Are you wondering Which Display Technology Is Best for your needs? At pioneer-technology.com, we break down the complexities of modern display technologies, offering you a clear and concise guide to help you make the right choice. Choosing the right display involves understanding the nuances of each technology, from LCDs to the cutting-edge MicroLEDs. Understanding display technology will allow you to choose the right product when you keep up with display innovations.
1. What is LCD Technology?
LCDs, or liquid crystal displays, represent the most mature display technology. LCD’s utilize two primary components. Those components are a backlight and a liquid crystal layer.
Liquid crystals are rod-shaped molecules that alter their orientation when exposed to an electric current. This property is used to allow or block light, aided by color filters to produce subpixels of red, green, and blue. At a reasonable distance, our eyes perceive these as a single color.
Since liquid crystals do not emit light, LCDs rely on a backlight, typically white or blue. The liquid crystal layer then regulates how much of this light passes through. The perceived image quality depends heavily on the backlight’s brightness and color uniformity.
 LCD close-up showing how colors are formed.
LCD close-up showing how colors are formed.
LCD vs. LED: Understanding the Marketing Hype
Many manufacturers brand their televisions as LED models instead of LCD. However, this is primarily a marketing strategy. These LED displays still utilize a liquid crystal layer. The main difference is that they use LEDs for the backlight instead of cathode fluorescent lamps (CFLs). LEDs offer several advantages such as being smaller, more energy-efficient, and longer-lasting. Fundamentally, these are still LCDs.
Types of LCDs
Let’s look at the various types of LCDs and their unique characteristics:
1.1 Twisted Nematic (TN)
 Amazfit Neo profile image with backlight on
Amazfit Neo profile image with backlight on
Twisted nematic (TN) was the earliest LCD technology. It set the stage for the industry’s transition from CRT displays. TN displays feature liquid crystals in a twisted, helical structure. In their default “off” state, light passes through two polarizing filters. When voltage is applied, the crystals untwist to block the light.
TN panels are energy-efficient and inexpensive to manufacture. They have been used for decades in devices like handheld calculators and digital watches. The system can also produce color images using red, blue, and green subpixels.
However, TN displays have drawbacks, including narrow viewing angles and poor color accuracy. Many use subpixels that output only 6 bits of brightness, limiting the color output to 64 shades of red, green, and blue. In comparison, 8 and 10-bit displays reproduce 256 and 1,024 shades of each primary color, respectively.
While TN panels were once popular for their low cost and fast response times, the industry has largely moved away from them due to superior alternatives like IPS and VA. You might still find them in low-end personal devices like budget Chromebooks. TN panels remain popular among competitive gamers due to their low response times.
Pros of TN Displays:
- Low production cost
- Energy efficient
- Fast response times
Cons of TN Displays:
- Low color accuracy
- Narrow viewing angles
- Low contrast ratio
1.2 In-Plane Switching (IPS)
 LG
LG
In-plane switching (IPS) technology marks a significant upgrade in image quality over TN displays. In an IPS display, liquid crystals are oriented parallel to the panel. In this state, light is blocked. This is the opposite of what occurs in a TN display. When voltage is applied, the crystals rotate in the same plane, allowing light to pass through. The technology is called in-plane switching because of this mechanism.
IPS displays were created to provide wider viewing angles than TN panels. IPS panels also offer superior color accuracy and bit-depth. While most TN panels are limited to the sRGB color space, IPS can support more expansive gamuts. These parameters are essential for HDR content and for creative professionals.
While IPS displays offer significant benefits, they have some drawbacks. The technology is not as energy-efficient as TN, nor is it as cheap to produce. Despite these minor issues, IPS remains the optimal choice if color accuracy and viewing angles are important to you.
Pros of IPS Displays:
- Wide viewing angles
- Excellent color accuracy
Cons of IPS Displays:
- Slower response times than TN
- Not very energy efficient
1.3 Vertical Alignment (VA)
 Samsung CJ89 Super Wide Screen Monitor
Samsung CJ89 Super Wide Screen Monitor
In a VA panel, liquid crystals are oriented vertically. They are perpendicular to the panel. This arrangement blocks more of the backlight. As a result, VA panels produce deeper blacks and offer better contrast than other LCD types. VA panels can match IPS in terms of bit-depth and color gamut coverage.
However, VA technology is still developing. Early VA implementations had slow response times, leading to ghosting behind fast-moving objects. This occurs because it takes longer for the crystals to change orientation.
However, companies like LG are experimenting with pixel overdrive to improve response times. VA displays also have narrower viewing angles than IPS panels. Most VA displays outperform even the best TN implementations.
Pros of VA Displays:
- Excellent contrast for LCD technology
- High color accuracy
Cons of VA Displays:
- Limited viewing angles
- Slow refresh rate
2. What is OLED Technology?
 Odyssey OLED G8 CES 2025
Odyssey OLED G8 CES 2025
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. The organic part refers to carbon-based chemical compounds. These compounds emit light when exposed to an electric current.
OLED differs from LCD. The compounds used in OLEDs emit their light. OLEDs are an emissive technology. This means that OLEDs do not need a backlight. Therefore, OLEDs are thinner and lighter than LCD panels.
Each organic molecule in an OLED panel emits light. With OLED each pixel can be controlled. Current can be taken away and the pixel turns off. This allows OLEDs to produce remarkable black levels, superior to LCDs. Besides the high contrast ratio, turning off pixels also reduces power consumption.
The exceptional contrast makes the technology worth it. Other benefits exist too. OLEDs have high color accuracy and are extremely versatile. Foldable smartphones such as the Samsung Galaxy Flip series use AMOLED’s physical flexibility.
OLED’s weakness is its susceptibility to permanent image retention or screen burn-in. A static image on the screen can become embossed, burned-in, or age differently over time. Manufacturers use mitigation strategies to prevent burn-in. Tandem OLED stacks two panels to reduce heat output and increase brightness. We’ve seen this display on the latest iPad Pro models and the Dell XPS line.
2.1 AMOLED and POLED Technologies
 Samsung Galaxy Z Fold 6 multitasking 2
Samsung Galaxy Z Fold 6 multitasking 2
Both AMOLED and POLED are terms in the smartphone industry. The AM in AMOLED refers to the use of an active matrix circuit for supplying current. The active matrix circuit opposes the passive matrix (PM) approach. The P in POLED indicates the use of a plastic substrate at the base. Plastic is thinner, lighter, and more flexible than glass. Super AMOLED is a display with an integrated touch screen digitizer.
Samsung uses the Super AMOLED branding. Many of its displays use a plastic substrate. Smartphones with curved screens require the flexibility of plastic. Almost every POLED display uses an active matrix. The distinction between AMOLED vs POLED has diminished recently.
OLED subtypes aren’t as varied as LCDs. Only a handful of companies manufacture OLEDs so there’s less quality variance. Samsung manufactures most OLEDs in the smartphone industry. LG Display has a near-monopoly on the large-sized OLED market. LG Display supplies panels to Sony, Vizio, and other giants in the television industry.
Pros of OLED Displays:
- High color accuracy
- Wide viewing angles
- Exceptional contrast
- Brighter than conventional LCDs
Cons of OLED Displays:
- Expensive
- Possibility of burn-in after prolonged use
3. What is Mini-LED Technology?
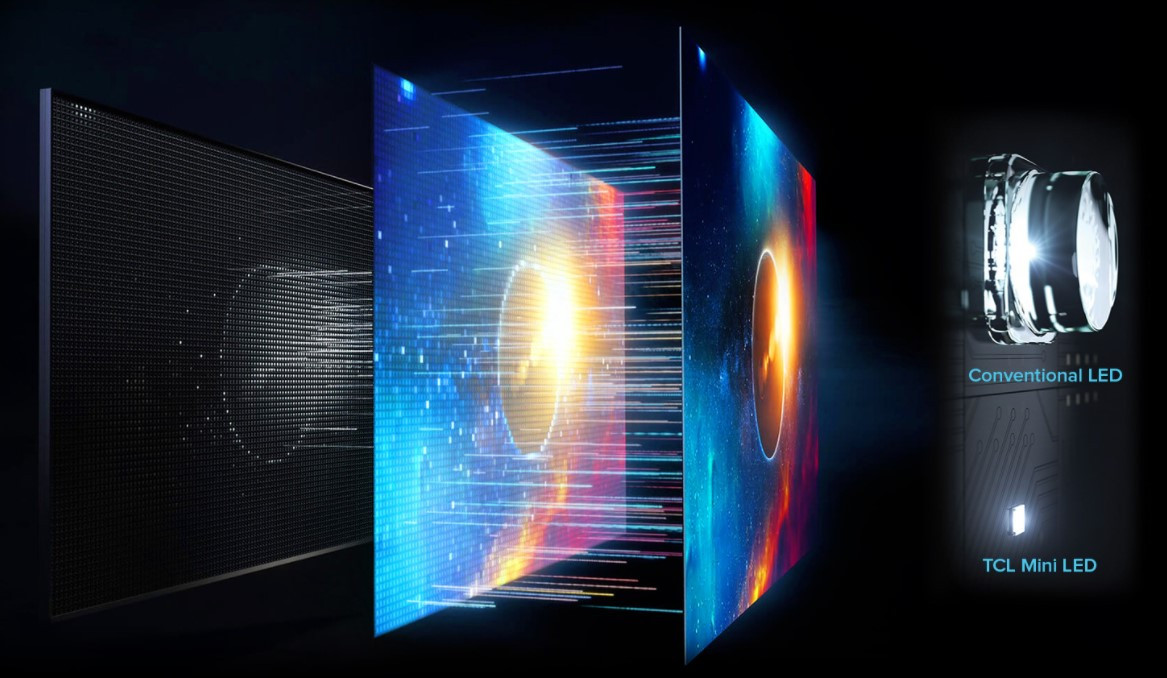 TCL graphic showing benefits of mini led
TCL graphic showing benefits of mini led
Mini-LED improves contrast and image quality at the backlight level.
The backlights in conventional LCDs have two modes of operation. Those modes are on and off. This means that the display relies on the liquid crystal layer to block light in darker scenes. When the liquid crystal layer fails, the display produces grays instead of true black.
Some displays divide the backlight into zones of LEDs. These zones can be controlled individually. They can be dimmed or turned off completely. As a result, these displays have deeper black levels and higher contrast. The difference is apparent in darker scenes.
Full array local dimming has become ubiquitous in higher-end LCD televisions. This technique wasn’t viable for smaller displays like laptops or smartphones. In larger devices like monitors and TVs, there is the risk of not having enough dimming zones.
Like the name suggests, mini-LEDs are smaller than the LEDs in conventional backlights. Each mini-LED measures 0.008 inches or 200 microns across.
3.1 What are the Benefits of Mini-LED Technology?
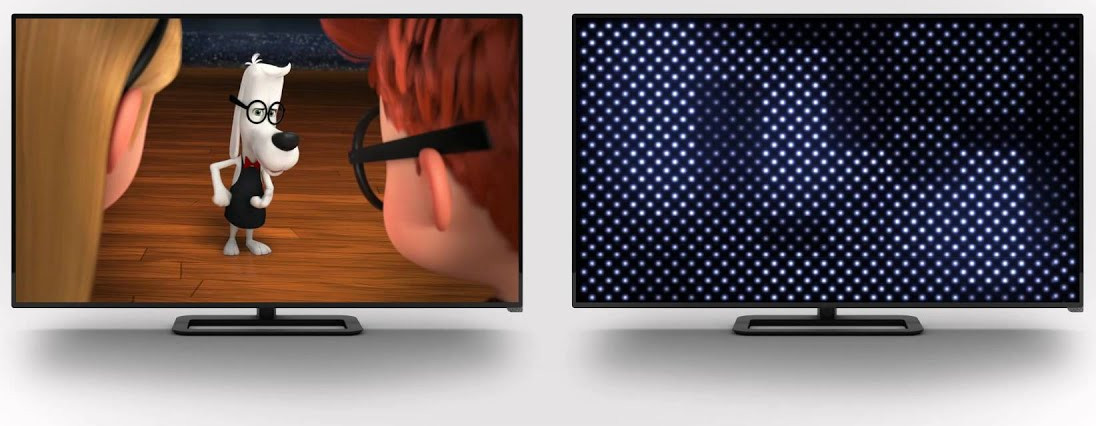 LED Backlight Array TV
LED Backlight Array TV
Mini-LEDs allow display manufacturers to increase the number of local dimming zones from a few hundred to several thousand. The quantity of zones equals control over the backlight. Their smaller footprint also makes them perfect for smaller devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops. The abundance of LEDs helps boost the display’s brightness.
Tiny, bright objects against a black background look better on a mini-LED display than on one with conventional LED backlighting. The contrast ratio isn’t in the same ballpark as OLED.
Mini-LED allows displays to have thousands of dimming zones for improved contrast.
Most mini-LED displays don’t have enough dimming zones to match OLEDs in contrast. The 2021 iPad Pro was among the first consumer devices to adopt mini-LED technology. With 2,500 zones across 12.9 inches, some users reported blooming or halos around bright objects. This is one of the reasons why Apple moved on to tandem OLED in 2024.
Mini-LEDs can eventually deliver better contrast than conventional local dimming implementations. Mini-LED displays rely on traditional LCD technologies. Thus, mini-LED displays aren’t prone to burn-in like OLEDs.
Pros of Mini-LED Displays:
- Improved contrast and deeper blacks
- Higher brightness
Cons of Mini-LED Displays:
- Relatively expensive
- Increased complexity, making backlight repairs harder
4. What is Quantum Dot Technology?
 Samsung Neo QLED 8k 5
Samsung Neo QLED 8k 5
Quantum dot technology is a selling point for many mid-range televisions. Quantum dot technology is Samsung’s marketing shorthand which is QLED. Quantum dot displays are conventional LCDs with an additional layer sandwiched between.
Traditional LCDs pass white light through multiple filters to get a specific color. Many older display types fully cover the standard RGB (sRGB) color gamut. The same cannot be said for wider gamuts like DCI-P3. Coverage of DCI-P3 is important because it’s predominantly used in HDR content.
Quantum dots are crystals that emit color when shined with blue or ultraviolet light. Quantum dot displays use a blue backlight instead of white.
A quantum dot display contains billions of nanocrystals spread across a thin film. When the backlight is turned on, these crystals produce shades of green and red. The shade depends on the size of the crystal.
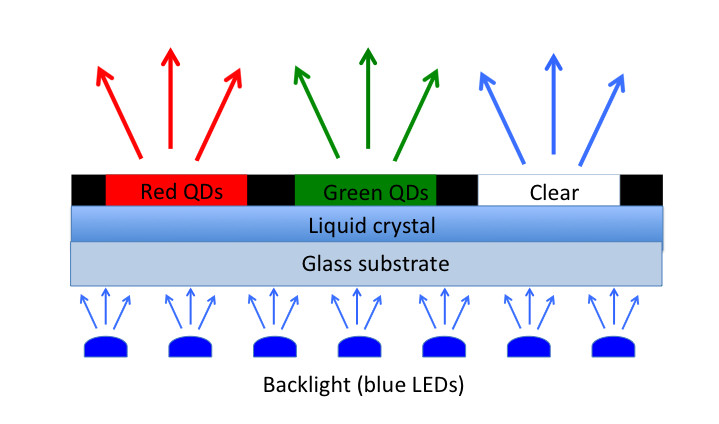 QDCF diagram
QDCF diagram
When combined with traditional LCD color filters, quantum dot displays cover a greater percentage of the visible light spectrum. Quantum dot displays deliver richer and more accurate colors. The colors deliver a satisfactory HDR experience. Since the crystals emit their own light, you also get a tangible bump in brightness compared to traditional LCDs.
Quantum dots help traditional LCDs achieve a wider color gamut. Quantum dots deliver a satisfactory HDR experience. Quantum dot technology does not improve LCD’s pain points such as contrast and viewing angles. Combine quantum dots with local dimming or mini-LED technologies for these. Samsung’s high-end Neo QLED TVs combine QLED with Mini-LED tech to match OLED’s deep blacks.
Pros of Quantum Dot Displays:
- High color accuracy
- High brightness
- No burn-in or durability concerns
Cons of Quantum Dot Displays:
- Depending on LCD implementation, could exhibit low contrast and slow response times
5. What is Quantum Dot OLED (QD-OLED) Technology?
 samsung display qd-oled layers
samsung display qd-oled layers
Quantum-dot OLED, or QD-OLED, combines quantum dots and OLED. It aims to eliminate the drawbacks of traditional OLEDs and LCD-based quantum dot displays.
In a traditional OLED panel, each pixel is composed of four white sub-pixels. The idea is that white contains the entire color spectrum. Then you can use red, green, and blue color filters to obtain an image. However, this process is inefficient. Blocking large portions of the light source leads to brightness loss by the time the image reaches your eyes.
Modern OLED implementations combat this. They leave the fourth sub-pixel white (without any color filters) to improve brightness. However, they still usually fall short in brightness, especially against high-end LCDs with larger backlights.
QD-OLED aims to eliminate the drawbacks of traditional OLEDs and LCD-based quantum dot displays.
QD-OLED uses a different subpixel arrangement. The displays start with blue emitters instead of white. Instead of color filters, they use quantum dots. Quantum dots produce shades of green and red. Quantum dots convert the blue light into various colors instead of filtering it. This preserves the display’s brightness.
According to Samsung Display, QD-OLED brings better color accuracy. These displays don’t have a fourth white sub-pixel. Therefore, color information is rendered correctly even at higher brightness levels. Quantum dots allow displays to achieve higher color gamut coverage and offer wider viewing angles than color filters.
It’s early days for the technology. Traditional OLEDs have enjoyed a decade-long head start. It remains to be seen if QD-OLED televisions and monitors can compete in price and durability. Burn-in with organic compounds may also be an issue.
Pros of QD-OLED Displays:
- Higher brightness than traditional OLEDs
- Wider viewing angles
- Near-perfect black levels
Cons of QD-OLED Displays:
- Long-term durability unknown
- Potentially expensive until the technology matures
6. What is MicroLED Technology?
 Samsung
Samsung
MicroLED is the newest display type and the most exciting. MicroLED displays use LEDs that are smaller than those in mini-LED backlights. Mini-LEDs are around 200 microns. MicroLEDs are as small as 50 microns. For context, human hair is thicker at 75 microns.
You can build an entire display out of microLEDs. The result is an emissive display. MicroLED is much like OLED. However, MicroLED does not use OLED’s organic component. There’s no backlight. Each pixel can be turned off completely to represent black. MicroLED delivers a high contrast ratio and wide viewing angles.
Brightness is another aspect where microLED displays surpass existing technologies. OLED displays top out at 2,000 nits. Manufacturers claim that microLED can deliver a peak brightness output of 10,000 nits.
MicroLEDs one-up existing display types in almost every way. Consumer products are still years away.
MicroLED displays can be modular. Manufacturers have created giant video walls using a grid of smaller microLED panels.
Samsung offers The Wall microLED display in configurations from 72 inches to 300 inches and beyond. With a million-dollar price tag, it is not a consumer product. Still, it offers a glimpse into the future of televisions and display technology.
MicroLED displays will become more accessible and cheaper. OLED is only a decade old and has already become ubiquitous.
Pros of MicroLED Displays:
- Highest brightness of any display type
- Exceptional contrast
- No image retention or burn-in
Cons of MicroLED Displays:
- Still an unproven and expensive technology
- Not commercially produced in smaller sizes yet
7. FAQ about Display Technology
7.1 Which display technology offers the best contrast ratio?
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) technology provides the best contrast ratio due to its ability to completely turn off individual pixels, resulting in perfect blacks.
7.2 What display technology is best for gaming?
For gaming, TN (Twisted Nematic) panels are often preferred for their fast response times and high refresh rates. However, IPS (In-Plane Switching) panels also offer good color accuracy and viewing angles, making them a viable option for gamers who prioritize visual quality.
7.3 Which display type is most energy-efficient?
TN (Twisted Nematic) panels are generally the most energy-efficient display type due to their simple design and low power requirements.
7.4 What is the difference between QLED and OLED?
QLED (Quantum Dot LED) is an LCD-based technology that uses quantum dots to enhance color and brightness. OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) is an emissive technology where each pixel produces its own light and color.
7.5 Which display technology is the most expensive?
MicroLED technology is currently the most expensive display technology due to its complex manufacturing process and high material costs.
7.6 Which display technology offers the widest viewing angles?
IPS (In-Plane Switching) panels typically offer the widest viewing angles with minimal color shift or contrast loss.
7.7 What are the disadvantages of OLED displays?
The main disadvantages of OLED displays are their susceptibility to burn-in (permanent image retention) and their higher cost compared to LCD panels.
7.8 How does Mini-LED improve LCD displays?
Mini-LED backlighting significantly improves the contrast ratio and black levels of LCD displays by using smaller LEDs and more local dimming zones.
7.9 Which display technology is best for outdoor use?
LCD panels with high brightness and anti-glare coatings are generally better for outdoor use due to their ability to overcome ambient light.
7.10 What is QD-OLED technology?
QD-OLED (Quantum Dot OLED) combines the self-emissive properties of OLED with quantum dots to enhance color and brightness, offering improved performance compared to traditional OLED displays.
8. Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Choosing the best display technology depends on your priorities. OLED and Mini-LED offer cutting-edge performance. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each technology is essential for making an informed decision.
Stay updated with the latest trends and innovations in display technology at pioneer-technology.com. Explore our in-depth articles and expert analyses to find the perfect display for your needs.
Ready to dive deeper into the world of pioneering technology? Visit pioneer-technology.com today and discover the latest breakthroughs, trends, and insights that are shaping our future. Don’t just keep up with technology—stay ahead of it. Explore our articles now! For further information, contact us at Address: 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305, United States or Phone: +1 (650) 723-2300.
