and capable of meeting the growing demands of their customers.
2.2. Core Services Offered by Azure
What are the fundamental services that Azure offers? These include computing, storage, networking, and databases.
- Computing: Azure offers a range of computing options, including Virtual Machines (VMs), Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), and Azure Functions. VMs allow you to run any operating system and application, while AKS simplifies the deployment and management of containerized applications. Azure Functions enables serverless computing, allowing you to run code without managing servers.
- Storage: Azure provides various storage solutions, including Azure Blob Storage for unstructured data, Azure Files for file shares, and Azure Queue Storage for message queuing.
- Networking: Azure Networking services include Virtual Network, Azure Load Balancer, and Azure DNS. These services allow you to create isolated networks, distribute traffic, and manage domain name resolution.
- Databases: Azure offers a variety of database services, including Azure SQL Database, Azure Cosmos DB, and Azure Database for MySQL. Azure SQL Database is a fully managed relational database, while Azure Cosmos DB is a globally distributed, multi-model database.
2.3. Integrating Third-Party Applications with Azure
Can you integrate third-party applications with Azure? Absolutely, many vendors make their software available directly through Azure.
The Azure Marketplace offers a wide range of third-party applications that can be easily deployed and integrated with Azure services. This allows businesses to leverage specialized tools and services without needing to build them from scratch. The costs for these applications vary, often involving a subscription fee plus usage fees for the underlying infrastructure.
2.4. Customer Support Options for Azure
What kind of support can you expect from Microsoft for Azure? Microsoft offers several support plans, ranging from basic to enterprise-level.
Microsoft provides five different customer support options for Azure:
- Basic: Included with all Azure accounts, providing access to online documentation and community support.
- Developer: Offers technical support for development and testing environments.
- Standard: Provides technical support for production environments with a service level agreement (SLA).
- Professional Direct: Offers enhanced support with a dedicated support engineer.
- Enterprise (Premier): Provides the highest level of support with proactive services and personalized guidance.
These support plans vary in scope and price, with the Developer support costing $29 per month, Standard support at $100 per month, and Professional Direct support at $1,000 per month. Pricing for Enterprise support is not publicly disclosed.
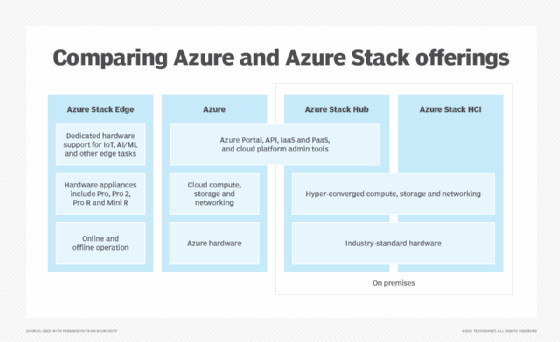 Chart comparing Azure Stack offerings: Azure Stack Edge, Azure, Azure, Azure Stack Hub and Azure Stack HCI.
Chart comparing Azure Stack offerings: Azure Stack Edge, Azure, Azure, Azure Stack Hub and Azure Stack HCI.
3. Real-World Applications: What is Microsoft Azure Used For?
How is Microsoft Azure being used in practice? Its diverse services make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Microsoft Azure is used for a plethora of applications, ranging from running virtual machines and hosting databases to developing and deploying AI models. Its versatility makes it an indispensable tool for modern businesses.
3.1. Running Containers and Virtual Machines
Why is Azure popular for running containers and VMs? It provides scalable compute resources for various infrastructure components.
Running virtual machines (VMs) or containers in the Microsoft cloud is one of the most popular uses for Microsoft Azure. These compute resources can host infrastructure components, such as domain name system (DNS) servers, Windows Server services, such as Internet Information Services, networking services, such as firewalls, or third-party applications. Microsoft also supports the use of third-party operating systems, such as Linux.
3.2. Hosting Databases in the Cloud
How does Azure simplify database management? It offers serverless relational and nonrelational databases.
Azure is also commonly used as a platform for hosting databases in the cloud. Microsoft offers serverless relational databases, such as Azure SQL, and nonrelational databases, such as NoSQL. These services provide scalable and fully managed database solutions, reducing the operational overhead for businesses.
3.3. Backup and Disaster Recovery Solutions
Why choose Azure for backup and disaster recovery? It provides reliable and cost-effective archival storage.
The Azure platform is frequently used for backup and disaster recovery. Many organizations use Azure for archival storage in order to meet their long-term data retention or disaster recovery requirements. Azure’s global network of data centers ensures that data is replicated across multiple locations, providing resilience against data loss.
3.4. Application Development and Hosting
How does Azure streamline application development? Its PaaS capabilities enable instant deployment and scaling.
The Azure platform is utilized for application development, hosting, and testing. With Azure’s PaaS capabilities, developers can instantly deploy and scale apps without managing the underlying infrastructure or code. This speeds up the development lifecycle and allows developers to focus on building features.
3.5. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
What AI tools does Azure offer? Azure Machine Learning and Azure AI Studio are powerful resources for building and deploying AI models.
Azure offers various ML tools, including Azure Machine Learning and Azure AI Studio, that businesses can utilize to build, deploy, and train ML models. These tools are especially beneficial for organizations adopting ML and AI for predictive analytics, customer insights, and automation.
3.6. Internet of Things (IoT) Applications
How does Azure support IoT solutions? It provides a comprehensive suite of services for connecting and managing IoT devices.
Azure provides a comprehensive suite of services designed specifically for IoT applications, including Azure IoT Hub and Azure Stream Analytics. These tools assist organizations in connecting, monitoring, and managing IoT devices and facilitate real-time data collection and analysis.
4. The Advantages: Benefits of Azure for Modern Businesses
What are the key advantages of using Microsoft Azure for modern businesses? Scalability, cost efficiency, and global reach are just the beginning.
Microsoft Azure provides numerous advantages that are specifically designed to meet the needs of contemporary businesses. These benefits include scalability, cost efficiency, AI and advanced analytics, global reach and high availability, security and compliance, modern development processes, hybrid cloud capabilities, and support for open source technologies.
4.1. Scalability and Flexibility
How does Azure help businesses scale? Resources can be quickly adjusted based on demand.
Azure enables businesses to quickly adjust resources based on their demand. For example, the resources can be scaled up or down during rapid business growth or seasonal shifts. This flexibility ensures that businesses can optimize their resource utilization and avoid over-provisioning.
4.2. Cost Efficiency and Savings
What kind of cost savings can you expect from Azure? Migrating to Azure can substantially lower IT costs.
Migrating to Azure can substantially lower the IT costs for businesses compared to maintaining their own on-premises infrastructure. With a PAYG pricing model, organizations only pay for the resources they use, helping them manage budgets and reduce capital expenses.
4.3. AI and Advanced Analytics
How does Azure enhance decision-making? It offers advanced analytics tools and AI services.
Azure offers advanced analytics tools and AI services that help businesses extract valuable insights from their data and enhance their decision-making processes. These tools enable businesses to identify trends, predict outcomes, and optimize their operations.
4.4. Global Reach and High Availability
Why is Azure’s global infrastructure important? It ensures applications and data are accessible from anywhere.
Azure’s global infrastructure enables businesses to access applications and data from anywhere and also ensures high availability and redundancy. For example, even if one component fails, applications and data remain accessible to the end users.
4.5. Security and Compliance Measures
How does Azure ensure data security? It provides multilayered protection and compliance certifications.
Azure provides enhanced security through its multilayered protection across its data centers and infrastructure. The platform includes various security measures and compliance certifications, enabling businesses to safeguard their data from threats, maintain customer trust, and meet regulatory standards.
4.6. Modern Development Processes
How does Azure support modern development? It accommodates a range of development frameworks and tools.
Azure accommodates a range of development frameworks and tools, facilitating the adoption of modern practices such as DevOps. This fosters collaboration and also speeds up the application development lifecycle.
4.7. Hybrid Cloud Capabilities
What are the benefits of Azure’s hybrid cloud? It enables organizations to combine on-premises resources with cloud services.
Azure facilitates hybrid cloud environments, enabling organizations to effortlessly combine on-premises resources with cloud services. This setup is especially helpful for businesses that require a blend of both compliance and performance needs.
4.8. Support for Open Source Technologies
Why is open source support important? It provides organizations with the flexibility to use their preferred systems and frameworks.
To provide organizations with the flexibility to utilize their preferred systems and frameworks, Azure is compatible with a broad range of open source tools and technologies, such as Linux and Kubernetes.
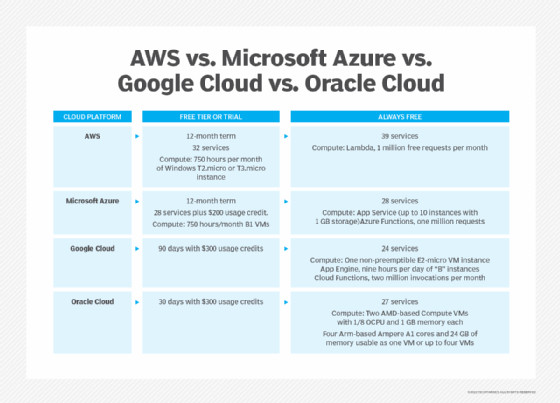 Chart comparing Oracle, AWS, Azure and Google cloud platforms and their services.
Chart comparing Oracle, AWS, Azure and Google cloud platforms and their services.
5. Common Concerns: Addressing Privacy and Security in Azure
How does Microsoft address privacy and security concerns in Azure? Data protection and regulatory compliance are top priorities.
Data security concerns and regulatory compliance requirements make privacy a major issue for cloud subscribers. To address these worries, Microsoft has created the online Trust Center, which provides detailed information about the company’s security, privacy, and compliance initiatives.
5.1. Microsoft’s Commitment to Data Privacy
What assurances does Microsoft provide regarding customer data? Data is only used to provide agreed-upon services.
According to the Trust Center, Microsoft will only use customer data if it is necessary to provide the agreed-upon services, and it will never disclose customer data to government agencies unless it is required by law.
5.2. Security Services Offered by Azure
What security services does Azure offer? Identity and access management (IAM) and firewalls are critical.
Azure provides numerous security services, such as identity and access management (IAM) and firewalls, to help Azure users establish a secure infrastructure and monitor for intrusion in a timely manner. Security services are critical to public cloud adoption by helping users safeguard the privacy of sensitive data and important workloads.
6. Navigating Costs: Azure Pricing and Cost Management
How does Azure pricing work, and how can you manage costs effectively? Understanding the pay-as-you-go model and utilizing cost management tools is essential.
Similar to other public cloud providers, Azure primarily uses a PAYG pricing model that charges based on usage. However, if a single application uses multiple Azure services, each service might involve multiple pricing tiers. It’s common for one service to use a subset of other services — each adding to the total cost of the intended service.
6.1. Understanding the Pay-As-You-Go Model
What does pay-as-you-go mean in practice? You only pay for the resources you consume.
The pay-as-you-go (PAYG) model means that you are only charged for the specific resources and services that you use. This can include compute time, storage, network bandwidth, and other services. This model allows for greater flexibility and cost control compared to traditional fixed-cost IT infrastructure.
6.2. Factors Influencing Azure Costs
What factors affect Azure costs? VM usage, storage, networking, and reporting tools all contribute.
For example, a common application running in a VM might incur one cost. The storage instance associated with the workload might incur a second cost. Networking services and reporting tools might all drive additional costs for the workload. Alternatively, services such as Azure Functions are free, but users pay for the compute and other resources needed to run the function for the duration of the function’s execution — usually to the closest second.
6.3. Strategies for Cost Optimization
How can you minimize Azure costs? Reviewing and managing cloud usage is crucial.
Given the many factors involved in cloud service pricing, an organization should review and manage its cloud usage to minimize costs. Azure-native tools, such as Microsoft Cost Management, can help monitor, visualize, and optimize cloud spending. It’s also possible to use third-party tools, such as IBM Cloudability, along with emerging FinOps practices to manage Azure resource usage and associated costs.
7. Staying Informed: Significant Azure Outages
What should you know about Azure outages? Understanding past incidents helps in planning for resilience.
Microsoft Azure has a history of major outages dating back to early 2012. Reviewing these incidents helps users understand potential risks and the importance of having robust disaster recovery plans.
7.1. Notable Outages in Azure History
What are some significant Azure outages? Past incidents include DNS issues, cooling system failures, and DDoS attacks.
Here are some of the more significant outages that have occurred over the years:
- Feb. 29, 2012: A disruption occurred as a result of the leap day bug.
- July 26, 2012: The West Europe region experienced an interruption that lasted for about two and a half hours.
- Feb. 22, 2013: A major outage prevented customers across all regions from being able to access Windows Azure Storage Blobs, tables, and queues using HTTPS.
- Oct. 30, 2013: Users across the United States, Europe, and Asia experienced an outage lasting for about eight hours. This outage was attributed to an issue with swapping virtual IP addresses.
- Nov. 18, 2014: An outage lasting for nearly 10 hours caused storage connectivity issues.
- Dec. 3, 2015: Many customers in Europe were unable to access Office 365 for approximately four hours.
- Sept. 15, 2016: A DNS issue caused problems for Azure users around the world for several hours.
- March 15, 2017: An issue in one of Microsoft’s data centers spread around the world and ultimately affected 26 of Microsoft’s 28 data centers, resulting in a worldwide outage that lasted for about seven hours.
- Sept. 29, 2017: A seven-hour outage occurred in northern Europe due to the accidental discharge of a fire suppression system.
- June 20, 2018: Customers in northern Europe experienced an outage lasting nearly 11 hours following a temperature issue at one of the data centers.
- Sept. 4, 2018: Lightning strikes caused a voltage increase in a south-central United States data center, resulting in issues with the cooling system. Customers across 10 regions were ultimately affected because of service dependencies.
- May 2, 2019: A DNS outage caused several Azure services to become unavailable for nearly three hours.
- March 15, 2021: An Azure Active Directory outage caused a 14-hour outage in multiple Microsoft services, including Azure, Office, Teams, Dynamics 365, Xbox Live, and more. A smaller DNS outage followed on April 1, 2021.
- Oct. 13, 2021: Azure VM services and some other Azure services became unavailable for about eight hours.
- Jan. 23, 2023: Azure faced a three-hour outage affecting its core Microsoft 365 offerings, including services such as Outlook and Teams. This disruption was attributed to network issues within Azure, which affected a wide range of users and organizations relying on these services.
- July 30, 2024: Azure suffered a major global outage lasting for almost eight hours, which affected various Microsoft services, including Azure, Microsoft 365 products, and LinkedIn. This global outage was a result of a sophisticated DDoS attack, which was worsened by a vulnerability in Microsoft’s DDoS Protection Standard.
7.2. Resources for Tracking Azure Status
Where can you find information on current and past Azure incidents? The Azure status history page provides detailed information.
Microsoft maintains a complete index of all outages/issues for the last five years. Users can research specific outages, detailed implications, underlying causes, and fixes at Microsoft’s Azure status history page.
8. Competitive Landscape: Azure vs. Other Cloud Providers
How does Azure compare to other major cloud providers? Understanding the competitive landscape helps in making informed decisions.
Microsoft Azure is one of several major public cloud service providers operating on a large global scale. Other major clouds include Google Cloud, AWS, Oracle, IBM Cloud, and Alibaba Cloud. Currently, there is a lack of standardization among cloud services and capabilities.
8.1. Key Competitors in the Cloud Market
Who are Azure’s main competitors? AWS, Google Cloud, and others offer similar services.
Most cloud providers offer a broad suite of similar services, but no two cloud providers offer the same service in the exact same way. Cloud providers rely on APIs and other integrations to handle provisioning and services programmatically.
8.2. Distinguishing Features of Azure
What sets Azure apart from its competitors? Hybrid cloud capabilities and open source support are key differentiators.
Because each provider uses unique APIs, the onus is on users to accommodate differences between cloud providers. Thus, migrating a workload from one cloud to another might require significant recoding of the application or rearchitecting of the cloud environment to support the workload. This makes it difficult for a business to use more than one public cloud provider when pursuing a multi-cloud strategy. Third-party cloud management tools can reduce some of these challenges.
8.3. Alternatives for Small to Midsize Businesses
Are there other options besides the major cloud providers? DigitalOcean is a popular alternative.
In addition to major cloud providers, Azure faces competition in the small to midsize sector. For example, DigitalOcean is a popular alternative for small to midsize companies looking for cloud services.
9. A Look Back: The History of Microsoft Azure
How did Azure become the cloud platform it is today? Its evolution from Windows Azure to a comprehensive cloud suite is a story of innovation.
Microsoft first unveiled its plans to introduce a cloud computing service called Windows Azure in 2008. Preview versions of the service became available and developed, leading to its commercial launch in early 2010. Although early iterations of Azure cloud services fell behind more established offerings, such as AWS, the portfolio continued to evolve and support a larger base of programming languages, frameworks, and operating systems.
9.1. The Early Days of Windows Azure
What was the initial vision for Azure? It started as a platform for developers.
Initially, Azure was primarily a Platform as a Service (PaaS) offering, designed to provide developers with an environment to build and deploy applications. However, Microsoft quickly realized the growing demand for more flexible solutions.
9.2. The Rebranding to Microsoft Azure
Why was the name changed? It reflected a broader scope beyond Windows-based services.
In 2014, Microsoft rebranded Windows Azure to Microsoft Azure, reflecting its broader scope beyond just Windows-based services. By early 2014, Microsoft had added and updated a wide range of services including Azure SQL, Windows Azure CTP, Windows Azure Connect, Traffic Manager, and HPC scheduler. Microsoft recognized that the implications of cloud computing stretched far beyond Windows, and the service was rebranded as Microsoft Azure. In addition, Azure rolled out the first public previews of Machine Learning services.
9.3. Key Milestones in Azure’s Development
What are some significant milestones in Azure’s growth? The introduction of key services like Azure Resource Manager and Azure IoT Central marked significant progress.
In the following years, Azure introduced Sonic (a cross-platform Linux distribution), Azure Resource Manager Portal (2015), Azure Service Fabric (2016), Azure Service Fabric Mesh (2018), and Azure IoT Central (2018). Today, Azure is regarded as a strong commercial competitor to other public cloud providers.
10. Securing Your Cloud: IAM Frameworks in Azure
How do IAM frameworks in Azure help secure your cloud environment? They provide robust identity and access control.
All major cloud providers, including Microsoft Azure, Amazon AWS, and Google Cloud, offer robust IAM frameworks, but they differ in their features, configuration, resource hierarchy, and pricing models.
10.1. Importance of IAM in Cloud Security
Why is IAM crucial for cloud security? It helps protect sensitive data and workloads.
IAM is critical to public cloud adoption by helping users safeguard the privacy of sensitive data and important workloads. It ensures that only authorized users have access to specific resources, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
10.2. Comparing IAM Services Across Providers
How do IAM services differ between Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud? Understanding these differences is key to selecting the right option.
Compare these IAM differences to help select the best option for your organizational needs and technology ecosystems. Each provider offers unique features and capabilities, so it’s important to evaluate your specific requirements and choose the framework that best aligns with your security policies.
10.3. Best Practices for Implementing IAM in Azure
What are the best practices for implementing IAM in Azure? Implementing multi-factor authentication and regularly reviewing access controls are crucial steps.
To effectively implement IAM in Azure, it’s essential to follow best practices such as using multi-factor authentication, regularly reviewing access controls, and implementing the principle of least privilege. This ensures that users only have access to the resources they need, minimizing the potential impact of security breaches.
FAQ: Understanding Microsoft Cloud Technology
1. What exactly is Microsoft cloud technology?
Microsoft cloud technology, primarily known as Azure, is a comprehensive suite of cloud computing services providing computing power, storage, analytics, and AI. It enables businesses to build, deploy, and manage applications through a global network of data centers.
2. How does Microsoft Azure differ from other cloud platforms?
Azure distinguishes itself with its hybrid cloud capabilities, robust security features, and strong support for open-source technologies. It seamlessly integrates with existing Microsoft products and offers a wide range of services tailored to various business needs.
3. What are the main benefits of using Microsoft Azure for my business?
Key benefits include scalability, cost efficiency, innovation, global reach, and enhanced security. Azure’s pay-as-you-go model helps manage budgets, while its AI and analytics tools enhance decision-making.
4. Is Microsoft Azure secure enough for sensitive business data?
Yes, Azure provides enhanced security through multilayered protection across its data centers and infrastructure. It includes various security measures and compliance certifications, enabling businesses to safeguard their data from threats and meet regulatory standards.
5. How can I manage and optimize costs when using Microsoft Azure?
Use Azure-native tools like Microsoft Cost Management and third-party tools such as IBM Cloudability to monitor, visualize, and optimize cloud spending. Regularly review and manage cloud usage to minimize costs.
6. What support options are available if I encounter issues with Azure?
Microsoft offers five different customer support options for Azure: Basic, Developer, Standard, Professional Direct, and Enterprise (Premier). These plans vary in scope and price, catering to different needs and levels of support.
7. Can I integrate third-party applications with Microsoft Azure?
Yes, the Azure Marketplace offers a wide range of third-party applications that can be easily deployed and integrated with Azure services, allowing businesses to leverage specialized tools without building them from scratch.
8. How does Microsoft ensure data privacy in Azure?
Microsoft is committed to data privacy and only uses customer data as necessary to provide agreed-upon services. The online Trust Center provides detailed information about Microsoft’s security, privacy, and compliance initiatives.
9. What are some common use cases for Microsoft Azure?
Common use cases include running containers and virtual machines, hosting databases in the cloud, backup and disaster recovery solutions, application development and hosting, machine learning and artificial intelligence, and Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
10. How can I stay updated on the latest Azure features and services?
Stay updated by regularly visiting the pioneer-technology.com for detailed insights, analyses, and updates on Microsoft Azure and other leading cloud technologies.
Microsoft cloud technology is a game-changer for businesses aiming to thrive in the digital age. From its robust infrastructure and diverse services to its commitment to security and innovation, Azure offers a comprehensive solution for modern IT challenges. Embrace the power of the cloud and unlock new possibilities for your organization.
Ready to explore the full potential of Microsoft Azure and stay ahead of the curve in cloud technology? Visit pioneer-technology.com today to discover our in-depth articles, expert analyses, and latest updates on the world’s leading tech platforms. Don’t miss out on the insights that will drive your business forward.

