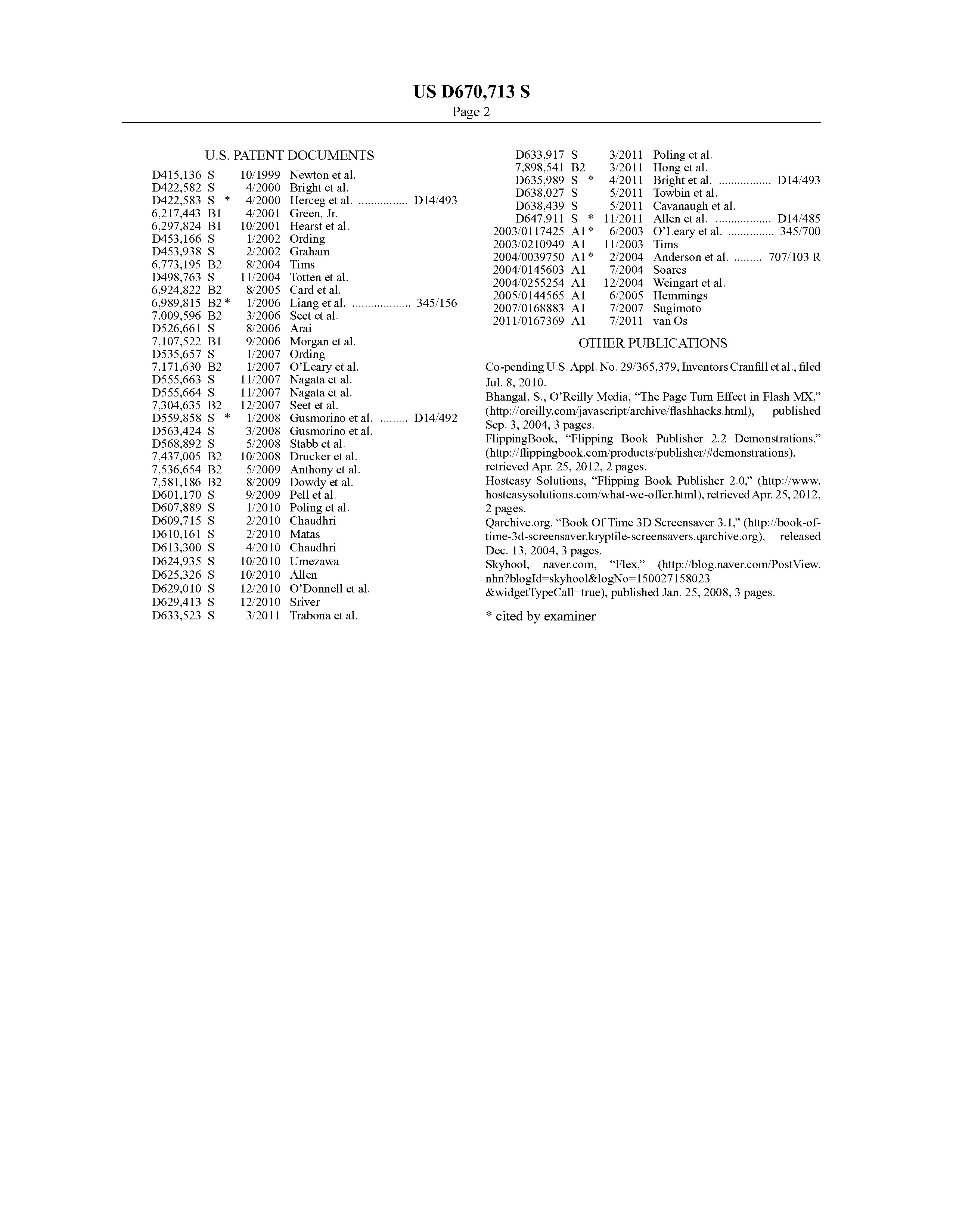
Patent technology, a cornerstone of innovation, safeguards intellectual property and fosters technological advancement. At pioneer-technology.com, we unravel the complexities of patent technology, offering insights into its definition, applications, and profound benefits. Explore cutting-edge innovations, discover intellectual asset protection strategies, and delve into the realm of technology patents with us.
1. What is Patent Technology?
Patent technology is a legally protected innovation, granting exclusive rights to the inventor for a specified period. This legal protection prevents others from manufacturing, using, or selling the invention without permission, thereby incentivizing innovation and investment in research and development.
A patent is an exclusive right granted for an invention, which allows the patent holder to exclude others from making, using, or selling the invention. Patents are a critical component of the intellectual property system, encouraging innovation by providing inventors with a period of exclusivity to profit from their inventions. This exclusivity encourages further investment in research and development, leading to new and improved technologies that benefit society. According to a study by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO), patents significantly contribute to economic growth, job creation, and global competitiveness.
1.1. Key Aspects of Patent Technology
- Legal Protection: Patents provide a legal framework to protect inventions from unauthorized use, ensuring inventors can reap the rewards of their creativity and hard work.
- Exclusive Rights: Patent holders have the exclusive right to make, use, and sell their inventions for a set period, typically 20 years from the date of application.
- Incentive for Innovation: Patents incentivize innovation by offering inventors a period of market exclusivity, allowing them to recoup their investment and generate profits.
1.2. The Role of Patent Technology in Innovation
Patent technology plays a vital role in driving innovation across various industries. By providing legal protection and exclusive rights, patents encourage inventors and businesses to invest in research and development, leading to new and improved products, processes, and services. This fosters a competitive environment, driving technological advancement and economic growth.
Consider the pharmaceutical industry, where patents are critical for protecting new drugs and therapies. Developing a new drug can cost billions of dollars and take many years of research. Patents allow pharmaceutical companies to recoup their investment and continue to innovate, leading to new treatments for diseases and improved healthcare outcomes.
2. What Technologies Can Be Patented?
Various technologies can be patented, encompassing design, plant, and utility patents, each safeguarding different aspects of innovation. These patents cover a wide range of inventions, from novel designs to new plant varieties and useful processes, machines, and compositions of matter.
- Design Patents: Protect the ornamental design of a functional item.
- Plant Patents: Protect new and distinct plant varieties.
- Utility Patents: Protect new and useful inventions, including processes, machines, manufactures, and compositions of matter.
2.1. Design Patents: Protecting Ornamental Designs
Design patents protect the ornamental design of a functional item, such as the shape, configuration, or surface ornamentation. These patents are granted for products with unique visual attributes, ensuring that competitors cannot replicate the aesthetic appeal of the product.
For example, Apple has secured numerous design patents for the distinctive appearance of its iPhones and other devices. These patents protect the unique design elements of Apple’s products, preventing competitors from creating products that look too similar.
Apple iPhone design patent highlighting the importance of protecting ornamental designs.
2.2. Plant Patents: Safeguarding New Plant Varieties
Plant patents protect new and distinct plant varieties that have been asexually reproduced. These patents grant the inventor the exclusive right to reproduce, sell, and use the new plant variety, encouraging innovation in agriculture and horticulture.
For instance, a plant breeder who develops a new variety of rose with unique color and fragrance can obtain a plant patent to protect their invention. This patent prevents others from reproducing and selling the new rose variety without permission, allowing the breeder to profit from their innovation.
2.3. Utility Patents: Protecting Useful Inventions
Utility patents are the most common type of patent, protecting new and useful inventions, including processes, machines, manufactures, and compositions of matter. These patents cover a wide range of technologies, from software algorithms to medical devices.
Consider the invention of the modern smartphone. Numerous utility patents protect the various technologies that make smartphones possible, including the touchscreen display, the operating system, and the cellular communication technology.
3. What Technologies Cannot Be Patented?
While many technologies can be patented, certain categories are excluded from patent protection, including abstract ideas, laws of nature, and physical phenomena. These exclusions aim to prevent the monopolization of fundamental concepts and ensure that innovation remains open and accessible.
3.1. Abstract Ideas
Abstract ideas, such as mathematical formulas, mental processes, and business methods, are not patentable. These concepts are considered too fundamental to be monopolized by a single inventor.
For example, a method of organizing data using a specific algorithm would be considered an abstract idea and would not be eligible for patent protection unless it is implemented in a specific and non-obvious way within a tangible application.
3.2. Laws of Nature
Laws of nature, such as gravity and electromagnetism, are not patentable. These fundamental principles are considered to be part of the common heritage of humankind and cannot be exclusively owned by any one individual or entity.
3.3. Physical Phenomena
Physical phenomena, such as the properties of light and sound, are not patentable. Like laws of nature, these phenomena are considered to be fundamental aspects of the universe and cannot be monopolized.
4. Patent Application Guidelines: Ensuring a Successful Application
To increase the likelihood of a patent application’s approval, inventors should adhere to essential guidelines, including ensuring novelty, non-obviousness, utility, and providing a clear and comprehensive description of the invention. Following these guidelines can significantly improve the chances of obtaining a patent and protecting your invention.
4.1. Novelty: Ensuring Your Invention is New
To be patentable, an invention must be novel, meaning it must be new and not previously known or described in the prior art. Prior art includes any existing evidence of the invention, such as publications, patents, and public disclosures.
Before filing a patent application, it is crucial to conduct a thorough prior art search to ensure that the invention is indeed novel. This search can help identify any existing technologies that may invalidate the patent application.
4.2. Non-Obviousness: Demonstrating Inventive Step
An invention must also be non-obvious, meaning it must not be an obvious modification or combination of existing technologies. The invention must represent a significant inventive step that would not have been readily apparent to a person skilled in the art.
To demonstrate non-obviousness, it is important to highlight the unique features and advantages of the invention and explain why it would not have been obvious to someone with knowledge of the existing technology.
4.3. Utility: Demonstrating Practical Usefulness
An invention must be useful, meaning it must have a practical application and be capable of achieving a specific result. The invention must be more than just a theoretical concept; it must be able to solve a problem or improve an existing technology.
To demonstrate utility, it is important to clearly describe the intended use of the invention and explain how it provides a tangible benefit.
4.4. Clear and Comprehensive Description: Enabling Reproduction
A patent application must include a clear and comprehensive description of the invention, enabling a person skilled in the art to reproduce and use the invention without undue experimentation. The description must be detailed enough to allow others to understand how the invention works and how to make and use it.
The description should include drawings, diagrams, and examples to illustrate the invention and explain its operation.
5. What are the Advantages of Patented Technology?
Patented technology offers numerous advantages, including exclusivity, financial gain, and legal protection, providing inventors and businesses with a competitive edge and incentivizing further innovation. These benefits can lead to increased market share, revenue, and long-term growth.
5.1. Exclusivity: Securing a Competitive Edge
Patents grant exclusive rights to an invention for a set period, preventing unauthorized use and providing a legal framework to safeguard investments. This exclusivity provides a competitive edge, differentiating products or processes and establishing market leadership.
For example, a company that patents a new type of battery technology can gain a significant competitive advantage over its rivals. The patent prevents competitors from using the same technology, allowing the company to dominate the market for batteries.
5.2. Financial Gain: Monetizing Innovation
Patents provide significant financial advantages for inventors and businesses. The exclusive rights granted by a patent allow inventors to license their technology to third parties, resulting in revenue through royalties. Licensing agreements can establish a consistent income flow, especially when the patented invention or process is groundbreaking and in high demand.
For instance, a university that patents a new medical device can license the technology to a medical device manufacturer. The university receives royalties from the manufacturer for each device sold, providing a valuable source of revenue.
5.3. Legal Protection: Defending Intellectual Property
Patents serve as legal deterrents, dissuading potential infringers from unlawfully utilizing an inventor’s intellectual property. If someone does infringe upon a patented invention, the patent holder has the option to initiate legal proceedings to uphold their rights and pursue suitable compensation.
The patent system provides a strong mechanism to safeguard inventors against infringement, enabling them to protect their innovative ideas and investments effectively.
If a competitor infringes on a patented invention, the patent holder can sue the infringer for damages. The patent holder can also seek an injunction to stop the infringer from continuing to use the invention.
6. Big Tech Companies Increase Their Patented Technologies: A Trend Analysis
Leading technology companies such as Google, Apple, and Microsoft are significantly increasing their patent activity, reflecting a growing recognition of the strategic importance of intellectual property in the technology sector. This trend underscores the value of patents in securing market share, protecting innovation, and driving future growth.
From 2009 onwards, the “big five” tech companies have collectively filed over 52,000 patents, with Microsoft leading the way with 16,840 filings. This trend indicates a rising interest in patent applications within the technology sector, with a specific focus on artificial intelligence.
The increase of AI-related patents by these companies suggests a strategic emphasis on thought processes in machines. Considering the surge in popularity AI image generation tools and AI writing tools have had, it makes sense that big tech companies are looking to invest more in this area going forward.
6.1. Strategic Implications of Increased Patent Activity
The increased patent activity among big tech companies has several strategic implications:
- Securing Market Share: Patents can help companies secure market share by preventing competitors from using their technology.
- Protecting Innovation: Patents protect companies’ investments in research and development, ensuring that they can reap the rewards of their innovation.
- Driving Future Growth: Patents can drive future growth by creating new revenue streams through licensing and commercialization.
6.2. Focus on Artificial Intelligence
The increasing number of AI-related patents reflects the growing importance of artificial intelligence in the technology sector. AI is being used in a wide range of applications, from self-driving cars to medical diagnosis.
Companies that can develop and patent new AI technologies will have a significant competitive advantage in the years to come.
7. Case Studies: Examples of Successful Patent Technology
Several case studies highlight the successful application of patent technology, demonstrating its ability to protect innovation, drive market leadership, and generate financial returns. These examples provide valuable insights into the strategic use of patents and their impact on business success.
7.1. Apple’s Design Patents: Protecting Product Aesthetics
Apple has successfully used design patents to protect the unique aesthetics of its products, such as the iPhone and iPad. These patents have helped Apple differentiate its products from competitors and maintain its position as a market leader.
 Apple iPad design patent
Apple iPad design patent
Apple iPad design patent showcasing how design patents are used to protect product aesthetics.
7.2. Qualcomm’s Wireless Communication Patents: Licensing Revenue
Qualcomm holds numerous patents related to wireless communication technologies, such as CDMA and LTE. The company generates significant revenue by licensing its patents to other companies in the mobile industry.
7.3. Pfizer’s Pharmaceutical Patents: Protecting Drug Development
Pfizer holds patents for several blockbuster drugs, such as Lipitor and Viagra. These patents have allowed Pfizer to recoup its investment in drug development and generate substantial profits.
8. The Future of Patent Technology: Trends and Predictions
The future of patent technology is likely to be shaped by several key trends, including the increasing importance of software and AI patents, the globalization of patent protection, and the rise of patent litigation. Understanding these trends is essential for inventors and businesses looking to navigate the evolving patent landscape.
8.1. Increasing Importance of Software and AI Patents
As software and AI become increasingly important in all aspects of our lives, the number of patents related to these technologies is likely to continue to grow. Companies that can develop and patent new software and AI technologies will have a significant competitive advantage in the future.
8.2. Globalization of Patent Protection
The patent system is becoming increasingly globalized, with companies seeking patent protection in multiple countries around the world. This trend reflects the growing importance of international markets and the need to protect inventions in all major economies.
8.3. Rise of Patent Litigation
Patent litigation is becoming increasingly common, as companies seek to enforce their patent rights and prevent competitors from infringing on their inventions. This trend is likely to continue as the value of patents increases and the competition for market share intensifies.
9. Common Misconceptions About Patent Technology
Several common misconceptions surround patent technology, including the belief that patents are only for large corporations and that obtaining a patent is too expensive. Debunking these myths can help inventors and businesses better understand the patent system and its benefits.
9.1. Patents are Only for Large Corporations
One common misconception is that patents are only for large corporations. In reality, patents are available to anyone who invents something new and useful, regardless of their size or resources.
Small businesses and individual inventors can benefit greatly from patent protection, as it can help them secure funding, attract investors, and compete with larger companies.
9.2. Obtaining a Patent is Too Expensive
Another common misconception is that obtaining a patent is too expensive. While it is true that the patent application process can be costly, there are several ways to reduce the expenses.
For example, inventors can file a provisional patent application, which provides a lower-cost way to establish an early filing date. They can also seek assistance from pro bono legal services or patent assistance programs.
9.3. Patents Guarantee Market Success
It is important to remember that a patent does not guarantee market success. A patent simply gives the inventor the right to exclude others from making, using, or selling the invention.
To be successful, the inventor must also develop a viable business plan, secure funding, and effectively market the invention to potential customers.
10. Expert Insights on Patent Technology from Pioneer-Technology.com
At pioneer-technology.com, we provide expert insights and resources to help you navigate the complex world of patent technology. Our team of experienced professionals offers guidance on patent searching, application preparation, and enforcement strategies.
10.1. Comprehensive Patent Search Tools
Our website offers access to comprehensive patent search tools, allowing you to quickly and easily identify existing patents and prior art. This can help you determine whether your invention is novel and patentable.
10.2. Expert Guidance on Patent Application Preparation
Our team of patent experts can provide guidance on all aspects of the patent application process, from drafting the application to responding to office actions. We can help you prepare a strong and effective patent application that maximizes your chances of success.
10.3. Strategies for Patent Enforcement
We also offer strategies for patent enforcement, helping you protect your patent rights and prevent infringement. Our team can help you develop a comprehensive patent enforcement plan that includes monitoring the market for potential infringers, sending cease and desist letters, and pursuing litigation if necessary.
Patent search interface demonstrating the tools available for efficient patent searching.
Ready to explore the world of patent technology and unlock the potential of your innovations? Visit pioneer-technology.com today to discover our comprehensive resources, expert insights, and cutting-edge analysis.
Don’t let the complexities of patent law hold you back. Let pioneer-technology.com be your guide to navigating the patent landscape and protecting your intellectual property. Contact us at [Address: 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States. Phone: +1 (650) 723-2300] or visit our website at pioneer-technology.com to learn more.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Patent Technology
1. What is the difference between a patent and a trademark?
A patent protects an invention, while a trademark protects a brand name or logo. Patents prevent others from making, using, or selling the invention, while trademarks prevent others from using the brand name or logo in a way that is likely to cause confusion.
2. How long does a patent last?
A utility patent typically lasts for 20 years from the date of application, while a design patent lasts for 15 years from the date of grant.
3. Can I patent an idea?
No, you cannot patent an idea. To be patentable, an invention must be concrete and have a practical application.
4. What is prior art?
Prior art is any existing evidence of the invention, such as publications, patents, and public disclosures.
5. How do I conduct a patent search?
You can conduct a patent search by using online patent databases, such as the USPTO website or Google Patents. You can also hire a professional patent search firm.
6. What is a provisional patent application?
A provisional patent application is a lower-cost way to establish an early filing date for a patent application. It is not examined and does not result in a patent unless a regular patent application is filed within one year.
7. What is a patent infringement?
Patent infringement is the unauthorized use of a patented invention.
8. What are the remedies for patent infringement?
The remedies for patent infringement include damages and an injunction.
9. How do I enforce my patent rights?
You can enforce your patent rights by monitoring the market for potential infringers, sending cease and desist letters, and pursuing litigation if necessary.
10. Where can I find more information about patent technology?
You can find more information about patent technology on the USPTO website, the WIPO website, and at pioneer-technology.com.
