The technological, at its core, represents the application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes, driving innovation and shaping our world. At pioneer-technology.com, we delve into the dynamic realm where technology intersects with human ingenuity, constantly pushing boundaries and solving complex problems. Exploring beyond the basics, discover cutting-edge tech, digital transformation strategies, and future tech trends.
Table of Contents
- What Is The Technological?
- What Are The Key Characteristics of Technological Advancements?
- What Are The Different Types of Technologies?
- What Are The Applications Of The Technological Across Various Industries?
- What Are The Benefits Of Embracing The Technological?
- What Are The Challenges And Risks Associated With The Technological?
- What Is The Role Of Research And Development In Driving The Technological?
- What Is The Impact Of The Technological On Society And Culture?
- What Are The Future Trends In The Technological?
- How Can I Stay Updated On The Latest Technological Advancements?
- FAQ
1. What Is The Technological?
The technological encompasses the application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes, especially in industry. It involves tools, techniques, systems, and methods used to solve problems, improve processes, and enhance human capabilities. According to a report by the National Academy of Engineering, technology bridges the gap between scientific discoveries and real-world applications, driving innovation and progress across various sectors.
Expanding on this definition, it’s essential to understand that “the technological” isn’t just about gadgets and gizmos. It’s a broad field encompassing a vast array of disciplines and approaches. It includes:
- Innovation: The creation of new ideas, methods, or products.
- Engineering: The design, development, and construction of solutions.
- Applied Science: Using scientific principles to develop practical applications.
- Manufacturing: The production of goods using technological processes.
- Information Technology: The use of computers and software to manage and process information.
 Technological advancements
Technological advancements
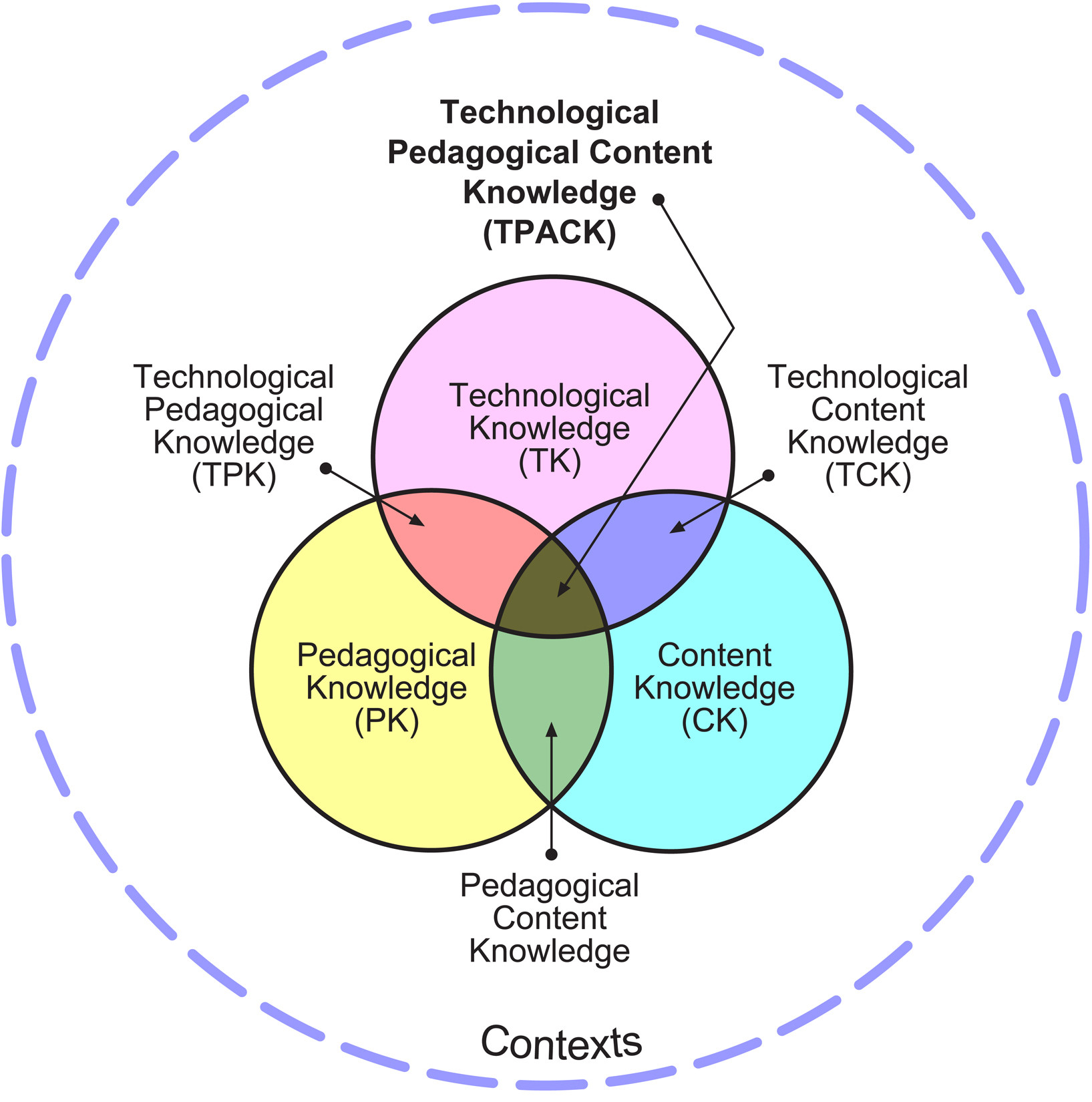
The term “the technological” can also be viewed through the lens of Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK), a framework that highlights the complex interplay between technology, pedagogy, and content knowledge in effective teaching. This framework underscores the importance of understanding how technology interacts with teaching methods and subject matter to enhance learning outcomes.
2. What Are The Key Characteristics of Technological Advancements?
Technological advancements are marked by several key characteristics that distinguish them from simple improvements or modifications. These characteristics drive progress and influence how technology impacts society.
- Innovation: Technological advancements introduce something new, whether it’s a product, process, or idea. Innovation often involves combining existing technologies in novel ways or creating entirely new ones. According to research from Stanford University’s Department of Computer Science, innovation in AI has led to breakthroughs in natural language processing, enabling more human-like interactions with machines.
- Efficiency: New technologies typically offer improvements in efficiency, allowing tasks to be completed faster, with fewer resources, and at a lower cost. For example, the development of automated manufacturing processes has significantly increased production rates while reducing labor costs.
- Scalability: Advancements often possess the ability to be scaled up or down to meet changing demands. Cloud computing, for instance, provides scalable resources that can be adjusted based on an organization’s needs, offering flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
- Automation: Many technological advancements involve automation, which reduces the need for human intervention. This can lead to increased productivity and reduced errors. The rise of robotic process automation (RPA) in business operations exemplifies this trend.
- Connectivity: Modern technologies are increasingly interconnected, enabling seamless communication and data sharing. The Internet of Things (IoT) connects devices and systems, allowing them to exchange data and coordinate activities, leading to smarter and more efficient operations.
- Disruption: Advancements can disrupt existing markets and industries, creating new opportunities while rendering older technologies obsolete. The shift from traditional film photography to digital photography is a prime example of disruptive innovation.
- Complexity: Technological advancements often involve complex systems and intricate designs. This complexity requires specialized knowledge and skills to develop, implement, and maintain these technologies.
- Ethical Considerations: New technologies raise ethical questions about privacy, security, bias, and social impact. Addressing these ethical considerations is crucial to ensure that technology is used responsibly and for the benefit of society.
3. What Are The Different Types of Technologies?
The technological landscape is incredibly diverse, encompassing a wide array of fields and applications. Here’s an overview of some of the main types of technologies:
| Technology Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Information Technology | Encompasses the use of computers, software, and networks to create, process, store, and manage information. Includes areas like software development, data analytics, cybersecurity, and cloud computing. |
| Biotechnology | Involves the use of biological systems, organisms, or derivatives to create or modify products or processes. Includes genetic engineering, biopharmaceuticals, and agricultural biotechnology. |
| Nanotechnology | Deals with the manipulation of matter on an atomic and molecular scale. Has applications in medicine, materials science, electronics, and energy. |
| Materials Science | Focuses on the discovery and design of new materials with specific properties. Includes the development of advanced polymers, composites, and ceramics. |
| Energy Technology | Involves the development of new sources of energy, as well as technologies for energy storage, distribution, and conservation. Includes solar power, wind energy, nuclear power, and battery technology. |
| Robotics | Deals with the design, construction, operation, and application of robots. Used in manufacturing, healthcare, exploration, and logistics. |
| Artificial Intelligence | Involves the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. Includes machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. |
| Telecommunications | Focuses on the transmission of information over distances using electronic means. Includes mobile communications, fiber optics, and satellite technology. |
| Aerospace Technology | Involves the design, development, and production of aircraft and spacecraft. Includes propulsion systems, navigation systems, and materials for aerospace applications. |
| Medical Technology | Encompasses a wide range of technologies used in healthcare, including diagnostic equipment, medical devices, and therapeutic treatments. Includes imaging technologies, surgical robots, and implantable devices. |
4. What Are The Applications Of The Technological Across Various Industries?
The applications of the technological are vast and span virtually every industry. Here are some notable examples:
- Healthcare: Medical technology has revolutionized healthcare, with advancements in imaging, diagnostics, and treatment options. According to a report by the World Health Organization, technologies like MRI, CT scans, and robotic surgery have improved the accuracy and effectiveness of medical interventions.
- Manufacturing: Automation and robotics have transformed manufacturing processes, increasing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving product quality. The use of 3D printing and advanced materials has also enabled the creation of complex and customized products.
- Agriculture: Agricultural technology, or agritech, has increased crop yields, reduced resource consumption, and improved farming practices. Technologies like precision agriculture, drones, and genetically modified crops are helping farmers optimize their operations.
- Finance: Financial technology, or fintech, has disrupted traditional banking and financial services, offering new ways to manage money, invest, and access credit. Mobile banking, online payment platforms, and blockchain technology are transforming the financial landscape.
- Transportation: The transportation industry has been transformed by advancements in automotive technology, including electric vehicles, autonomous driving systems, and ride-sharing platforms. These technologies promise to make transportation safer, more efficient, and more sustainable.
- Education: Educational technology, or edtech, has enhanced teaching and learning experiences, providing access to online courses, interactive learning tools, and personalized learning platforms. These technologies are making education more accessible and engaging for students of all ages.
- Energy: Energy technology is crucial for addressing the world’s growing energy needs while reducing carbon emissions. Renewable energy technologies like solar, wind, and geothermal are becoming increasingly affordable and efficient, while energy storage technologies are improving the reliability of renewable energy sources.
Alt: A cityscape at dusk with blurred car lights, symbolizing urban technological applications.
5. What Are The Benefits Of Embracing The Technological?
Embracing the technological offers numerous benefits for individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. These benefits include:
- Increased Productivity: Technologies automate tasks, streamline processes, and improve efficiency, leading to increased productivity and output.
- Improved Communication: Technologies facilitate communication and collaboration, enabling people to connect and share information more easily.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Technologies provide access to data and analytics, enabling better-informed decision-making.
- Cost Reduction: Technologies reduce costs by automating tasks, optimizing resource utilization, and improving efficiency.
- Innovation and Creativity: Technologies foster innovation and creativity by providing new tools and platforms for experimentation and collaboration.
- Improved Quality of Life: Technologies improve quality of life by providing access to healthcare, education, entertainment, and other essential services.
- Economic Growth: Technologies drive economic growth by creating new industries, jobs, and opportunities.
- Sustainability: Technologies enable sustainable practices by reducing waste, conserving resources, and promoting renewable energy.
- Global Connectivity: Technologies connect people and cultures, fostering understanding and collaboration on a global scale.
6. What Are The Challenges And Risks Associated With The Technological?
While the technological offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges and risks that must be addressed:
- Job Displacement: Automation and artificial intelligence can lead to job displacement as machines replace human workers in certain tasks.
- Privacy Concerns: Technologies collect and analyze vast amounts of data, raising concerns about privacy and data security.
- Security Risks: Technologies are vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches, which can compromise sensitive information and disrupt operations.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Technologies raise ethical dilemmas related to bias, discrimination, and the potential for misuse.
- Digital Divide: Access to technology is not evenly distributed, creating a digital divide between those who have access and those who do not.
- Dependence and Addiction: Over-reliance on technology can lead to dependence and addiction, affecting mental and physical health.
- Environmental Impact: The production, use, and disposal of technology can have a negative impact on the environment, contributing to pollution and resource depletion.
- Social Isolation: Excessive use of technology can lead to social isolation and a decline in face-to-face interactions.
- Misinformation and Manipulation: Technologies can be used to spread misinformation and manipulate public opinion, undermining trust and democracy.
7. What Is The Role Of Research And Development In Driving The Technological?
Research and development (R&D) plays a crucial role in driving the technological by:
- Generating New Knowledge: R&D generates new knowledge and insights that form the foundation for technological advancements.
- Developing New Technologies: R&D develops new technologies and prototypes that can be commercialized and brought to market.
- Improving Existing Technologies: R&D improves existing technologies, making them more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective.
- Solving Complex Problems: R&D solves complex problems and addresses societal challenges through technological innovation.
- Attracting Investment: R&D attracts investment from both public and private sectors, fueling further technological development.
- Fostering Collaboration: R&D fosters collaboration between researchers, engineers, and entrepreneurs, accelerating the pace of innovation.
- Training Future Innovators: R&D trains future innovators and technologists, ensuring a pipeline of talent for the technology sector.
- Promoting Economic Growth: R&D promotes economic growth by creating new industries, jobs, and opportunities.
- Enhancing Competitiveness: R&D enhances competitiveness by enabling organizations and nations to stay ahead of the curve in technology.
 Role of research
Role of research
According to a report by the National Science Foundation, countries that invest heavily in R&D tend to have stronger economies and higher levels of technological innovation.
8. What Is The Impact Of The Technological On Society And Culture?
The technological has a profound impact on society and culture, shaping how we live, work, and interact with one another. Some key impacts include:
- Globalization: Technologies have facilitated globalization by connecting people and cultures, enabling the exchange of ideas, goods, and services on a global scale.
- Social Change: Technologies have driven social change by challenging traditional norms, empowering marginalized groups, and promoting social justice.
- Cultural Transformation: Technologies have transformed culture by creating new forms of expression, communication, and entertainment.
- Political Influence: Technologies have influenced politics by enabling new forms of activism, campaigning, and governance.
- Economic Restructuring: Technologies have restructured the economy by creating new industries, jobs, and business models, while also disrupting traditional sectors.
- Educational Opportunities: Technologies have expanded educational opportunities by providing access to online courses, learning resources, and personalized learning platforms.
- Healthcare Improvements: Technologies have improved healthcare by enabling new diagnostic tools, treatments, and healthcare delivery models.
- Environmental Challenges: Technologies have contributed to environmental challenges by increasing energy consumption, pollution, and resource depletion, while also offering solutions for sustainable development.
- Ethical Considerations: Technologies have raised ethical considerations related to privacy, security, bias, and the potential for misuse, requiring careful consideration and regulation.
9. What Are The Future Trends In The Technological?
The technological landscape is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging all the time. Some of the most significant future trends include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI will continue to advance, with applications in a wide range of industries, including healthcare, finance, transportation, and manufacturing. Expect to see more sophisticated AI systems that can perform complex tasks, make autonomous decisions, and interact with humans in more natural ways.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT will continue to expand, with more devices and systems connected to the internet, generating vast amounts of data. This data will be used to optimize processes, improve efficiency, and create new services.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology will be used for more than just cryptocurrencies. It will be applied to supply chain management, healthcare, voting, and other areas where security and transparency are important.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): VR and AR will become more mainstream, with applications in gaming, entertainment, education, and training. Expect to see more immersive and interactive experiences that blur the line between the physical and digital worlds.
- 5G Technology: 5G technology will provide faster and more reliable wireless connectivity, enabling new applications like autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and smart cities.
- Biotechnology: Biotechnology will continue to advance, with new therapies, diagnostics, and personalized medicine approaches emerging. Gene editing, regenerative medicine, and bioprinting will transform healthcare.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing will revolutionize fields like cryptography, drug discovery, and materials science. While still in its early stages, quantum computing has the potential to solve problems that are impossible for classical computers.
- Sustainable Technology: Sustainable technology will become increasingly important as the world grapples with climate change and resource scarcity. Expect to see more innovations in renewable energy, energy storage, and sustainable materials.
 Future trends
Future trends
10. How Can I Stay Updated On The Latest Technological Advancements?
Staying updated on the latest technological advancements requires a proactive and multifaceted approach. Here are some tips:
- Read Industry Publications: Subscribe to industry publications, blogs, and newsletters that cover technology news, trends, and analysis. Examples include TechCrunch, Wired, and MIT Technology Review.
- Attend Conferences and Events: Attend technology conferences, webinars, and industry events to learn about new products, services, and trends.
- Follow Experts on Social Media: Follow technology experts, influencers, and thought leaders on social media platforms like Twitter, LinkedIn, and YouTube.
- Take Online Courses: Enroll in online courses and certifications to learn new skills and stay up-to-date on the latest technologies. Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity offer a wide range of technology courses.
- Join Professional Organizations: Join professional organizations and associations related to your field to network with peers and access resources.
- Participate in Online Communities: Participate in online forums, communities, and discussion groups to share knowledge, ask questions, and learn from others.
- Experiment with New Technologies: Experiment with new technologies and tools to gain hands-on experience and understand their capabilities and limitations.
- Read Research Papers: Read research papers and articles published in academic journals to stay informed about cutting-edge research and developments.
- Visit pioneer-technology.com: Regularly visit pioneer-technology.com for in-depth articles, analyses, and updates on the latest technological advancements. We provide comprehensive coverage of emerging technologies, digital transformation strategies, and future tech trends.
Staying informed about the technological is essential for professionals, students, and anyone interested in understanding the future. By adopting a proactive and curious approach, you can stay ahead of the curve and leverage technology to achieve your goals.
FAQ
Q1: What is the difference between technology and science?
Technology is the application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes, while science is the systematic study of the natural world through observation and experimentation.
Q2: How does technology impact the environment?
Technology can have both positive and negative impacts on the environment. It can contribute to pollution and resource depletion, but it can also provide solutions for sustainable development.
Q3: What are the ethical considerations of AI?
The ethical considerations of AI include bias, discrimination, privacy, security, and the potential for misuse.
Q4: How can I protect my privacy online?
You can protect your privacy online by using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, using a VPN, and being cautious about the information you share.
Q5: What is the future of work in the age of automation?
The future of work in the age of automation will likely involve a shift towards more creative, knowledge-based, and interpersonal roles. Workers will need to develop new skills and adapt to changing job requirements.
Q6: How does technology affect education?
Technology affects education by providing access to online courses, interactive learning tools, and personalized learning platforms. It can enhance teaching and learning experiences and make education more accessible.
Q7: What are the benefits of using cloud computing?
The benefits of using cloud computing include scalability, cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and improved collaboration.
Q8: How can technology help improve healthcare?
Technology can help improve healthcare by enabling new diagnostic tools, treatments, and healthcare delivery models. Telemedicine, remote monitoring, and electronic health records are some examples.
Q9: What is the role of technology in promoting sustainability?
Technology can play a crucial role in promoting sustainability by enabling renewable energy, energy efficiency, waste reduction, and resource conservation.
Q10: What are the key skills needed for a career in technology?
The key skills needed for a career in technology include programming, data analysis, problem-solving, communication, and adaptability.
Stay Ahead with Pioneer-Technology.com
Navigating the ever-evolving technological landscape can be challenging. At pioneer-technology.com, we provide you with the insights, analysis, and resources you need to stay informed and make the most of technological advancements.
Ready to dive deeper? Explore our latest articles, discover cutting-edge technologies, and unlock the potential of digital transformation. Visit pioneer-technology.com today and embark on your journey to technological mastery.
For more information, you can reach us at:
Address: 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States
Phone: +1 (650) 723-2300
Website: pioneer-technology.com

