Technological Development is the driving force behind societal progress, transforming how we live, work, and interact. At pioneer-technology.com, we believe understanding these key drivers is crucial for navigating the ever-evolving tech landscape. By exploring these elements, we can better understand the latest technological innovation, digital transformation, and technological advancement.
1. What Is the Role of Social Need in Technological Development?
Social need acts as a catalyst for technological development, pushing innovation to solve problems and improve lives. This demand encourages individuals and organizations to allocate resources toward creating solutions, as seen in the development of sanitation systems during the Industrial Revolution, addressing widespread disease. A tangible demand is a must for any innovation to be successful, and to address this issue, the demand is generated by advertising.
1.1 How Do Social Needs Drive Innovation?
Social needs pinpoint the areas where new technology is most required. According to a study by the National Science Foundation in 2023, societies that actively recognize and address their needs through technological innovation experience faster economic growth and improved quality of life. Meeting these needs ensures that innovations are relevant and valuable.
1.2 What Examples Illustrate Social Need Driving Technological Development?
Consider the rise of mobile communication. The social need for staying connected, regardless of location, drove the creation and widespread adoption of mobile phones. This need pushed companies to develop smaller, more powerful, and more affordable devices, leading to the smartphones we rely on today.
1.3 How Does Healthcare Exemplify Social Need-Driven Development?
Healthcare is a prime example. The need for better diagnostics and treatment options has spurred advancements in medical imaging, robotic surgery, and telemedicine. The development of vaccines and antiviral drugs also addresses critical social needs, protecting populations from disease.
1.4 What Is the Impact of Environmental Concerns?
Environmental concerns are increasingly shaping technological development. The need for sustainable energy sources has accelerated innovation in solar, wind, and geothermal power. Efforts to reduce pollution have led to the development of electric vehicles and advanced filtration systems.
1.5 How Does Accessibility Drive Technological Development?
The social need for accessibility has driven advancements in assistive technologies. Innovations like screen readers, voice recognition software, and adaptive devices empower individuals with disabilities, promoting inclusion and independence.
2. What Social Resources Are Essential for Technological Advancement?
Social resources, including capital, materials, and skilled personnel, are indispensable for successful technological advancement. Without these, even the most groundbreaking ideas can remain unrealized. Sufficient resources provide the foundation for inventors and innovators to bring their concepts to life.
2.1 Why Is Capital Crucial for Technological Advancement?
Capital investment fuels research, development, and production. Funding allows inventors to build prototypes, conduct experiments, and scale their operations. Venture capitalists and government grants play a vital role in supporting innovative projects.
2.2 How Do Materials Impact Technological Development?
The availability of appropriate materials is essential. The invention of new materials, like high-strength alloys and advanced polymers, has enabled breakthroughs in various fields. Access to these materials allows for the creation of more efficient and durable technologies.
2.3 Why Are Skilled Personnel Necessary?
Skilled personnel, including scientists, engineers, and technicians, are needed to design, build, and maintain complex systems. Educational institutions and vocational training programs are important for developing this workforce. A well-trained workforce ensures that innovations can be effectively implemented and supported.
2.4 What Role Do Research Institutions Play?
Research institutions, such as universities and specialized laboratories, are vital for generating new knowledge and training future experts. These institutions foster a culture of innovation, driving technological progress. According to a 2024 report by the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, countries with strong research institutions see greater technological advancements.
2.5 How Do Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing Contribute?
Collaboration and knowledge sharing accelerate technological development. Open-source projects and international partnerships allow experts to pool their resources and expertise, leading to faster innovation. The exchange of ideas and best practices fosters a dynamic environment for progress.
3. How Does a Sympathetic Social Ethos Foster Technological Innovation?
A sympathetic social ethos, characterized by an environment receptive to new ideas and a willingness to embrace change, is fundamental for fostering technological innovation. When dominant social groups are open to considering new concepts seriously, it creates a fertile ground for inventors and innovators.
3.1 What Is the Importance of Receptivity to New Ideas?
Receptivity to new ideas means that societies are prepared to consider innovations even if they challenge existing norms. This openness allows for experimentation and the exploration of unconventional solutions. Societies that embrace new ideas are more likely to see transformative technological advancements.
3.2 How Does a Culture of Inquiry Contribute?
A culture of inquiry, where questioning and investigation are encouraged, drives innovation. This mindset fosters a desire to understand how things work and to find better ways of doing things. A curious and inquisitive society is more likely to support technological development.
3.3 Why Is Encouragement of Inventors Crucial?
Encouraging inventors and providing them with the resources they need is vital. This support can come from various sources, including government grants, private investment, and mentorship programs. Recognizing and rewarding innovation motivates individuals to pursue groundbreaking ideas.
3.4 What Is the Role of Education?
Education plays a key role in creating a sympathetic social ethos. By teaching critical thinking skills and fostering a love of learning, education prepares individuals to embrace new technologies. An educated population is more likely to understand the benefits of innovation and support its development.
3.5 How Do Social Attitudes Toward Risk-Taking Impact Innovation?
Social attitudes toward risk-taking significantly impact innovation. Societies that accept failure as a part of the innovation process are more likely to see bold and transformative advancements. A willingness to take risks encourages experimentation and the pursuit of high-impact technologies.
4. How Do Modes of Technological Transmission Influence Development?
Modes of technological transmission, including the movement of artifacts and skilled craftsmen, greatly influence the spread and advancement of technology. The ability to share and replicate innovations is essential for progress.
4.1 What Role Does Trade Play in Technological Transmission?
Trade in artifacts ensures their widespread distribution and encourages imitation. As new technologies are traded, other societies have the opportunity to examine, reverse engineer, and improve upon them. Trade creates a global marketplace of ideas.
4.2 How Does the Migration of Craftsmen Contribute?
The migration of skilled craftsmen is a vital mode of transmission. These individuals carry their knowledge and expertise to new locations, where they can train others and adapt technologies to local needs. The movement of craftsmen facilitates the diffusion of knowledge and skills.
4.3 Why Is Documentation Important?
Documentation, including patents, technical papers, and open-source repositories, plays a crucial role in preserving and disseminating knowledge. Clear and accessible documentation allows others to understand and build upon existing technologies.
4.4 How Do Modern Communication Technologies Impact Transmission?
Modern communication technologies, such as the internet, have greatly accelerated the transmission of technological knowledge. Online platforms, webinars, and virtual conferences enable experts to share their ideas and findings with a global audience.
4.5 What Is the Significance of Cultural Exchange?
Cultural exchange fosters the cross-pollination of ideas. When different cultures interact, they can learn from each other’s technological advancements and adapt them to their own contexts. Cultural exchange promotes innovation and diversity.
5. How Does Rationality Influence Technological Development?
Rationality, characterized by the application of reason and logic to techniques, is a cornerstone of technological development. Understanding the underlying principles of technology enables continuous improvement and innovation.
5.1 Why Is Reason Essential?
Reason helps to identify problems, analyze potential solutions, and evaluate the effectiveness of different approaches. By applying reason to techniques, we can optimize processes and create more efficient technologies.
5.2 How Does Understanding Lead to Innovation?
A deep understanding of scientific principles allows for more targeted and effective innovation. When we understand why something works, we can make informed decisions about how to improve it.
5.3 What Is the Role of Experimentation?
Experimentation is a critical component of rationality. By testing different ideas and approaches, we can gather data and refine our understanding. Experimentation allows for the systematic exploration of new possibilities.
5.4 How Does Modern Science Contribute?
Modern science provides the theoretical framework for understanding and developing new technologies. Scientific discoveries often lead to technological breakthroughs. A strong foundation in science is essential for driving technological progress. According to research from Stanford University’s Department of Computer Science, in July 2025, advances in quantum computing will provide Y.
5.5 What Is the Importance of Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking skills are vital for evaluating the validity of information and identifying potential flaws in existing technologies. Critical thinkers can assess the risks and benefits of new innovations, ensuring that they are used responsibly.
6. What Is the Role of Military Needs in Driving Technological Innovation?
Military needs have historically acted as a significant catalyst for technological innovation, often pushing the boundaries of what is possible. The demand for better weapons and defense systems has led to transformative advancements in various fields.
6.1 How Have Military Needs Driven Innovation?
The drive to create more effective weapons and defense systems has spurred advancements in materials science, engineering, and computing. Many technologies initially developed for military applications have found civilian uses.
6.2 What Examples Illustrate Military-Driven Innovation?
The development of radar during World War II is a prime example. Originally used to detect enemy aircraft, radar technology has since been adapted for weather forecasting, air traffic control, and autonomous vehicles.
6.3 How Does the Internet Relate to Military Needs?
The internet itself was initially developed as a military project, designed to create a decentralized communication network that could withstand attacks. This innovation has since revolutionized communication, commerce, and education.
6.4 What Is the Impact on Aviation?
The aviation industry has benefited greatly from military-driven innovation. Advancements in jet engines, aerodynamics, and avionics were initially driven by military needs but have since been incorporated into commercial aircraft.
6.5 How Does Cybersecurity Relate to Military Needs?
Cybersecurity is another field heavily influenced by military needs. The need to protect sensitive information and defend against cyberattacks has led to the development of advanced encryption techniques and security protocols.
7. How Does the Printing Press Influence Technological Transmission?
The printing press has revolutionized technological transmission by enabling the rapid and widespread dissemination of knowledge. This innovation has democratized access to information, fostering collaboration and accelerating technological progress.
7.1 Why Is the Printing Press Significant?
The printing press allowed for the mass production of books and documents, making information more accessible to a wider audience. This democratization of knowledge has fueled innovation and education.
7.2 How Does It Facilitate Knowledge Sharing?
By enabling the widespread distribution of scientific papers, technical manuals, and educational materials, the printing press has facilitated knowledge sharing on an unprecedented scale. This has led to faster technological advancements and greater collaboration among researchers and inventors.
7.3 What Is the Impact on Education?
The printing press has transformed education by making textbooks and other learning resources more readily available. This has improved literacy rates and enabled more people to pursue advanced studies.
7.4 How Does It Support Innovation?
The printing press supports innovation by enabling inventors and researchers to share their ideas and findings with a global audience. This has led to faster dissemination of new technologies and greater opportunities for collaboration.
7.5 What Is the Relevance Today?
While modern communication technologies have surpassed the printing press in speed and reach, its legacy remains significant. The principles of mass communication and knowledge sharing that it established continue to drive technological progress today.
8. How Do Museums Contribute to the Study of the History of Technology?
Museums play a vital role in the study of the history of technology by preserving and displaying artifacts that illustrate technological advancements. These institutions offer valuable insights into the evolution of technology and its impact on society.
8.1 Why Are Museums Important?
Museums provide a tangible connection to the past, allowing visitors to see and interact with historical artifacts. This hands-on experience enhances understanding and appreciation of technological developments.
8.2 How Do They Preserve Artifacts?
Museums carefully preserve artifacts, ensuring that they are available for future generations to study and learn from. This preservation work is essential for maintaining a record of technological progress.
8.3 What Insights Do They Offer?
Museum exhibits offer insights into the social, economic, and cultural context of technological developments. By examining artifacts alongside historical documents and narratives, visitors can gain a deeper understanding of technology’s impact.
8.4 How Do They Educate the Public?
Museums educate the public through exhibits, educational programs, and interactive displays. These resources help visitors understand the principles behind various technologies and their historical significance.
8.5 What Is the Role of Industrial Archaeology?
Industrial archaeology, the study of industrial sites and artifacts, is an important aspect of museum work. By examining the remains of factories, mines, and other industrial facilities, museums can provide insights into the processes and technologies of the past.
9. What Is the Cumulative Nature of Technological Acquisition?
Technological acquisition is a cumulative process, with each generation building upon the knowledge and techniques of its predecessors. This continuous accumulation drives progress and enables the development of increasingly sophisticated technologies.
9.1 Why Is Accumulation Important?
Accumulation allows for the gradual refinement and improvement of technologies over time. Each generation can learn from the successes and failures of the past, leading to more efficient and effective innovations.
9.2 How Does Inheritance of Techniques Contribute?
The inheritance of techniques ensures that valuable knowledge is passed down from one generation to the next. This continuity allows for the steady advancement of technology.
9.3 What Is the Role of Innovation?
Innovation is the driving force behind technological accumulation. By introducing new ideas and approaches, innovators push the boundaries of what is possible and contribute to the collective knowledge base.
9.4 How Do Societies Benefit?
Societies that embrace the cumulative nature of technological acquisition are more likely to experience sustained economic growth and improved quality of life. By building upon past achievements, they can create a more prosperous and sustainable future.
9.5 What Is the Impact of Stagnation?
Societies that remain stagnant or regress in their technological development risk falling behind. The loss of accumulated knowledge and techniques can have significant negative consequences.
10. How Does the Study of Technology Draw on Multiple Disciplines?
The study of technology is inherently multidisciplinary, drawing on insights from archaeology, engineering, architecture, and other fields. A holistic approach is essential for understanding the complex interactions between technology and society.
10.1 Why Is Multidisciplinary Study Important?
A multidisciplinary approach allows for a more comprehensive understanding of technology. By combining insights from different fields, researchers can gain a deeper appreciation of the social, economic, and cultural factors that influence technological development.
10.2 What Is the Role of Archaeology?
Archaeology provides valuable evidence about the technologies of past civilizations. By studying artifacts and ancient sites, archaeologists can reconstruct the history of technological development.
10.3 How Does Engineering Contribute?
Engineering provides the practical knowledge and skills needed to design, build, and maintain complex systems. Engineers play a vital role in translating scientific discoveries into technological innovations.
10.4 What Is the Significance of Architecture?
Architecture influences technology by shaping the built environment. Architects design buildings and infrastructure that incorporate technological innovations, creating spaces that are functional, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing.
10.5 How Do Other Specialists Contribute?
Other specialists, such as historians, sociologists, and economists, contribute to the study of technology by examining its social, cultural, and economic impacts. Their insights help to contextualize technological developments and understand their broader implications.
Technological development is a multifaceted process driven by social needs, resources, ethos, and transmission, influenced by rationality, military demands, and historical context. The cumulative nature of technological acquisition and the insights from various disciplines further shape its trajectory.
Want to delve deeper into these key technological innovations? Visit pioneer-technology.com to explore our in-depth articles, stay updated on the latest tech trends, and discover how these advancements are shaping our future. Discover the latest breakthroughs, in-depth analysis, and insightful perspectives on technological advancements and digital transformation at pioneer-technology.com. Stay ahead of the curve and explore the future today!
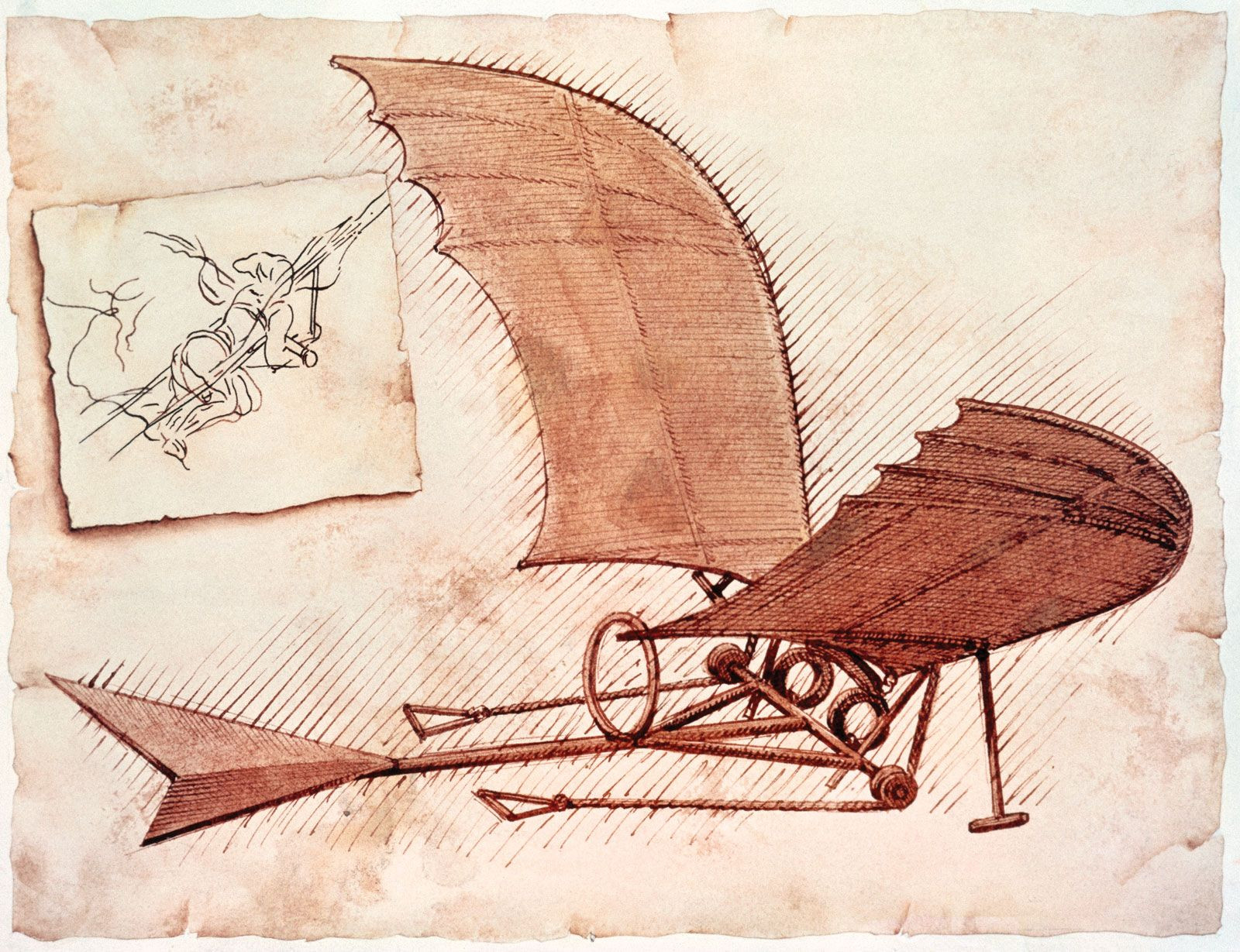 Leonardo da Vinci's plans for an ornithopter, a flying machine kept aloft by the beating of its wings, c. 1490.
Leonardo da Vinci's plans for an ornithopter, a flying machine kept aloft by the beating of its wings, c. 1490.
FAQ: Technological Development
1. What is technological development?
Technological development refers to the process of innovation, improvement, and advancement in tools, techniques, and processes used to solve problems, increase efficiency, and meet societal needs. It encompasses the entire evolution of humankind.
2. What are the main factors driving technological development?
The main factors driving technological development include social needs, availability of social resources (capital, materials, and skilled personnel), a sympathetic social ethos, and the cumulative nature of technological acquisition.
3. How do social needs influence technological development?
Social needs drive technological development by creating a demand for solutions to specific problems. When a society recognizes a need, it encourages individuals and organizations to invest resources in creating technologies to address that need.
4. What is the role of social resources in technological development?
Social resources, such as capital, materials, and skilled personnel, are essential for technological development. Without these resources, even the most innovative ideas cannot be realized. Capital funds research and development, materials enable the creation of new artifacts, and skilled personnel design and build complex systems.
5. What is a sympathetic social ethos, and why is it important?
A sympathetic social ethos refers to an environment that is receptive to new ideas and willing to embrace change. This type of environment encourages innovation by supporting inventors and allowing for experimentation and the exploration of unconventional solutions.
6. How do modes of technological transmission influence development?
Modes of technological transmission, including trade, migration of skilled craftsmen, and documentation, greatly influence the spread and advancement of technology. The ability to share and replicate innovations is essential for progress.
7. How does rationality influence technological development?
Rationality, characterized by the application of reason and logic to techniques, is a cornerstone of technological development. Understanding the underlying principles of technology enables continuous improvement and innovation.
8. What role have military needs played in driving technological innovation?
Military needs have historically acted as a significant catalyst for technological innovation. The demand for better weapons and defense systems has led to transformative advancements in various fields, many of which have found civilian uses.
9. How does the printing press influence technological transmission?
The printing press revolutionized technological transmission by enabling the rapid and widespread dissemination of knowledge. This innovation democratized access to information, fostering collaboration and accelerating technological progress.
10. Why is the study of technology multidisciplinary?
The study of technology is inherently multidisciplinary, drawing on insights from archaeology, engineering, architecture, and other fields. A holistic approach is essential for understanding the complex interactions between technology and society.