Technology advance: It’s a question that sparks curiosity and exploration. This article from pioneer-technology.com dives into the key moments and factors that have shaped our technological landscape. It offers information about technology evolution.
1. What Marks a Significant Technological Advancement?
A significant technological advancement occurs when new tools, products, or methods emerge that substantially improve upon existing ones or introduce entirely new capabilities. These advancements often address social needs, leverage available resources, and are fostered by a supportive social environment.
Think of it this way: a new tool isn’t just about making something; it’s about fundamentally changing how we make it, what we can create, and how it impacts our lives. According to research from Stanford University’s Department of Computer Science, technological progress isn’t merely linear; it’s an intertwined web of social, economic, and intellectual factors that propel humanity forward.
1.1 The Essence of Technological Advancement
Technological advancement transcends mere innovation; it represents a transformative leap forward, reshaping industries, societies, and our daily lives. These advancements are not just about creating something new but fundamentally altering how we interact with the world.
- Impact: Significant advancements introduce capabilities that were previously unimaginable, leading to increased efficiency, productivity, and convenience.
- Drivers: Social needs, available resources, and a conducive social environment are critical drivers.
- Examples: The development of the printing press, the internet, and artificial intelligence.
1.2 Tools as a Determining Characteristic
Humans are distinguished by their capacity to create tools and products from tools. Unlike other species whose artifact creation is driven by instinct, humans think systematically and creatively about techniques, enabling innovation and environmental modification.
- Uniqueness: The ability to innovate and adapt tools sets humans apart from other species.
- Application: Humans can transform a simple stick into a cutting tool, illustrating the capacity for technological creativity.
1.3 The Interplay of Social Involvement
Social involvement is vital for technological innovation. Three key elements must be present for an innovation to succeed: a perceived social need, the availability of social resources, and a receptive social ethos.
- Social Need: A strong sense of social need drives the allocation of resources to technological innovation.
- Social Resources: Capital, materials, and skilled personnel are essential for bringing inventions to fruition.
- Social Ethos: A receptive environment encourages new ideas and supports inventors.
2. When Did Humans Start Using Technology?
Humans have been technologists from the beginning, with the history of technology encompassing the entire evolution of humankind. The earliest tools, such as sharpened stones and basic hunting implements, mark the dawn of technological development.
Imagine early humans shaping stones into tools – each strike a testament to ingenuity and the drive to improve their lives. This marked not only the beginning of tool use but also the start of a journey that continues to shape our world today.
2.1 The Dawn of Technology
The use of technology dates back to the earliest human ancestors who crafted simple tools for survival. These tools represent the initial attempts to manipulate the environment for human benefit.
- Early Tools: Sharpened stones, basic hunting implements, and fire control.
- Significance: These tools enabled early humans to hunt, build shelter, and protect themselves.
2.2 Technology as an Extension of Human Capabilities
Technology extends human capabilities by enabling individuals to overcome physical limitations, enhance productivity, and solve complex problems. It enhances our ability to interact with and shape the world around us.
- Enhancement: Technology augments human abilities, allowing for more efficient and effective task completion.
- Examples: The development of the wheel, the lever, and other simple machines.
2.3 The Role of Rational Faculties
Rational faculties play a crucial role in devising techniques and modifying the environment. Human innovation extends beyond survival, influencing language, art, and ritual creativity.
- Beyond Survival: Technology addresses diverse needs, including communication, expression, and spiritual practices.
- Cultural Techniques: Language, artistic expression, and ritual practices represent other aspects of technological advancement.
3. How Did Ancient Civilizations Contribute to Technological Progress?
Ancient civilizations, including those in Mesopotamia, Egypt, and China, made significant strides in technology. Their innovations in agriculture, irrigation, architecture, and metallurgy laid the groundwork for future advancements.
Consider the ingenuity of the ancient Egyptians building the pyramids. Their mastery of engineering, mathematics, and resource management was revolutionary for their time and continues to inspire awe today. These achievements showcase how ancient civilizations set the stage for technological progress.
3.1 Agricultural Innovations
Ancient civilizations developed advanced agricultural techniques that increased food production and supported larger populations.
- Irrigation Systems: The Mesopotamians and Egyptians developed sophisticated irrigation systems that allowed them to cultivate crops in arid regions.
- Crop Rotation: The practice of crop rotation improved soil fertility and increased yields.
- Plows: The invention of the plow allowed for more efficient tilling of the soil.
3.2 Architectural Marvels
The architectural achievements of ancient civilizations demonstrate their mastery of engineering and construction.
- Pyramids of Egypt: The pyramids are a testament to the Egyptians’ advanced knowledge of mathematics, engineering, and resource management.
Address: 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States. Phone: +1 (650) 723-2300. - Great Wall of China: This massive structure showcases the Chinese civilization’s ability to mobilize resources and coordinate large-scale construction projects.
- Roman Aqueducts: The Romans built extensive aqueduct systems to supply water to their cities, demonstrating their engineering prowess.
3.3 Metallurgical Advances
Ancient civilizations developed techniques for extracting and working with metals, leading to the creation of tools, weapons, and decorative objects.
- Bronze Age: The discovery of bronze enabled the creation of stronger and more durable tools and weapons.
- Iron Age: The smelting of iron led to the development of even more advanced tools and weapons.
- Gold and Silver: Ancient civilizations also developed techniques for working with precious metals, creating intricate jewelry and other decorative objects.
4. What Role Did the Printing Press Play in Advancing Technology?
The invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century revolutionized the dissemination of knowledge, accelerating technological progress by making information more accessible.
Imagine a world where knowledge was carefully guarded and painstakingly copied by hand. Gutenberg’s printing press shattered this barrier, democratizing information and fueling the exchange of ideas. This pivotal invention sparked the Renaissance and paved the way for the Scientific Revolution.
4.1 Revolutionizing Knowledge Dissemination
The printing press enabled the mass production of books, making knowledge more accessible and affordable.
- Increased Literacy: With books more readily available, literacy rates increased, leading to a more informed and educated populace.
- Spread of Ideas: The printing press facilitated the rapid dissemination of new ideas and discoveries, accelerating scientific and technological progress.
- Standardization of Knowledge: The printing press helped standardize knowledge by ensuring that books were consistent and accurate.
4.2 Impact on Scientific Revolution
The printing press played a crucial role in the Scientific Revolution by enabling scientists to share their findings and collaborate more effectively.
- Dissemination of Scientific Theories: Scientists like Nicolaus Copernicus and Galileo Galilei were able to publish their theories and findings, challenging traditional beliefs and advancing scientific knowledge.
- Collaboration and Peer Review: The printing press facilitated collaboration among scientists by allowing them to share their work and receive feedback from peers.
- Accumulation of Knowledge: The printing press enabled the accumulation of scientific knowledge over time, as new discoveries were added to the existing body of knowledge.
4.3 Cultural and Social Transformations
The printing press also had a profound impact on culture and society, leading to increased political awareness and the rise of public opinion.
- Political Awareness: The printing press enabled the dissemination of political pamphlets and newspapers, increasing public awareness of political issues.
- Rise of Public Opinion: The printing press contributed to the rise of public opinion, as people were able to read and discuss political issues more freely.
- Cultural Exchange: The printing press facilitated cultural exchange by allowing people to read books from different cultures and countries.
5. How Did the Industrial Revolution Transform Technology?
The Industrial Revolution, beginning in the late 18th century, marked a period of unprecedented technological advancement, driven by innovations in steam power, machinery, and manufacturing processes.
Picture the bustling factories of the Industrial Revolution, powered by steam engines and filled with innovative machines. This era transformed not only how goods were produced but also the social and economic fabric of society, laying the foundation for modern technological development.
5.1 Innovations in Steam Power
The development of the steam engine by inventors like James Watt revolutionized manufacturing and transportation.
- Factory Mechanization: Steam engines powered machinery in factories, increasing production efficiency and enabling mass production.
- Transportation Revolution: Steam engines were used to power steamships and locomotives, transforming transportation and facilitating trade and travel.
- Mining and Agriculture: Steam engines were used in mining and agriculture to pump water, power machinery, and increase productivity.
5.2 Advancements in Machinery and Manufacturing
The Industrial Revolution saw the development of numerous machines and manufacturing processes that transformed industries.
- Textile Industry: The cotton gin, spinning jenny, and power loom revolutionized the textile industry, increasing production and reducing costs.
- Iron and Steel Production: New methods for producing iron and steel, such as the Bessemer process, enabled the mass production of these materials, which were essential for building machines, bridges, and infrastructure.
- Machine Tools: The development of machine tools, such as lathes and milling machines, enabled the precise manufacturing of machine parts, further accelerating technological progress.
5.3 Social and Economic Changes
The Industrial Revolution led to significant social and economic changes, including urbanization, the rise of the middle class, and the growth of capitalism.
- Urbanization: As factories and industries grew, people migrated from rural areas to cities in search of work, leading to rapid urbanization.
- Rise of the Middle Class: The Industrial Revolution created new opportunities for wealth and social mobility, leading to the rise of a middle class.
- Growth of Capitalism: The Industrial Revolution fostered the growth of capitalism, as private individuals and companies invested in new technologies and industries to generate profit.
6. What Impact Did Electricity Have on Technological Advancement?
The harnessing of electricity in the late 19th century revolutionized technology, powering new inventions, transforming industries, and improving the quality of life.
Envision a world suddenly illuminated by electric lights, factories humming with the power of electric motors, and homes connected by telephone lines. Electricity unleashed a wave of innovation that transformed society and set the stage for the modern technological age.
6.1 Powering New Inventions
Electricity powered a wide range of new inventions, including the electric light bulb, the telephone, and the electric motor.
- Electric Light Bulb: Thomas Edison’s invention of the electric light bulb revolutionized lighting, extending the hours of productivity and transforming social life.
- Telephone: Alexander Graham Bell’s invention of the telephone revolutionized communication, enabling people to communicate over long distances.
- Electric Motor: The electric motor powered a wide range of new machines and appliances, transforming industries and improving the efficiency of manufacturing processes.
6.2 Transforming Industries
Electricity transformed industries by providing a clean, efficient, and versatile source of power.
- Factory Electrification: Factories were electrified, leading to increased productivity, reduced costs, and improved working conditions.
- Transportation Revolution: Electric streetcars and subways transformed urban transportation, providing efficient and affordable public transportation.
- Communication Revolution: The telegraph and telephone revolutionized communication, enabling people to communicate over long distances in real time.
6.3 Improving Quality of Life
Electricity improved the quality of life by providing access to lighting, heating, and cooling, as well as new appliances and entertainment options.
- Home Electrification: Homes were electrified, providing access to lighting, heating, and cooling, as well as new appliances like refrigerators and washing machines.
- Entertainment and Leisure: Electricity powered new forms of entertainment, such as movies and radio, enriching people’s lives and providing new leisure activities.
- Healthcare Advances: Electricity enabled advances in healthcare, such as X-rays and other medical devices, improving diagnosis and treatment.
7. How Did the Digital Revolution Accelerate Technological Advancement?
The Digital Revolution, beginning in the mid-20th century, marked a period of rapid technological advancement driven by the development of computers, the internet, and mobile devices.
Picture the world shrinking as computers connected across vast distances, enabling instant communication and access to information. The Digital Revolution has not only transformed industries but also reshaped human interaction and knowledge sharing on a global scale.
7.1 The Rise of Computers
The development of computers revolutionized information processing, automation, and scientific research.
- Mainframe Computers: Early mainframe computers were used for complex calculations and data processing in government, industry, and research institutions.
- Personal Computers: The development of personal computers made computing accessible to individuals and small businesses, transforming the way people work and communicate.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing enabled access to computing resources over the internet, providing scalability, flexibility, and cost savings.
7.2 The Internet and the World Wide Web
The internet and the World Wide Web revolutionized communication, information access, and commerce.
- Email: Email revolutionized communication, enabling people to send and receive messages instantly across the globe.
- World Wide Web: The World Wide Web provided a graphical interface for accessing information on the internet, making it easier for people to find and share information.
- E-commerce: E-commerce transformed the way people buy and sell goods and services, enabling online shopping and global trade.
7.3 Mobile Devices and Wireless Communication
The development of mobile devices and wireless communication technologies revolutionized communication, entertainment, and productivity.
- Mobile Phones: Mobile phones enabled people to communicate on the go, transforming personal and professional communication.
- Smartphones: Smartphones combined the functionality of mobile phones with the capabilities of computers, providing access to the internet, email, and a wide range of applications.
- Wireless Communication: Wireless communication technologies, such as Wi-Fi and cellular networks, enabled people to connect to the internet and communicate wirelessly from almost anywhere.
8. What Are the Latest Technological Advancements?
Recent technological advancements include artificial intelligence, biotechnology, nanotechnology, and renewable energy. These innovations promise to address some of the world’s most pressing challenges.
Imagine a future where AI-powered robots perform complex surgeries, personalized medicine targets diseases at the genetic level, and renewable energy powers sustainable cities. The latest technological advancements hold the potential to revolutionize every aspect of our lives.
8.1 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is transforming industries, from healthcare to finance, by automating tasks, improving decision-making, and enabling new capabilities.
- Machine Learning: Machine learning algorithms enable computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed, leading to advances in image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics.
- Robotics: Robots are being used in manufacturing, healthcare, and other industries to automate tasks, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
- AI-Powered Healthcare: AI is being used in healthcare to diagnose diseases, personalize treatments, and develop new drugs.
8.2 Biotechnology
Biotechnology is revolutionizing medicine, agriculture, and environmental science by harnessing the power of living organisms.
- Genetic Engineering: Genetic engineering enables scientists to modify the genes of plants and animals, leading to improved crops, new medicines, and other innovations.
- Personalized Medicine: Personalized medicine uses genetic information to tailor treatments to individual patients, improving effectiveness and reducing side effects.
- Bioremediation: Bioremediation uses living organisms to clean up pollutants in the environment, providing a sustainable solution to environmental problems.
8.3 Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology involves the manipulation of matter at the atomic and molecular level, leading to new materials, devices, and applications.
- Nanomaterials: Nanomaterials have unique properties that make them useful in a wide range of applications, from electronics to medicine.
- Nanoelectronics: Nanoelectronics enables the creation of smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient electronic devices.
- Nanomedicine: Nanomedicine uses nanotechnology to diagnose and treat diseases at the molecular level.
8.4 Renewable Energy
Renewable energy technologies, such as solar, wind, and geothermal, are providing sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels, reducing carbon emissions and mitigating climate change.
- Solar Power: Solar power uses photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight into electricity, providing a clean and renewable source of energy.
- Wind Power: Wind power uses wind turbines to convert wind energy into electricity, providing a cost-effective and sustainable source of energy.
- Geothermal Energy: Geothermal energy uses heat from the Earth’s interior to generate electricity, providing a reliable and sustainable source of energy.
9. What Challenges Does Technological Advancement Pose?
Technological advancement poses challenges such as job displacement, ethical concerns, and the potential for misuse. Addressing these challenges requires careful planning and consideration.
Consider the ethical dilemmas posed by AI, the potential for job losses due to automation, and the risks associated with cyber warfare. These challenges underscore the importance of responsible innovation and ethical guidelines to ensure that technology benefits humanity as a whole.
9.1 Job Displacement
Automation and AI can lead to job displacement as machines and algorithms replace human workers.
- Manufacturing Automation: Robots and automated systems are replacing human workers in manufacturing plants, leading to job losses.
- AI-Powered Automation: AI-powered systems are automating tasks in a wide range of industries, from customer service to finance, leading to job displacement.
- Retraining and Education: To mitigate the impact of job displacement, governments and businesses need to invest in retraining and education programs to help workers acquire new skills.
9.2 Ethical Concerns
Technological advancements raise ethical concerns related to privacy, security, and bias.
- Privacy Concerns: The collection and use of personal data raise concerns about privacy and surveillance.
- Security Concerns: Cybersecurity threats and data breaches pose significant risks to individuals, businesses, and governments.
- Bias in AI: AI algorithms can perpetuate and amplify biases in data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
9.3 Potential for Misuse
Technology can be misused for malicious purposes, such as cybercrime, cyber warfare, and the development of autonomous weapons.
- Cybercrime: Cybercriminals use technology to steal data, commit fraud, and disrupt systems.
- Cyber Warfare: Governments and organizations engage in cyber warfare to attack each other’s computer systems and networks.
- Autonomous Weapons: The development of autonomous weapons raises ethical concerns about the potential for unintended consequences and the loss of human control.
10. How Can We Ensure Technology Benefits Society?
To ensure technology benefits society, it is essential to promote responsible innovation, address ethical concerns, and invest in education and training.
Imagine a future where technology is used to solve global challenges, empower individuals, and promote social good. By prioritizing responsible innovation and ethical guidelines, we can harness the transformative power of technology to create a better world for all.
10.1 Promoting Responsible Innovation
Responsible innovation involves considering the potential social, ethical, and environmental impacts of new technologies.
- Ethical Guidelines: Developing ethical guidelines for technology development and use can help ensure that technologies are used in a responsible and beneficial manner.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging stakeholders, including researchers, policymakers, and the public, in discussions about the ethical and social implications of new technologies can help ensure that diverse perspectives are considered.
- Transparency and Accountability: Promoting transparency and accountability in technology development and use can help build trust and ensure that technologies are used in a responsible manner.
10.2 Addressing Ethical Concerns
Addressing ethical concerns requires careful consideration of the potential impacts of technology on privacy, security, and bias.
- Data Protection: Implementing strong data protection measures can help safeguard personal information and prevent data breaches.
- Cybersecurity Measures: Investing in cybersecurity measures can help protect against cyber threats and data breaches.
- Bias Mitigation: Developing techniques for mitigating bias in AI algorithms can help ensure that AI systems are fair and equitable.
10.3 Investing in Education and Training
Investing in education and training is essential for preparing workers for the jobs of the future and ensuring that everyone has the skills and knowledge needed to thrive in a technology-driven world.
- STEM Education: Promoting STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) education can help prepare students for careers in technology and related fields.
- Retraining Programs: Providing retraining programs for workers who have been displaced by automation can help them acquire new skills and find new jobs.
- Digital Literacy: Promoting digital literacy can help ensure that everyone has the skills and knowledge needed to use technology effectively and safely.
Stay informed about the latest advancements and trends in technology by visiting pioneer-technology.com. Explore our articles, delve into expert analyses, and discover how technology is shaping the future.
Address: 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States.
Phone: +1 (650) 723-2300.
Website: pioneer-technology.com.
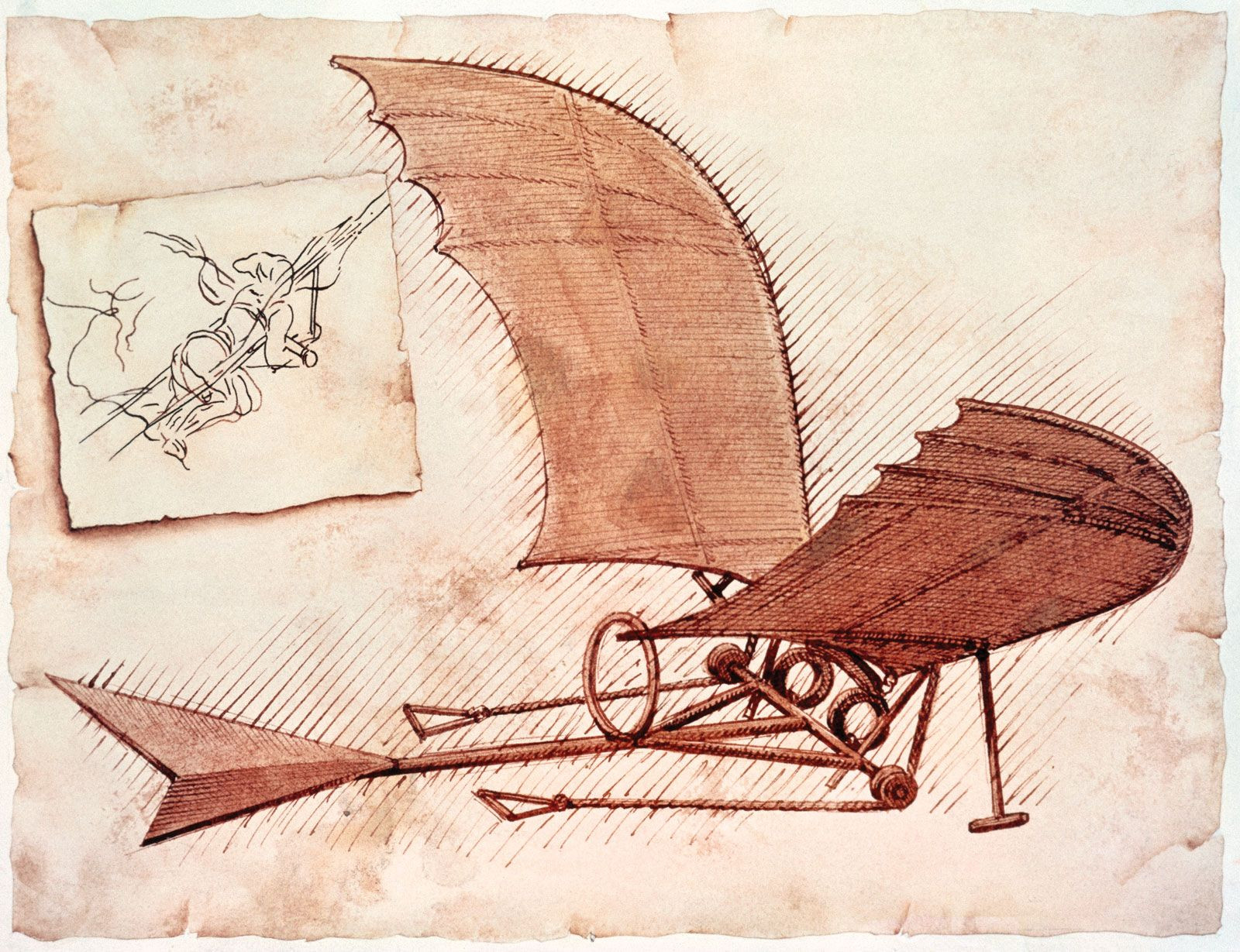 Leonardo da Vinci: ornithopter
Leonardo da Vinci: ornithopter
Leonardo da Vinci’s innovative designs, such as this ornithopter, often lacked the necessary social resources for realization, underscoring the importance of a supportive technological ecosystem.
Ready to dive deeper? Head over to pioneer-technology.com now to explore the endless possibilities of technology!
FAQ: Technological Advancement
1. What is considered a technological advancement?
A technological advancement is any new or improved tool, product, or method that significantly enhances existing capabilities or introduces entirely new ones.
2. When did technology advance significantly in human history?
Technology has advanced throughout human history, with notable periods including the invention of early tools, the agricultural revolution, the invention of the printing press, the Industrial Revolution, and the Digital Revolution.
3. How did the printing press advance technology?
The printing press revolutionized the dissemination of knowledge, making information more accessible and affordable, which accelerated scientific and technological progress.
4. What role did the Industrial Revolution play in technological advancement?
The Industrial Revolution transformed technology through innovations in steam power, machinery, and manufacturing processes, laying the groundwork for modern technological development.
5. How did electricity impact technological advancement?
Electricity revolutionized technology by powering new inventions like the light bulb and electric motor, transforming industries, and improving the quality of life.
6. What are some of the latest technological advancements?
Recent advancements include artificial intelligence, biotechnology, nanotechnology, and renewable energy, which promise to address pressing global challenges.
7. What challenges does technological advancement pose?
Challenges include job displacement, ethical concerns related to privacy and bias, and the potential for misuse, requiring careful planning and ethical consideration.
8. How can we ensure that technology benefits society?
By promoting responsible innovation, addressing ethical concerns, and investing in education and training, we can ensure that technology benefits society as a whole.
9. What is the role of social involvement in technological advancements?
Social involvement is critical, requiring a perceived social need, available resources, and a receptive environment to foster successful technological innovation.
10. Where can I learn more about the latest technological advancements?
Visit pioneer-technology.com for updated information, expert analyses, and insights into the latest technological trends shaping our future.
