Technological knowledge encompasses the understanding and ability to use, manage, and assess technology effectively, and pioneer-technology.com is dedicated to providing you with the insights you need to thrive in the digital age. By exploring the depths of technological proficiency, including the latest advancements and applications, you’ll discover how to leverage technology to enhance various facets of life and work. This includes digital literacy, technical expertise, and innovation competence.
1. Unveiling Technological Knowledge: What Is It and Why Is It Crucial?
Technological knowledge is the comprehension and proficiency in utilizing, managing, and evaluating technology effectively. This encompasses a broad spectrum, ranging from basic digital literacy to advanced technical expertise and the capacity for innovation.
What is Technological Knowledge?
Technological knowledge (TK) refers to the understanding and skills necessary to use, manage, and assess technology. According to the National Research Council (NRC, 1999), TK involves understanding information technology broadly enough to apply it productively in work and everyday life, recognizing when technology can assist or impede goals, and adapting to changes in information technology.
Think of technological knowledge as more than just knowing how to use a specific app or device. It’s about understanding the underlying principles of technology and how it can be applied to solve problems, improve efficiency, and create new opportunities. It’s a dynamic skill set that evolves with the ever-changing landscape of technology.
Why is Technological Knowledge Crucial?
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, technological knowledge is no longer a luxury but a necessity. Here’s why:
- Career Advancement: Many jobs require a basic level of technological proficiency, and advanced roles demand specialized knowledge.
- Personal Empowerment: Technology empowers individuals to access information, communicate, and participate in society.
- Innovation and Problem-Solving: Understanding technology enables individuals to develop innovative solutions to complex problems.
- Economic Growth: A technologically skilled workforce drives economic growth and competitiveness.
- Adaptability: The ability to learn and adapt to new technologies is crucial for staying relevant in a constantly changing world.
The Benefits of Developing Technological Knowledge
Developing strong technological knowledge skills offers a multitude of benefits across various aspects of life:
- Enhanced Productivity: Use technology to automate tasks, streamline workflows, and improve efficiency.
- Improved Communication: Communicate effectively using a variety of digital tools and platforms.
- Greater Access to Information: Access and evaluate information from a wide range of sources.
- Increased Creativity: Use technology to express creativity and explore new ideas.
- Better Decision-Making: Make informed decisions based on data and analysis.
 Technological Knowledge
Technological Knowledge
2. Deconstructing the Layers: Key Components of Technological Knowledge
Technological knowledge isn’t a monolithic entity; it’s composed of several distinct but interconnected components. Let’s break down these layers:
Digital Literacy
Digital literacy is the foundational layer of technological knowledge, encompassing the ability to use digital devices, communication tools, and networks to locate, evaluate, use, and create information.
According to the American Library Association, digital literacy is “the ability to use information and communication technologies to find, evaluate, create, and communicate information, requiring both cognitive and technical skills.”
- Finding Information: Effectively using search engines and online databases to locate relevant information.
- Evaluating Information: Critically assessing the credibility and reliability of online sources.
- Using Information: Applying information effectively to solve problems and make informed decisions.
- Creating Information: Producing original content using digital tools and platforms.
- Communicating Information: Sharing information and collaborating effectively using digital communication tools.
Technical Proficiency
Technical proficiency goes beyond basic digital literacy, encompassing the ability to understand and apply technical concepts and skills. This includes:
- Understanding Hardware and Software: Comprehending the basic principles of how computer hardware and software work.
- Troubleshooting Technical Issues: Identifying and resolving common technical problems.
- Programming Fundamentals: Understanding basic programming concepts and languages.
- Data Analysis: Collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data using appropriate tools and techniques.
- Cybersecurity Awareness: Understanding and mitigating cybersecurity risks.
Innovation Competence
Innovation competence is the highest level of technological knowledge, encompassing the ability to use technology to create new products, services, and processes.
- Creative Thinking: Generating new ideas and approaches to problem-solving.
- Design Thinking: Applying a human-centered approach to designing innovative solutions.
- Prototyping and Testing: Creating and testing prototypes to validate ideas and gather feedback.
- Project Management: Managing technology-related projects effectively.
- Entrepreneurship: Launching and scaling new technology-based ventures.
3. Navigating the Landscape: Types of Technological Knowledge
Technological knowledge isn’t a one-size-fits-all concept. It varies depending on the context and application. Here are some key types of technological knowledge:
General Technological Knowledge
This encompasses a broad understanding of technology and its applications across various domains. It includes:
- Basic Computer Skills: Using operating systems, software applications, and internet browsers.
- Digital Communication: Communicating effectively using email, messaging apps, and social media.
- Information Literacy: Finding, evaluating, and using information effectively.
- Cybersecurity Awareness: Understanding and mitigating cybersecurity risks.
- Emerging Technologies: Awareness of new and emerging technologies and their potential impact.
Domain-Specific Technological Knowledge
This refers to specialized knowledge of technology within a specific industry or field. Examples include:
- Healthcare Technology: Using electronic health records, medical imaging software, and telemedicine platforms.
- Financial Technology (FinTech): Understanding blockchain, cryptocurrency, and digital payment systems.
- Educational Technology (EdTech): Using learning management systems, online learning platforms, and educational apps.
- Manufacturing Technology: Operating computer-aided design (CAD) software, robotic systems, and 3D printers.
- Agricultural Technology (AgriTech): Using precision farming techniques, drone technology, and data analytics for crop management.
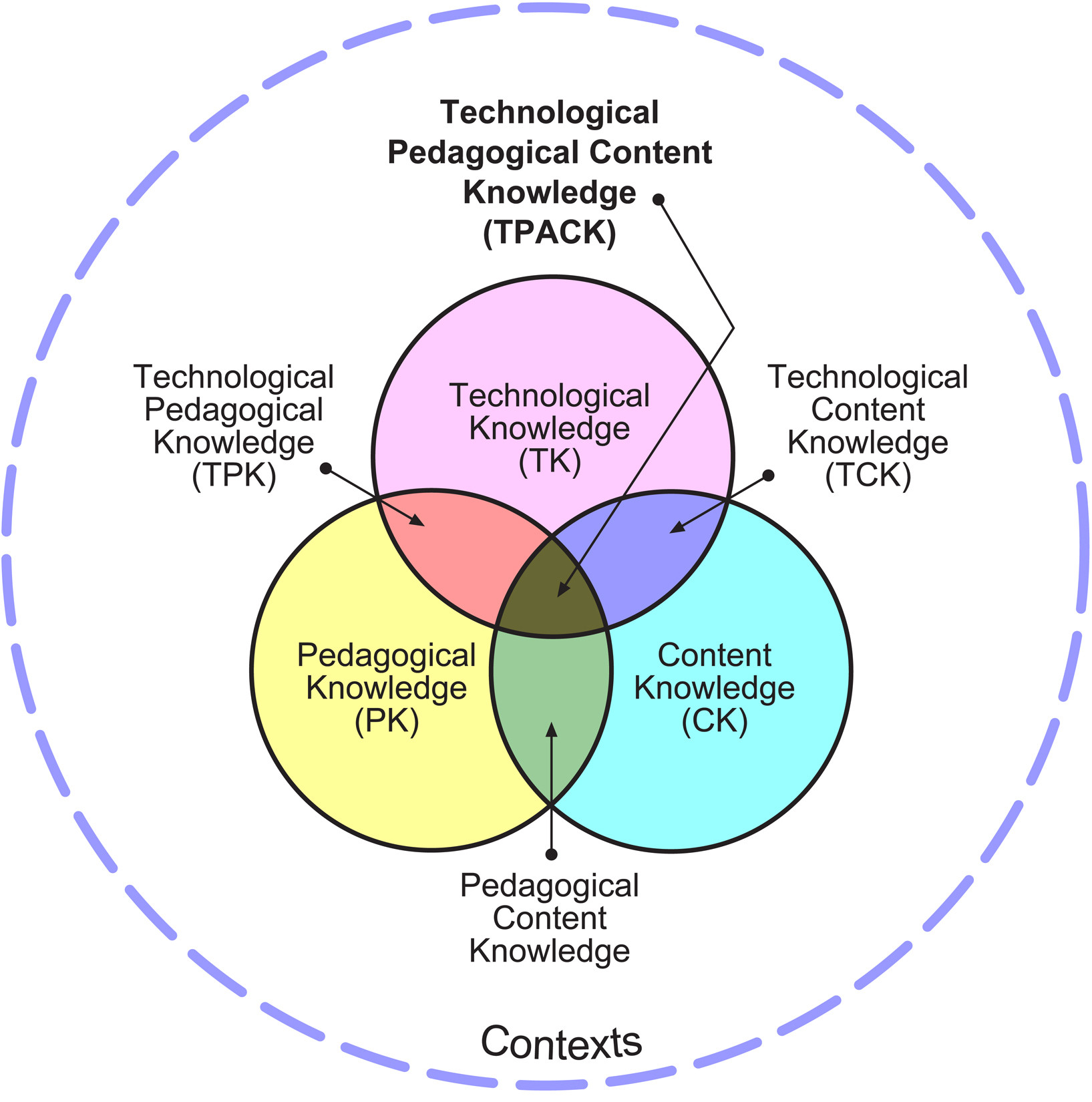
Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK)
TPACK is a framework that describes the knowledge teachers need to effectively integrate technology into their teaching. It encompasses:
- Content Knowledge (CK): Knowledge of the subject matter being taught.
- Pedagogical Knowledge (PK): Knowledge of teaching methods and strategies.
- Technology Knowledge (TK): Knowledge of technology and its applications.
- Pedagogical Content Knowledge (PCK): Knowledge of how to teach specific content effectively.
- Technological Content Knowledge (TCK): Knowledge of how technology can be used to represent and understand content.
- Technological Pedagogical Knowledge (TPK): Knowledge of how technology can be used to enhance teaching and learning.
- Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK): The integration of all three knowledge domains to create effective technology-enhanced learning experiences.
4. The Technological Knowledge Framework (TPACK): A Deep Dive
The TPACK framework, developed by Mishra and Koehler, is a cornerstone for understanding how technology, pedagogy, and content intersect to create effective teaching and learning experiences.
Understanding the Core Components of TPACK
The TPACK framework identifies seven key components:
- Content Knowledge (CK): This refers to the teacher’s knowledge of the subject matter, including concepts, theories, and evidence. According to Shulman (1986), this also includes knowledge of established practices and approaches toward developing such knowledge.
- Pedagogical Knowledge (PK): This encompasses the teacher’s knowledge of teaching methods and strategies, including classroom management, lesson planning, and assessment.
- Technology Knowledge (TK): This is the teacher’s knowledge of technology and its applications, including hardware, software, and digital resources. The NRC (1999) suggests that this includes understanding information technology broadly enough to apply it productively.
- Pedagogical Content Knowledge (PCK): This refers to the teacher’s knowledge of how to teach specific content effectively, including understanding common misconceptions and alternative teaching strategies.
- Technological Content Knowledge (TCK): This is the teacher’s knowledge of how technology can be used to represent and understand content, including the affordances and constraints of different technologies.
- Technological Pedagogical Knowledge (TPK): This refers to the teacher’s knowledge of how technology can be used to enhance teaching and learning, including the pedagogical affordances of different technologies.
- Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK): This is the integration of all three knowledge domains to create effective technology-enhanced learning experiences, requiring an understanding of the representation of concepts using technologies.
Applying the TPACK Framework in Education
The TPACK framework can be applied in various ways to improve technology integration in education:
- Curriculum Design: Use TPACK to design curricula that effectively integrate technology, pedagogy, and content.
- Teacher Training: Train teachers to develop their TPACK skills and effectively use technology in the classroom.
- Professional Development: Provide ongoing professional development opportunities for teachers to enhance their TPACK skills.
- Assessment: Assess teachers’ TPACK skills and provide feedback for improvement.
- Research: Conduct research to further understand the TPACK framework and its applications in education.
Benefits of Using the TPACK Framework
Using the TPACK framework offers several benefits:
- Improved Technology Integration: TPACK helps teachers integrate technology more effectively into their teaching practices.
- Enhanced Student Learning: TPACK can lead to improved student learning outcomes through more engaging and effective instruction.
- Increased Teacher Confidence: TPACK can increase teachers’ confidence in their ability to use technology effectively.
- Better Curriculum Design: TPACK can inform the design of more effective and relevant curricula.
- Greater Innovation: TPACK can foster innovation in teaching and learning practices.
5. Assessing Your Technological Knowledge: How Do You Measure Up?
Understanding your current level of technological knowledge is the first step towards improvement. Here are some ways to assess your skills:
Self-Assessment
Self-assessment involves evaluating your own skills and knowledge based on specific criteria. This can be done through:
- Checklists: Use checklists to identify areas where you have strong skills and areas where you need improvement.
- Rating Scales: Use rating scales to rate your proficiency in different areas of technological knowledge.
- Reflective Journals: Keep a reflective journal to track your learning and identify areas for growth.
Formal Assessments
Formal assessments are standardized tests that measure your knowledge and skills in a specific area. Examples include:
- Certifications: Obtain certifications in specific technologies or software applications.
- Skills Tests: Take online skills tests to assess your proficiency in different areas of technological knowledge.
- Academic Courses: Enroll in academic courses to learn and assess your knowledge of technology.
Practical Application
The best way to assess your technological knowledge is to apply it in real-world situations. This can be done through:
- Projects: Work on technology-related projects to demonstrate your skills and knowledge.
- Internships: Participate in internships to gain practical experience in a technology-related field.
- Volunteer Work: Volunteer your skills to help organizations with their technology needs.
- Personal Projects: Undertake personal projects that involve the use of technology.
6. Level Up: Strategies for Enhancing Your Technological Knowledge
Regardless of your current skill level, there are numerous ways to enhance your technological knowledge and stay ahead of the curve:
Formal Education
Formal education provides a structured approach to learning about technology. This includes:
- University Degrees: Pursue a degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field.
- Online Courses: Take online courses from reputable institutions to learn specific skills or technologies.
- Bootcamps: Attend intensive coding bootcamps to learn programming and software development skills.
- Workshops and Seminars: Participate in workshops and seminars to learn about specific topics or technologies.
Self-Directed Learning
Self-directed learning involves taking control of your own learning and pursuing your interests and goals. This includes:
- Online Tutorials: Use online tutorials to learn specific skills or technologies.
- Books and Articles: Read books and articles to deepen your understanding of technology.
- Open-Source Projects: Contribute to open-source projects to gain practical experience and learn from others.
- Personal Projects: Undertake personal projects to explore new technologies and develop your skills.
Community Engagement
Engaging with the technology community can provide valuable learning opportunities and support. This includes:
- Online Forums: Participate in online forums to ask questions, share knowledge, and connect with other technology enthusiasts.
- Meetups and Conferences: Attend meetups and conferences to network with industry professionals and learn about new technologies.
- Hackathons: Participate in hackathons to collaborate with others and develop innovative solutions.
- Mentorship: Seek out mentors who can provide guidance and support.
Hands-On Experience
Hands-on experience is crucial for developing practical skills and knowledge. This includes:
- Building Projects: Build your own projects to apply what you have learned and develop new skills.
- Experimentation: Experiment with different technologies and tools to explore their capabilities.
- Troubleshooting: Practice troubleshooting technical issues to develop your problem-solving skills.
- Real-World Applications: Apply your skills in real-world situations to gain practical experience.
7. The Future is Now: Emerging Technologies to Watch
The world of technology is constantly evolving, and it’s important to stay informed about emerging technologies. Here are some key trends to watch:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is transforming industries and creating new opportunities for automation, personalization, and innovation. According to a report by McKinsey, AI could contribute $13 trillion to the global economy by 2030.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT is connecting devices and systems, creating new opportunities for data collection, analysis, and automation.
- Blockchain: Blockchain is a decentralized ledger technology that is transforming industries such as finance, supply chain management, and healthcare.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR are creating immersive experiences that are transforming industries such as gaming, education, and healthcare.
- 5G Technology: 5G technology is providing faster and more reliable wireless connectivity, enabling new applications such as autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
How Emerging Technologies Impact Technological Knowledge
Emerging technologies are constantly reshaping the landscape of technological knowledge, demanding continuous learning and adaptation. Here’s how:
- New Skill Sets: Emerging technologies require new skill sets, such as AI programming, data science, and blockchain development.
- Continuous Learning: Professionals need to engage in continuous learning to stay up-to-date with the latest advancements.
- Adaptability: The ability to adapt to new technologies is crucial for staying relevant in a rapidly changing world.
- Innovation: Emerging technologies create new opportunities for innovation and problem-solving.
- Ethical Considerations: Emerging technologies raise ethical considerations that need to be addressed.
Staying Ahead of the Curve
To stay ahead of the curve in the ever-evolving world of technology, consider the following strategies:
- Follow Industry News: Stay informed about the latest technology news and trends by following industry publications and blogs.
- Attend Conferences and Webinars: Attend industry conferences and webinars to learn about new technologies and network with professionals.
- Join Online Communities: Join online communities to connect with other technology enthusiasts and share knowledge.
- Experiment with New Technologies: Experiment with new technologies to explore their capabilities and develop your skills.
- Seek Out Mentorship: Seek out mentors who can provide guidance and support.
8. Ethical Considerations: Navigating the Responsible Use of Technology
Technological knowledge comes with a responsibility to use technology ethically and responsibly. Here are some key ethical considerations:
- Privacy: Protecting the privacy of individuals and organizations.
- Security: Ensuring the security of data and systems.
- Bias: Avoiding bias in algorithms and AI systems.
- Accessibility: Ensuring that technology is accessible to all individuals, regardless of their abilities.
- Transparency: Being transparent about how technology is used and its potential impact.
Promoting Ethical Technological Practices
To promote ethical technological practices, consider the following:
- Education: Educate yourself and others about the ethical implications of technology.
- Policies and Guidelines: Develop and implement policies and guidelines for the ethical use of technology.
- Accountability: Hold individuals and organizations accountable for their ethical behavior.
- Collaboration: Collaborate with others to develop ethical solutions to complex problems.
- Advocacy: Advocate for ethical technology practices and policies.
The Role of Technological Knowledge in Ethical Decision-Making
Technological knowledge plays a crucial role in ethical decision-making. By understanding the potential impacts of technology, individuals can make informed decisions that promote ethical and responsible use.
- Understanding the Technology: Understanding how technology works and its potential impacts.
- Identifying Ethical Issues: Identifying potential ethical issues related to the use of technology.
- Evaluating Alternatives: Evaluating alternative solutions and their ethical implications.
- Making Informed Decisions: Making informed decisions based on ethical considerations.
- Taking Responsibility: Taking responsibility for the ethical consequences of your actions.
9. Resources and Tools: Expanding Your Technological Horizons
To further enhance your technological knowledge, explore these valuable resources and tools:
- Online Learning Platforms: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer a wide range of technology courses and certifications.
- Coding Bootcamps: Bootcamps like General Assembly and Flatiron School provide intensive training in programming and software development.
- Open-Source Projects: Platforms like GitHub and GitLab host a vast collection of open-source projects that you can contribute to.
- Industry Publications: Publications like TechCrunch, Wired, and The Verge provide news and insights on the latest technology trends.
- Online Communities: Communities like Stack Overflow and Reddit’s r/technology offer forums for discussion and knowledge sharing.
Recommended Tools for Enhancing Technological Knowledge
Here’s a curated list of tools to supercharge your learning:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Visual Studio Code | A versatile code editor with support for various programming languages. |
| Anaconda | A distribution of Python and R for data science and machine learning. |
| Docker | A platform for containerizing applications and deploying them across different environments. |
| Postman | A tool for testing and documenting APIs. |
| Wireshark | A network protocol analyzer for capturing and analyzing network traffic. |
| Nmap | A network scanner for discovering hosts and services on a computer network. |
| Metasploit | A penetration testing framework for identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities in computer systems. |
| Burp Suite | A web application security testing tool for identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities in web applications. |
| OWASP ZAP | A free and open-source web application security scanner. |
10. Real-World Applications: How Technological Knowledge Makes a Difference
Technological knowledge isn’t just theoretical; it has practical applications across various industries and aspects of life.
Case Studies
Here are some examples of how technological knowledge is making a difference in the real world:
- Healthcare: AI-powered diagnostic tools are improving the accuracy and speed of medical diagnoses.
- Finance: Blockchain technology is enabling secure and transparent financial transactions.
- Education: Online learning platforms are providing access to education for students around the world.
- Manufacturing: Robotic systems are automating manufacturing processes and improving efficiency.
- Agriculture: Precision farming techniques are optimizing crop yields and reducing waste.
Transforming Industries
Technological knowledge is transforming industries and creating new opportunities for innovation and growth.
| Industry | Transformation |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | AI-powered diagnostic tools, telemedicine platforms, and electronic health records are improving the quality and efficiency of healthcare. |
| Finance | Blockchain technology, cryptocurrency, and digital payment systems are transforming the way financial transactions are conducted. |
| Education | Online learning platforms, educational apps, and virtual reality experiences are enhancing the learning experience and providing access to education for students worldwide. |
| Manufacturing | Robotic systems, computer-aided design (CAD) software, and 3D printers are automating manufacturing processes and improving efficiency. |
| Agriculture | Precision farming techniques, drone technology, and data analytics are optimizing crop yields and reducing waste. |
| Transportation | Autonomous vehicles, ride-sharing apps, and smart traffic management systems are transforming the way people and goods are transported. |
| Retail | E-commerce platforms, personalized recommendations, and supply chain management systems are transforming the way people shop and purchase goods. |
Personal Empowerment
Technological knowledge empowers individuals to access information, communicate, and participate in society. By developing strong technological skills, individuals can improve their career prospects, enhance their personal lives, and contribute to the betterment of society.
In conclusion, technological knowledge is not merely about understanding gadgets or software; it’s about empowering yourself with the skills to navigate, innovate, and thrive in a digital world. At pioneer-technology.com, we are committed to providing you with the insights and resources you need to enhance your technological proficiency and unlock your full potential.
Ready to dive deeper? Explore our articles, tutorials, and resources at pioneer-technology.com to stay ahead of the curve in the ever-evolving world of technology. Discover the latest advancements, practical tips, and expert insights that will empower you to navigate the digital landscape with confidence.
For any inquiries, feel free to reach out to us at Address: 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States. Phone: +1 (650) 723-2300. Website: pioneer-technology.com.
FAQ: Unlocking Your Technological Potential
1. What Exactly Does Technological Knowledge Mean?
Technological knowledge refers to the understanding and ability to use, manage, and evaluate technology effectively. It includes digital literacy, technical expertise, and innovation competence.
2. Why Is Technological Knowledge So Important in Today’s World?
Technological knowledge is crucial for career advancement, personal empowerment, innovation, economic growth, and adaptability in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
3. What Are the Key Components of Technological Knowledge?
The key components include digital literacy (using digital devices and networks), technical proficiency (understanding technical concepts), and innovation competence (creating new products and services).
4. How Does TPACK (Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge) Enhance Teaching?
TPACK enhances teaching by integrating technology, pedagogy, and content knowledge, leading to more effective and engaging learning experiences.
5. How Can I Assess My Own Level of Technological Knowledge?
You can assess your knowledge through self-assessment checklists, formal certifications, skills tests, and practical application in real-world projects.
6. What Are Some Effective Strategies for Improving My Technological Skills?
Effective strategies include formal education (university degrees, online courses), self-directed learning (online tutorials, books), community engagement (online forums, meetups), and hands-on experience (building projects, experimentation).
7. What Emerging Technologies Should I Be Paying Attention To?
Key emerging technologies to watch include artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR), and 5G technology.
8. What Are Some Ethical Considerations Related to Using Technology?
Ethical considerations include privacy, security, avoiding bias, ensuring accessibility, and maintaining transparency in how technology is used.
9. What Resources and Tools Can Help Me Expand My Technological Knowledge?
Useful resources and tools include online learning platforms (Coursera, edX), coding bootcamps (General Assembly), open-source projects (GitHub), and industry publications (TechCrunch).
10. How Can Technological Knowledge Be Applied in Real-World Scenarios?
Technological knowledge has real-world applications in healthcare (AI-powered diagnostics), finance (blockchain transactions), education (online learning), manufacturing (robotic systems), and agriculture (precision farming).

