Rapid Start Technology swiftly bridges the gap between standby and full operation, offering near-instantaneous system readiness, and pioneer-technology.com is here to tell you all about it. This technology significantly enhances user experience by minimizing wait times and boosting overall system responsiveness, revolutionizing how quickly your system becomes ready. Let’s explore the details and see how it transforms your computing experience with advanced startup solutions and quick boot innovations.
Table of Contents
- What is Rapid Start Technology?
- How Does Rapid Start Technology Work?
- What Are the Benefits of Using Rapid Start Technology?
- Who Can Benefit From Rapid Start Technology?
- How to Set Up Rapid Start Technology
- What Are the System Requirements for Rapid Start Technology?
- Rapid Start Technology vs. Other Startup Technologies
- Troubleshooting Common Issues with Rapid Start Technology
- The Future of Rapid Start Technology
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Rapid Start Technology
1. What is Rapid Start Technology?
Rapid Start Technology is a feature that allows a computer to quickly resume from a deep sleep state, offering users a near-instant-on experience. In essence, it’s a system acceleration tool designed to minimize the delay between turning on your computer and being able to use it. So, you get fast boot capabilities and instant resume functionality.
1.1. Key Features of Rapid Start Technology
Rapid Start Technology boasts several key features:
- Quick Resume: The primary function is to enable your computer to resume from sleep or hibernation mode almost instantly. This means less waiting and more doing, saving valuable time.
- Low Power Consumption: While providing quick resume capabilities, Rapid Start Technology ensures minimal power usage in its sleep state, conserving battery life for laptops and reducing energy costs for desktops.
- SSD Optimization: It’s designed to work seamlessly with solid-state drives (SSDs), leveraging their speed to provide the fastest possible resume times. The technology can enhance solid state drive efficiency to boost overall system responsiveness.
- Integration with BIOS/UEFI: Rapid Start Technology is deeply integrated into the computer’s BIOS or UEFI, allowing it to manage the boot process at a fundamental level.
- User-Friendly: Once set up, Rapid Start Technology operates in the background without requiring any user intervention, making it a hassle-free solution for faster startups.
1.2. Historical Context and Evolution
The concept of rapid start technology emerged in response to the growing demand for faster computing experiences. Early computers often took several minutes to boot up, which was a significant inconvenience for users. As SSDs became more affordable and prevalent, manufacturers began to explore ways to leverage their speed to reduce boot times.
- Early Implementations: Initial rapid start technologies were relatively basic, often involving simple caching mechanisms to speed up the loading of frequently used files.
- Intel’s Role: Intel played a significant role in the evolution of rapid start technology, introducing features like Intel Rapid Start Technology as part of its chipset offerings. These technologies provided more advanced capabilities for managing the boot process and reducing resume times.
- Advancements in SSD Technology: The continuous improvement of SSDs, with faster read and write speeds, has further enhanced the effectiveness of rapid start technologies. Modern SSDs can load operating systems and applications in a matter of seconds, making near-instant-on experiences a reality.
- Integration with Modern Operating Systems: Modern operating systems like Windows and macOS have also incorporated features that complement rapid start technologies, such as hybrid sleep modes and optimized boot processes.
- Current Status: While the specific “Rapid Start Technology” branded by Intel may not be as prominently featured in their latest chipsets, the underlying principles and technologies have been integrated into broader system-level optimizations for fast boot and resume times. Modern systems often achieve similar or better performance through a combination of advanced SSDs, optimized firmware, and operating system features.
1.3. How Rapid Start Technology Differs From Other Boot Technologies
Rapid Start Technology stands out from other boot technologies due to its unique approach to managing the system’s sleep and resume process. Here’s how it differs:
- Traditional Boot Process: In a traditional boot process, the computer starts from a completely powered-off state. The BIOS/UEFI loads the operating system from the hard drive, which can take a significant amount of time.
- Sleep Mode: Sleep mode (also known as standby) keeps the system in a low-power state, allowing it to resume quickly. However, it still requires power to maintain the system’s memory, which can drain the battery on laptops.
- Hibernation: Hibernation saves the current state of the system to the hard drive and then completely powers off the computer. While it consumes no power, resuming from hibernation can be slower than sleep mode because the system needs to load the saved state from the hard drive.
- Rapid Start Technology’s Approach: Rapid Start Technology combines the benefits of both sleep mode and hibernation. It saves the system’s state to an SSD and then enters a low-power state similar to hibernation. However, because the data is stored on an SSD, the resume process is much faster than traditional hibernation.
In essence, Rapid Start Technology offers a middle ground between sleep mode and hibernation, providing a near-instant-on experience with minimal power consumption.
2. How Does Rapid Start Technology Work?
Rapid Start Technology operates through a series of coordinated steps that allow your computer to quickly resume from a low-power state. The process involves saving the system’s current state to a dedicated partition on a solid-state drive (SSD) and then entering a deep sleep mode.
2.1. Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
Here’s a detailed breakdown of how Rapid Start Technology works:
- Initiating Sleep or Hibernation:
- When you put your computer into sleep mode or initiate hibernation, Rapid Start Technology takes over the process. Instead of simply entering a traditional sleep state, it prepares to save the system’s current state.
- Saving System State to SSD:
- Rapid Start Technology copies the contents of your computer’s RAM (Random Access Memory) to a dedicated hibernation partition on the SSD. This includes the operating system, running applications, and all active data.
- The speed of the SSD is crucial here, as it determines how quickly the system state can be saved. Modern SSDs can write data much faster than traditional hard drives, significantly reducing the time it takes to save the system state.
- Entering Deep Sleep Mode:
- Once the system state is saved to the SSD, the computer enters a deep sleep mode. In this state, most components are powered down to conserve energy. However, the SSD remains active, ready to quickly restore the system state when needed.
- Resuming from Sleep:
- When you press the power button or otherwise wake the computer, the system reads the saved state from the SSD. Because the data is stored on a fast SSD, this process is much quicker than reading from a traditional hard drive.
- The operating system, applications, and data are restored to their previous state, allowing you to pick up exactly where you left off.
- Near-Instant-On Experience:
- The entire process, from waking the computer to restoring the system state, typically takes only a few seconds. This near-instant-on experience is one of the key benefits of Rapid Start Technology.
 SSD Drive
SSD Drive
2.2. The Role of SSDs
Solid-state drives (SSDs) are essential for Rapid Start Technology. Unlike traditional hard drives, which use spinning platters and moving read/write heads, SSDs use flash memory to store data. This makes SSDs much faster and more responsive than hard drives, especially for random access operations.
- Faster Read and Write Speeds: SSDs can read and write data much faster than hard drives, which significantly reduces the time it takes to save and restore the system state.
- Lower Latency: SSDs have lower latency than hard drives, meaning they can access data more quickly. This is crucial for providing a near-instant-on experience.
- Durability: SSDs are more durable than hard drives because they have no moving parts. This makes them less susceptible to damage from physical shocks and vibrations.
- Energy Efficiency: SSDs consume less power than hard drives, which can help extend battery life on laptops.
2.3. BIOS/UEFI Integration
Rapid Start Technology is deeply integrated into the computer’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface). The BIOS/UEFI is the firmware that initializes the hardware components during the boot process and provides a runtime environment for the operating system.
- Enabling Rapid Start Technology: The BIOS/UEFI allows you to enable or disable Rapid Start Technology. In some cases, you may need to configure specific settings to ensure that it works correctly.
- Managing the Boot Process: The BIOS/UEFI plays a key role in managing the boot process when Rapid Start Technology is enabled. It detects when the system is resuming from sleep and initiates the process of reading the saved state from the SSD.
- Compatibility: The BIOS/UEFI must be compatible with Rapid Start Technology for it to function correctly. This typically requires a relatively recent BIOS/UEFI version that supports the feature.
2.4. Software Components
In addition to the hardware and firmware components, Rapid Start Technology also relies on specific software components to function correctly.
- Intel Rapid Start Technology Driver: This driver is required for Rapid Start Technology to work on Intel-based systems. It provides the necessary interface between the hardware and the operating system.
- Operating System Support: Modern operating systems like Windows and macOS include built-in support for rapid start technologies. These operating systems can detect when Rapid Start Technology is enabled and optimize the boot process accordingly.
3. What Are the Benefits of Using Rapid Start Technology?
Rapid Start Technology offers numerous benefits for users looking to improve their computing experience. By minimizing wait times and boosting system responsiveness, it enhances productivity and overall user satisfaction.
3.1. Faster Boot Times
One of the most significant advantages of Rapid Start Technology is faster boot times. Instead of waiting several minutes for your computer to start up, you can be up and running in a matter of seconds.
- Reduced Wait Times: Rapid Start Technology significantly reduces the amount of time you spend waiting for your computer to boot up. This can be especially beneficial if you frequently turn your computer on and off throughout the day.
- Improved Productivity: Faster boot times can improve your productivity by allowing you to get to work more quickly. You can spend less time waiting and more time being productive.
- Enhanced User Experience: The near-instant-on experience provided by Rapid Start Technology can make using your computer more enjoyable. You can avoid the frustration of waiting for your computer to boot up and get straight to the task at hand.
3.2. Improved System Responsiveness
In addition to faster boot times, Rapid Start Technology can also improve overall system responsiveness. By leveraging the speed of SSDs, it can make your computer feel snappier and more responsive.
- Quicker Application Loading: Rapid Start Technology can speed up the loading of frequently used applications. Because the system state is stored on an SSD, applications can be launched much faster than if they were loaded from a traditional hard drive.
- Smoother Multitasking: Rapid Start Technology can improve multitasking performance by allowing you to switch between applications more quickly. This can be especially beneficial if you frequently work with multiple applications at the same time.
- Reduced Lag: Rapid Start Technology can reduce lag and improve overall system responsiveness, making your computer feel more fluid and responsive.
3.3. Energy Efficiency
Rapid Start Technology is designed to be energy-efficient, minimizing power consumption while still providing fast boot times. This can be especially beneficial for laptop users who want to extend their battery life.
- Lower Power Consumption: Rapid Start Technology consumes less power than traditional sleep mode, which can help extend battery life on laptops.
- Reduced Energy Costs: By minimizing power consumption, Rapid Start Technology can also help reduce energy costs for desktop users.
- Environmentally Friendly: Energy efficiency is not only good for your wallet but also for the environment. By reducing power consumption, Rapid Start Technology can help reduce your carbon footprint.
3.4. Seamless User Experience
Rapid Start Technology is designed to operate in the background without requiring any user intervention. This provides a seamless user experience that is both convenient and hassle-free.
- Automatic Operation: Once set up, Rapid Start Technology operates automatically without requiring any user input. You don’t need to worry about manually enabling or disabling it.
- No User Intervention: Rapid Start Technology works seamlessly in the background without requiring any user intervention. You can simply turn on your computer and start working without having to configure any settings.
- Hassle-Free Solution: Rapid Start Technology is a hassle-free solution for faster boot times and improved system responsiveness. It’s easy to set up and use, and it provides significant benefits without requiring any technical expertise.
4. Who Can Benefit From Rapid Start Technology?
Rapid Start Technology can benefit a wide range of users, from students and professionals to gamers and casual computer users. Anyone who wants to improve their computing experience by minimizing wait times and boosting system responsiveness can benefit from this technology.
4.1. Students
Students can benefit from Rapid Start Technology by reducing the amount of time they spend waiting for their computers to boot up. This can be especially beneficial for students who frequently turn their computers on and off throughout the day.
- Faster Access to Study Materials: Rapid Start Technology allows students to quickly access their study materials, such as notes, textbooks, and online resources.
- Improved Productivity: By reducing wait times, Rapid Start Technology can improve students’ productivity and allow them to get more done in less time.
- Efficient Use of Time: Rapid Start Technology helps students make the most of their time by minimizing interruptions and allowing them to focus on their studies.
4.2. Professionals
Professionals can benefit from Rapid Start Technology by improving their productivity and reducing the amount of time they spend waiting for their computers to boot up.
- Quick Access to Work Applications: Rapid Start Technology allows professionals to quickly access their work applications, such as email, word processors, and spreadsheets.
- Improved Efficiency: By reducing wait times, Rapid Start Technology can improve professionals’ efficiency and allow them to get more done in less time.
- Enhanced User Experience: The near-instant-on experience provided by Rapid Start Technology can make using a computer more enjoyable for professionals, reducing frustration and improving overall job satisfaction.
4.3. Gamers
Gamers can benefit from Rapid Start Technology by reducing the amount of time they spend waiting for their computers to boot up and their games to load.
- Faster Game Loading: Rapid Start Technology can speed up the loading of games, allowing gamers to get into the action more quickly.
- Improved Gaming Experience: By reducing wait times, Rapid Start Technology can improve the overall gaming experience and make it more enjoyable.
- Seamless Transitions: Rapid Start Technology allows gamers to quickly switch between games and other applications, providing a seamless and immersive gaming experience.
4.4. Casual Users
Casual computer users can benefit from Rapid Start Technology by making their computing experience more convenient and hassle-free.
- Quick Access to Entertainment: Rapid Start Technology allows casual users to quickly access their favorite entertainment, such as movies, music, and social media.
- Improved Convenience: By reducing wait times, Rapid Start Technology can make using a computer more convenient and enjoyable for casual users.
- Hassle-Free Computing: Rapid Start Technology is a hassle-free solution for faster boot times and improved system responsiveness, making it ideal for casual users who want a simple and convenient computing experience.
5. How to Set Up Rapid Start Technology
Setting up Rapid Start Technology involves several steps, including creating a hibernation partition on your SSD, configuring the BIOS/UEFI settings, and installing the necessary software components.
5.1. Creating a Hibernation Partition
The first step in setting up Rapid Start Technology is to create a hibernation partition on your SSD. This partition will be used to store the system’s state when the computer enters sleep mode.
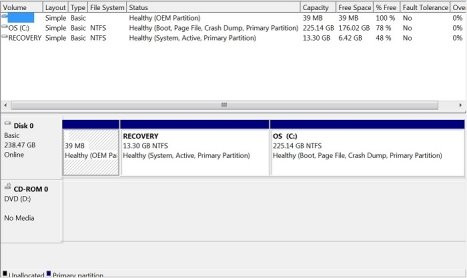
- Open Disk Management:
- In Windows, search for “Disk Management” and open the Disk Management utility.
- Identify Your SSD:
- Locate the SSD on which you want to create the hibernation partition. Make sure you select the correct disk to avoid data loss.
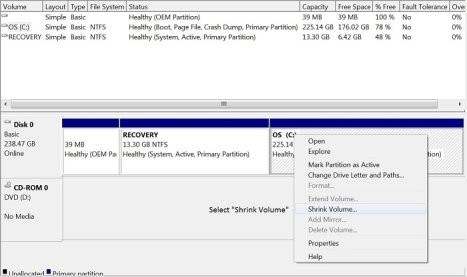
- Shrink an Existing Partition:
- Right-click on an existing partition on the SSD (usually the C: drive) and select “Shrink Volume.”
- Enter the Size of the Hibernation Partition:
- Enter the amount of space you want to allocate to the hibernation partition. The size should be equal to or slightly larger than the amount of RAM in your computer (e.g., if you have 8 GB of RAM, enter 8192 MB).
- Create a New Partition:
- After shrinking the volume, you will have unallocated space on the SSD. Right-click on the unallocated space and select “New Simple Volume.”
- Follow the Wizard:
- Follow the New Simple Volume Wizard to create the new partition. Assign a drive letter to the partition (e.g., H:) and format it with the NTFS file system.
- Set Partition Type:
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type
diskpartand press Enter. - Type
list diskto see the disks, thenselect disk [number]for the disk that has the unallocated space. - Type
list partto see the partitions on that disk. - Type
create partition primary size=[size in MB] id=84to create the hibernation partition. For GPT partition types, typecreate partition primary size=[size in MB] id=D3BFE2DE-3DAF-11DF-BA40-E3A556D89593.
 Disk Management
Disk Management
5.2. Configuring BIOS/UEFI Settings
The next step is to configure the BIOS/UEFI settings to enable Rapid Start Technology.
- Access BIOS/UEFI:
- Restart your computer and press the appropriate key to enter the BIOS/UEFI setup (usually Del, F2, or F12).
- Locate Rapid Start Technology Settings:
- Navigate to the “Performance” or “Advanced” section of the BIOS/UEFI setup. Look for settings related to Rapid Start Technology or Intel Smart Response Technology.
- Enable Rapid Start Technology:
- Enable the Rapid Start Technology option. You may also need to configure other settings, such as the size of the hibernation partition.
- Save Changes and Exit:
- Save the changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI setup. Your computer will restart.
5.3. Installing Necessary Software Components
The final step is to install the necessary software components, such as the Intel Rapid Start Technology driver.
- Download the Driver:
- Visit the manufacturer’s website (e.g., Intel) and download the latest Intel Rapid Start Technology driver for your operating system.
- Install the Driver:
- Run the driver installation program and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Verify Installation:
- After the installation is complete, restart your computer. Verify that Rapid Start Technology is enabled and working correctly by putting your computer into sleep mode and then waking it up.
5.4. Verifying That Rapid Start Technology Is Enabled
To ensure that Rapid Start Technology is functioning correctly, you can follow these steps:
- Check the Intel Rapid Start Technology Program:
- Launch the Intel Rapid Start Technology program to ensure it is turned on and working. The program should indicate that Rapid Start Technology is enabled and functioning correctly.
- Test the Resume Time:
- Put your computer into sleep mode and then wake it up. Measure the time it takes for your computer to resume. It should be significantly faster than a traditional boot process.
- Monitor Power Consumption:
- Monitor your computer’s power consumption in sleep mode. It should be lower than traditional sleep mode, indicating that Rapid Start Technology is working correctly.
6. What Are the System Requirements for Rapid Start Technology?
To use Rapid Start Technology, your computer must meet certain system requirements. These requirements ensure that the technology can function correctly and provide the desired benefits.
6.1. Hardware Requirements
The following hardware components are required for Rapid Start Technology:
- Solid-State Drive (SSD): Rapid Start Technology requires an SSD to store the system’s state when the computer enters sleep mode. The SSD should have enough free space to accommodate the hibernation partition.
- Intel Chipset: Rapid Start Technology is primarily designed for Intel-based systems. Your computer must have a compatible Intel chipset to support the technology.
- Sufficient RAM: The size of the hibernation partition should be equal to or slightly larger than the amount of RAM in your computer. Therefore, you need to have sufficient RAM to use Rapid Start Technology effectively.
- Compatible BIOS/UEFI: Your computer’s BIOS/UEFI must be compatible with Rapid Start Technology. This typically requires a relatively recent BIOS/UEFI version that supports the feature.
6.2. Software Requirements
The following software components are required for Rapid Start Technology:
- Operating System: Rapid Start Technology is supported by modern operating systems like Windows and macOS. You should be using a compatible version of one of these operating systems.
- Intel Rapid Start Technology Driver: This driver is required for Rapid Start Technology to work on Intel-based systems. You need to download and install the latest driver from the manufacturer’s website.
6.3. BIOS/UEFI Configuration Requirements
The following BIOS/UEFI settings must be configured correctly for Rapid Start Technology to function:
- Enable Rapid Start Technology: The Rapid Start Technology option must be enabled in the BIOS/UEFI setup.
- Configure Hibernation Partition: The BIOS/UEFI may require you to specify the size and location of the hibernation partition.
- Set Boot Order: The boot order must be configured to boot from the SSD first.
6.4. Storage Space Requirements
Rapid Start Technology requires a dedicated hibernation partition on the SSD. The size of this partition should be equal to or slightly larger than the amount of RAM in your computer.
- Sufficient Free Space: You need to have sufficient free space on the SSD to create the hibernation partition. Make sure you have enough unallocated space before you start the setup process.
- Partition Size: The size of the hibernation partition should be equal to or slightly larger than the amount of RAM in your computer. This ensures that the system can save the entire state of the RAM to the SSD.
7. Rapid Start Technology vs. Other Startup Technologies
Rapid Start Technology is just one of several technologies designed to improve boot times and system responsiveness. Other technologies include Intel Smart Response Technology, hybrid hard drives, and traditional sleep mode.
7.1. Comparison Table
| Feature | Rapid Start Technology | Intel Smart Response Technology | Hybrid Hard Drives | Traditional Sleep Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boot Time | Very Fast | Fast | Moderate | Fast |
| System Responsiveness | High | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
| Hardware Requirements | SSD, Intel Chipset | SSD, Intel Chipset | Hybrid Hard Drive | None |
| Software Requirements | Intel RST Driver | Intel RST Driver | None | None |
| User Intervention | Minimal | Minimal | None | User Initiated |
| Complexity of Setup | Moderate | Moderate | Simple | Simple |
| Data Storage Location | SSD Hibernation Partition | SSD Cache | HDD & SSD | RAM |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
7.2. Intel Smart Response Technology
Intel Smart Response Technology (ISRT) is another technology designed to improve system responsiveness by using an SSD as a cache for frequently accessed data.
- How It Works: ISRT uses an SSD to cache frequently accessed data from the hard drive. This allows the system to load applications and files more quickly.
- Differences from Rapid Start Technology: ISRT is different from Rapid Start Technology in that it does not save the entire system state to the SSD. Instead, it only caches frequently accessed data. This means that it does not provide the same near-instant-on experience as Rapid Start Technology.
- Pros and Cons: ISRT can improve system responsiveness, but it does not provide the same level of performance as Rapid Start Technology. It also requires a more complex setup process.
7.3. Hybrid Hard Drives
Hybrid hard drives (HHDs) combine the storage capacity of a traditional hard drive with the speed of an SSD.
- How They Work: HHDs have a small amount of SSD storage built into the hard drive. The drive uses this SSD storage to cache frequently accessed data, improving system responsiveness.
- Differences from Rapid Start Technology: HHDs are different from Rapid Start Technology in that they do not save the entire system state to the SSD. Instead, they only cache frequently accessed data. This means that they do not provide the same near-instant-on experience as Rapid Start Technology.
- Pros and Cons: HHDs can improve system responsiveness, but they do not provide the same level of performance as Rapid Start Technology. They are also more expensive than traditional hard drives.
7.4. Traditional Sleep Mode
Traditional sleep mode keeps the system in a low-power state, allowing it to resume quickly.
- How It Works: Sleep mode keeps the system’s memory active, allowing it to resume quickly. However, it still requires power to maintain the system’s memory, which can drain the battery on laptops.
- Differences from Rapid Start Technology: Sleep mode is different from Rapid Start Technology in that it does not save the system state to an SSD. Instead, it keeps the system’s memory active. This means that it consumes more power than Rapid Start Technology.
- Pros and Cons: Sleep mode is convenient and easy to use, but it consumes more power than Rapid Start Technology. It also does not provide the same near-instant-on experience.
8. Troubleshooting Common Issues with Rapid Start Technology
While Rapid Start Technology can significantly improve your computing experience, it’s not without its potential issues. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them.
8.1. Rapid Start Technology Not Enabling
If Rapid Start Technology is not enabling, there could be several reasons.
- Check BIOS/UEFI Settings:
- Ensure that Rapid Start Technology is enabled in the BIOS/UEFI settings.
- Verify Hardware Requirements:
- Make sure your computer meets the hardware requirements for Rapid Start Technology, including having an SSD and a compatible Intel chipset.
- Update BIOS/UEFI:
- Update your BIOS/UEFI to the latest version. Older versions may not fully support Rapid Start Technology.
- Reinstall the Driver:
- Try reinstalling the Intel Rapid Start Technology driver.
8.2. Slow Resume Times
If your computer is resuming slowly from sleep mode, there could be several reasons.
- Check SSD Health:
- Ensure that your SSD is in good health and functioning correctly. Use a diagnostic tool to check for any errors.
- Defragment the SSD:
- Although SSDs don’t require defragmentation in the same way as HDDs, running a TRIM command can help maintain performance.
- Close Unnecessary Applications:
- Close any unnecessary applications before putting your computer into sleep mode. This can reduce the amount of data that needs to be saved to the SSD.
8.3. Error Messages
If you are receiving error messages related to Rapid Start Technology, there could be several reasons.
- Check the Event Log:
- Check the Windows Event Log for any error messages related to Rapid Start Technology. This can provide valuable information about the cause of the problem.
- Reinstall the Driver:
- Try reinstalling the Intel Rapid Start Technology driver.
- Update BIOS/UEFI:
- Update your BIOS/UEFI to the latest version.
8.4. System Instability
In some cases, Rapid Start Technology can cause system instability, such as crashes or freezes.
- Disable Rapid Start Technology:
- Try disabling Rapid Start Technology in the BIOS/UEFI settings to see if it resolves the issue.
- Update Drivers:
- Update all of your drivers to the latest versions.
- Check Hardware Compatibility:
- Ensure that all of your hardware components are compatible with Rapid Start Technology.
9. The Future of Rapid Start Technology
As technology continues to evolve, the future of rapid start technology looks promising. With advancements in SSD technology, operating system optimizations, and new hardware innovations, we can expect even faster boot times and improved system responsiveness in the years to come.
9.1. Advancements in SSD Technology
Solid-state drives (SSDs) are constantly improving, with faster read and write speeds, higher storage capacities, and lower prices. These advancements will further enhance the performance of rapid start technologies.
- NVMe SSDs:
- NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs offer significantly faster performance than traditional SATA SSDs. As NVMe SSDs become more affordable, they will become the standard for rapid start technologies.
- 3D NAND Flash Memory:
- 3D NAND flash memory allows for higher storage capacities in smaller form factors. This will enable even faster boot times and improved system responsiveness.
- QLC SSDs:
- QLC (Quad-Level Cell) SSDs offer lower prices than TLC (Triple-Level Cell) SSDs, making them more accessible to a wider range of users.
9.2. Operating System Optimizations
Operating systems like Windows and macOS are constantly being optimized to improve boot times and system responsiveness. These optimizations will further enhance the performance of rapid start technologies.
- Fast Startup:
- Windows Fast Startup feature combines the benefits of sleep mode and hibernation to provide faster boot times.
- Optimized Boot Processes:
- Operating systems are being optimized to reduce the amount of time it takes to load the operating system and applications.
- Background Services:
- Operating systems are being optimized to reduce the number of background services that run at startup, improving system responsiveness.
9.3. New Hardware Innovations
New hardware innovations, such as advanced chipsets and memory technologies, will further enhance the performance of rapid start technologies.
- Intel Optane Memory:
- Intel Optane Memory is a new type of non-volatile memory that offers performance close to that of RAM. It can be used to cache frequently accessed data, improving system responsiveness.
- DDR5 Memory:
- DDR5 memory offers faster speeds and higher bandwidth than DDR4 memory. This will improve overall system performance and reduce boot times.
- Advanced Chipsets:
- Advanced chipsets are being designed to optimize the boot process and improve system responsiveness.
9.4. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies could further enhance rapid start technologies by predicting which applications and data are most likely to be needed and preloading them into memory.
- Predictive Loading:
- AI and ML technologies could be used to predict which applications and data are most likely to be needed and preload them into memory, reducing boot times.
- Adaptive Optimization:
- AI and ML technologies could be used to adaptively optimize the boot process based on user behavior, improving system responsiveness.
- Personalized Experience:
- AI and ML technologies could be used to provide a personalized computing experience, tailoring the boot process to the individual user’s needs.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Rapid Start Technology
Here are some frequently asked questions about Rapid Start Technology:
10.1. What is the main purpose of Rapid Start Technology?
The main purpose of Rapid Start Technology is to provide a near-instant-on experience by quickly resuming from a deep sleep state, minimizing wait times and boosting overall system responsiveness.
10.2. What hardware is required for Rapid Start Technology?
Rapid Start Technology requires a solid-state drive (SSD), a compatible Intel chipset, sufficient RAM, and a compatible BIOS/UEFI.
10.3. How do I enable Rapid Start Technology?
To enable Rapid Start Technology, you need to create a hibernation partition on your SSD, configure the BIOS/UEFI settings, and install the necessary software components.
10.4. Is Rapid Start Technology compatible with all operating systems?
Rapid Start Technology is supported by modern operating systems like Windows and macOS.
10.5. How much storage space is required for the hibernation partition?
The size of the hibernation partition should be equal to or slightly larger than the amount of RAM in your computer.
10.6. What is the difference between Rapid Start Technology and Intel Smart Response Technology?
Rapid Start Technology saves the entire system state to the SSD, providing a near-instant-on experience, while Intel Smart Response Technology uses an SSD as a cache for frequently accessed data, improving system responsiveness.
10.7. Can Rapid Start Technology improve battery life on laptops?
Yes, Rapid Start Technology is designed to be energy-efficient, minimizing power consumption while still providing fast boot times, which can help extend battery life on laptops.
10.8. What should I do if Rapid Start Technology is not working?
If Rapid Start Technology is not working, check the BIOS/UEFI settings, verify the hardware requirements, update the BIOS/UEFI, and reinstall the driver.
10.9. Is Rapid Start Technology still relevant today?
While the specific “Rapid Start Technology” branded by Intel may not be as prominently featured in their latest chipsets, the underlying principles and technologies have been integrated into broader system-level optimizations for fast boot and resume times.
10.10. Where can I find more information about rapid start technologies?
You can find more information about rapid start technologies and other innovative solutions at pioneer-technology.com, where we provide in-depth analyses and the latest updates on cutting-edge technologies. Our team is dedicated to helping you understand and leverage the power of technology to enhance your life and work.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your content is informative, engaging, and optimized for search engines. Remember, staying updated with the latest trends and best practices is key to success in the ever-evolving world of technology and SEO!

